Abstract
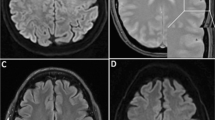
A 77 year old woman was hospitalized one hour after the onset of right hemiplegia and aphasia. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination was negative and MRA indicated occlusion of the left middle cerebral artery. Treatment with streptokinase was instituted (a 60 minute intravenous infusion of 1.5 MU of streptokinase in 100 ml of saline solution). Two hours after infusion, the patient's motor function clearly improved. An MRA examination performed six hours later showed partial recanalization of the obstructed vessel.
Our report demonstrates the potential usefulness of MRA monitoring during thrombolytic therapy.
Sommario
Una donna di 77 anni fu ricoverata a distanza di un'ora dall'insorgenza di emiplegia destra con afasia. Una Risonanza Magnetica dell'encefalo risultò negativa, mentre una Angio-RM indicava l'occlusione dell'arteria cerebrale media di sinistra; fu quindi intrapresa la terapia con streptokinasi.
Dopo due ore dall'infusione, le capacità motorie della paziente migliorano sensibilmente. Una Angio-RM effettuata sei ore più tardi evidenziò la parziale ricanalizzazione del vaso occluso. Questo caso dimostra la potenziale utilità del monitoraggio con Angio-RM nel corso della terapia trombolitica.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brott T.:Thrombolytic therapy for Stroke. Cerebrovascular and Brain Metabolism Review 3:91–113, 1991.
Fieschi C., Argentino C., Lenzi G.L., et al.:Clinical and instrumental evaluation of patients with ischaemic stroke within the first six hours. J. Neurol. Sci. 91:311–322, 1989.
Fieschi C., Carolei A., Frontoni M., et al.:Evaluation of Medical Therapies of Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2:47–50, 1992.
Fisher M., Sotak C.H., Minematsu K., Li L.:New magnetic resonance techniques for evaluating cerebrovascular disease. Ann. Neurol. 32:115–122, 1992.
Masaryk T.S., Modic M.T., Jeffrey S.R., Ruggieri P.M.:Intracranial circulation: preliminary clinical results with three-dimensional (volume) MR angiography. Radiology 171:793–799, 1989.
Pessin M.S., Del Zoppo G.J., Estol C.J.:Thrombolytic agents in the treatment of stroke. Clinical Neuropharmacol. vol. 13:271–289, 1990.
Ruggieri P.M., Masaryk T.J., Ross J.S.:Magnetic Resonance Angiography. Stroke 23:774–780, 1992.
Shuaib A., Lee D., Pelz D., et al.:The impact of magnetic resonance imaging on the management of acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 42:816–818, 1992.
Warach S., Li W., Ronthal M., Edelman R.R.:Acute Cerebral Ischemia: Evaluation with Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR imaging and MR Angiography. Radiology 182:41–47, 1992.
Wardlaw J.M., Warlow C.P.:Thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: does it work?. Stroke 23:1826–1839, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Federico, F., D'Aprile, P., Lamberti, P. et al. Magnetic resonance angiography monitoring of streptokinase in occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Ital J Neuro Sci 14, 629–632 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02339247
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02339247