Abstract
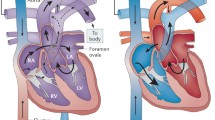
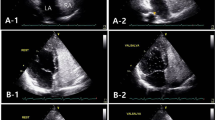
By means of transthoracic contrast echocardiography, the prevalence of a patent foramen ovale (PFO) was studied, in a continuous series of 48 patients aged less than 50 years with a recent episode of acute cerebral ischemia. A PFO was found in 11 subjects (23%). In the subgroup of younger patients (aged less than 30 years), the prevalence was much higher than in those aged 30 or more (58% against 11%, p=0.0022). In the 19 patients with clear evidence of extracardiac causal factors of cerebral ischemia, there was no PFO; of the remaining 29 subjects, a PFO was present in 11 (38%) (p=0.0015). In conclusion, the possibile presence of a PFO must be carefully investigated in subjects with cerebral ischemia aged less than 30, as well as in subjects aged between 30 and 50 in whom there is no acceptable explanation for their cerebral ischemic episode.
Sommario
La prevalenza della pervietà del forame ovale (PFO) è stata studiata, per mezzo della Eco-cardiografia transtoracica con iniezione di mezzo di contrasto, in una serie continua di 48 pazienti di età inferiore ai 50 anni, affetti da episodi acuti di ischemia cerebrale focale. La presenza di PFO è stata dimostrata in 11 soggetti (23%). Nel gruppo dei più giovani (sotto i 30 anni) la prevalenza di questa anomalia cardiaca è risultata molto più alta che in quello dei più anziani (58% contro 11%, p=0,0022). Inoltre, non vi era alcun caso di PFO tra i 19 soggetti in cui è stata dimostrata una evidente causa extracardiaca del disturbo cerebrovascolare, mentre la PFO era presente nel 38% degli altri 29 casi (p=0.0015). In conclusione, la presenza di PFO deve essere ricercata con cura nei pazienti cerebrovascolari ischemici di età inferiore a 30 anni così come in quelli tra i 30 ed i 50 in cui non sia dimostrabile una verosimile causa dell'episodio ischemico cerebrale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bevan H., Sharma K., Bradley W.:Stroke in young adults. Stroke, 21:382–386, 1990.
Bogousslavsky J., Hachinski V.C., Boughner D.R., et al.:Cardiac and arterial lesions in carotid transient ischemic attacks. Arch. Neurol., 43:223–228, 1986.
Bridges N.D., Hellenbrand W., Latson L., et al.:Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale after presumed paradoxical embolism. Circulation, 86:1902–1908, 1992.
Carolei A., Marini C., Ferranti E., Frontoni M., et al.:A prospective study of cerebral ischemia in the young. Analysis of pathogenic determinants. Stroke, 24:362–367, 1993.
Cohnheim J.:Thrombose und embolie. In: Vorlesungen über Allgemeine Pathologie, vol. 1, p. 134, Hirshwald, Berlin, 1877.
Delière T., Dubourg O., D'Enfert J., et al.:Embolies paradoxales à travers un foramen ovale perméable. Presse Méd., 12:2365–2369, 1983.
Di Tullio M., Sacco R.L., Gopal A., Mohr J.P., Homma S.:Patent foramen ovale as a risk factor for cryptogenic stroke. Ann. Intern. Med., 117:461–465, 1992.
Di Tullio M., Sacco R.L., Venketasubramanian N., et al.:Comparison of diagnostic techniques for the detection of a patent foramen ovale in stroke patients. Stroke, 24:1020–1024, 1993.
Dubourg O., Haroche G., Terdiman M., et al.:Perméabilité du foramen ovale dans l'embolie paradoxale. Presse Méd., 12:2371–2374, 1983.
Falk R.H.:PFO or UFO? The role of a patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke. Am. Heart. J., 121:1264–1266, 1991.
Furlan A.:The heart and stroke. Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1987.
Gautier J.C., Prodat-Diehl P., et al.:Accidents vasculaires cérébraux des sujets jeunes. Rev. Neurol., 145:437–442, 1989.
Gautier J.C., Dürr A., Koussa S., et al.:Parodoxical cerebral embolism with a patent foramen ovale. A report of 29 patients. Cerebrovasc. Dis., 1:193–202, 1991.
Hagen P.T., Scholz D.G., Edwards W.D.:Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin. Proc., 59:17–20, 1984.
Hart R.G.:Cardiogenic embolism to the brain. Lancet, 339:589–594, 1992.
Harvey J.R., Teague S.M., Anderson J.L., et al.:Clinically silent atrial septal defects with evidence for cerebral embolization. Ann. Intern. Med., 105:695–697, 1986.
Hausmann D., Mügge A., Becht I., Daniel W.G.:Diagnosis of patent foramen ovale by transesophageal echocardiography and association with cerebral and peripheral embolic events. Am. J. Cardiol., 70:668–672, 1992.
Jeanrenaud X., Bogousslavsky J., Payot M., et al.:Patent foramen ovale and cerebral infarct in young patients. Schweiz Med. Wochenschr, 120(22):823–829, 1990.
Jeanrenaud X., Kappenberger L.:Patent foramen ovale and stroke of unknown origin. Cerebrovasc. Dis., 1:184–192, 1991.
Jones H.R., Caplan L.R., Come P.C., Swinton N.W., Breslin D.J.:Cerebral emboli of paradoxical origin. Ann. Neurol., 13:314–319, 1983.
Lechat P., Mas J.L., Lascault G., et al.:Prevalence of patent foramen ovale in patients with stroke. N. Engl. J. Med., 318:1148–1152, 1988.
Lechat P., Lascault G., Mas J.L., Loron P., et al.:Prévalence du foramen ovale perméable chez les patients jeunes atteints d'accident ischémique cérébral. Arch. Mal. Coeur, 82:847–852, 1989.
Mas J.L.:Patent foramen ovale, stroke and paradoxical embolism. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1:181–183, 1991.
Mohr J.P.:Cryptogenic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med., 318:1197–1198, 1988.
Pearson A.C., Labovitz A.J., Tatineni S., Gomez C.R.:Superiority of transesophageal echocardiography in detecting cardiac sources of embolism in patients with cerebral ischemia of uncertain etiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 17:66–72, 1991.
Ranoux D., Cohen A., Cabanes L., Amarenco P., et al.:Patent foramen ovale: is stroke due to paradoxical embolism? Stroke, 24:31–34, 1993.
Sacco R.L., Ellenberg J.H., Mohr J.P., et al.:Infarcts of undetermined cause: the NINCDS stroke data bank. Ann. Neurol., 25:382–390, 1989.
Webster M.W., Chancellor A.M., Smith H.J., et al.:Patent foramen ovale in young stroke patients. Lancet., 2:11–12, 1988.
Zahn R., Nohl H., Zander M., Senges J.:Comparison of three echocardiographic methods in the detection of a patent foramen ovale. Circulation., 80, Suppl. II, 1355, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandolfo, C., Papagna, D., Rossi, M.A. et al. Focal cerebral ischemia and patent cardiac foramen ovale. Ital J Neuro Sci 15, 145–149 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02339206
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02339206