Abstract
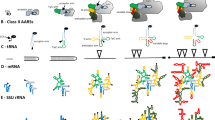
Determination of the entire nucleotide sequence of the aphid 28S ribosomal RNA gene (28S rDNA) revealed that it is 4,147 by in length with a G + C content of 60.3%. Based on the nucleotide sequence, we constructed a presumed secondary-structure model of the aphid 28S rRNA which indicated that the aphid 28S rRNA is characterized by the length and high G + C content of its variable regions. The G + C content of the aphid's variable regions was much higher than that of the entire sequence of the 28S rRNA, which formed a striking contrast to those ofDrosophila with the G + C content much lower than the entire 28S molecule. In this respect, the aphid 28S rRNA somewhat resembled those of vertebrates. This is the third report of a complete large-subunit rRNA sequence from an arthropod, and the first 28S rRNA sequence for a nondipterous insect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brosius J, Dull TJ, Noller HF (1980) Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene fromEscherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:201–204
Chan YL, Olvera J, Wool IG (1983) The structure of rat 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid inferred from the sequence of nucleotides in a gene. Nucleic Acids Res 11:7819–7831
Clark CG, Tague BW, Ware VC, Gerbi SA (1984)Xenopus laevis 28S ribosomal RNA: a secondary structure model and its evolutionary and functional implications. Nucleic Acids Res 12:6197–6220
Coen ES, Dover GA (1982) Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers ofDrosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 10: 7017–7026
Ellis RE, Sulston JE, Coulson AR (1986) The rDNAC. elegans: sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res 14:2345–2364
Fujiwara H, Ishikawa H (1986) Molecular mechanism of introduction of the hidden break into the 28S rRNA of insects: implication based on structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6393–6401
Gonzalez IL, Gorski JL, Campen TJ, Dorney DJ, Erickson JM, Sylvester JE, Schmickel RD (1985) Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7666–7670
Gorab E, de Lacoba MG, Botella LM (1995) Structural constraints in expansion segments from a midge 26S rDNA. J Mol Evol 41:1016–1021
Gorski JL, Gonzalez IL, Schmickel RD (1987) The secondary structure of human 28S rRNA: the structure and evolution of a mosaic rRNA gene. J Mol Evol 24:236–251
Grimaldi G, Paolo di Nocera P (1988) Multiple repeated units inDrosophila melanogaster ribosomal DNA spacer stimulate rRNA precursor transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5502–5506
Hadjiolov AA, Georgiev OI, Nosikov VV, Yavachev LP (1984) Primary and secondary structure of rat 28S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 12:3677–3693
Hancock JM, Dover GA (1988) Molecular coevolution among cryptically simple expansion segments of eukaryotic 26S/28S rRNAs. Mol Biol Evol 5:377–391
Hassouna N, Michot B, Bachellerie JP (1984) The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 12:3563–3583
Herrmann BG, Frischuf A-M (1987) Isolation of genomic DNA. In: Berger SL, Kimmel AR (eds) Methods enzymol, vol 152. Academic Press, New York, p 346
Ishikawa H (1976) Arthropod ribosomes: integrity of ribosomal ribonucleic acids from aphids and water-fleas. Biochim Biophys Acta 435:258–268
Ishikawa H (1977) Evolution of ribosomal RNA. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 58:1–7
Ishikawa H, Newburgh RW (1972) Studies of the thermal conversion of 28S RNA ofGalleria mellonella (L.) to an 18S product. J Mol Biol 64:135–144
Kjer KM, Baldridge GD, Fallon AM (1994) Mosquito large subunit ribosomal RNA: simultaneous alignment of primary and secondary structure. Biochim Biophys Acta 1217:147–155
Kwon O-Y, Ishikawa H (1992a) Unique structure in the intergenic and 5′ external transcribed spacer of rDNA from the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum. Eur J Biochem 206:935–940
Kwon O-Y, Ishikawa H (1992b) Nucleotide sequence and presumed secondary structure of the internal transcribed spacers of rDNA of the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 103:651–655
Kwon O-Y, Ogino K, Ishikawa H (1991) The longest 18S ribosomal RNA every known: nucleotide sequence and presumed secondary structure of the 18S rRNA of the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum. Eur J Biochem 202:827–833
Linares AR, Hancock JM, Dover GA (1991) Secondary structure constraints of the evolution ofDrosophila 28S ribosomal RNA expansion segments. J Mol Biol 219:381–390
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Michot B, Hassouna N, Bachellerie J-P (1984) Secondary structure of mouse 28S rRNA and general model for the folding of the large rRNA in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 12:4259–4279
Noller HF, Kop JA, Wheaton V, Brosius J, Gutell RR, Kopylov AM, Dohme F, Herr W, Stahl DA, Gupta R, Woese CR (1981) Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 9:6167–6189
Ogino K, Eda-Fujiwara H, Fujiwara H, Ishikawa H (1990) What causes the aphid 28S rRNA to lack the hidden break? J Mol Evol 30:509–513
Pavlakis GN, Jordan BR, Wurst RM, Vournakis JN (1979) Sequence and secondary structure ofDrosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res 7:2213–2238
Peral B (1988) A practical guide to molecular cloning. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York, p 542
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Staden R (1982) Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 10:4731–4751
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Iida Y, Sugiura M (1985) The complete nucleotide sequence of a rice 25S rRNA gene. Gene 37:255–259
Tautz D, Hancock JM, Webb DA, Tautz C, Dover GA (1988) Complete sequences of the rRNA genes ofDrosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 5:366–376
Veldman GM, Klootwijk J, de Regt VCHF, Planta RJ, Branlant C, Krol A, Ebel JP (1981) The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 9:6935–6952
Ware VC, Renkawitz R, Gerbi S (1985) rRNA processing: removal of only nineteen bases at the gap between 28Sα and β rRNAs inSciara coprophila. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3581–3597
Ware VC, Tague BW, Clark CG, Gourse RL, Brand RC, Gerbi SA (1983) Sequence analysis of 28S ribosomal DNA from the amphibianXenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res 11:7795–7817
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: H. Ishikawa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amako, D., Kwon, OY. & Ishikawa, H. Nucleotide sequence and presumed secondary structure of the 28S rRNA of pea aphid implication for diversification of insect rRNA. J Mol Evol 43, 469–475 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337519
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337519