Abstract
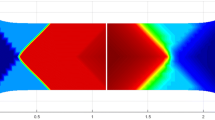
The effect of the fiber to matrix modulus of elasticity ratio varying from 1.0 to 200 was investigated for a two-dimensional plane-stress composite configuration having a simulated fiber volume fraction of 0.45 and containing a discontinuous fiber. Uniaxial loading parallel to the fibers was considered. Two independent techniques were used: moiré strain analysis and finite-element analysis. Displacements were measured from four experimental models by utilizing optical fringe-multiplication techniques. The finite-element method yielded stresses which agreed closely with those obtained from the experimental analysis. Matrix stress-concentration factor near the discontinuous fiber was found to increase rapidly with increasing modulus ratio, reaching a value of 20 for a modulus ratio of 200. The finite-element method was shown to be a valuable tool for micromechanical stress analysis of composite materials, and the accuracy of strain analysis by moiré-fringemultiplication techniques was demonstrated for problems containing sever strain gradients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
cross-sectional area
- E :
-
modulus of elasticity
- P :
-
force
- V f :
-
fiber-volume fraction
- ε:
-
strain
- ν:
-
Poisson's ratio
- σ:
-
maximum principal stress
- τ:
-
maximum shear stress
- c :
-
composite
- f :
-
fiber
- m :
-
matrix
References
Stone, D. E. W., “A Contribution to the Application of Photoelasticity to the Micromechanics of Composite Materials,”Jnl. of Strain Anal. 4 (2) (1969).
Durelli, A. J., Parks, V. J., Feng, H. C. and Chiang, F., “Strains and Stresses in Matrices with Inserts,” Report No. 12 on The Development of Experimental Stress Analysis Methods to Determine Stresses and Strains in Solid Propellant Grains, Mechanics Division, The Catholic University of America (May, 1967).
Carrara, A. S. and McGarry, F. J., “Matrix and Interface Stresses in a Discontinuous Fiber Composite Model,”Jnl. of Comp. Matls.,2 (2) (1968).
Chen, P. E. and Lavengood, R. E., “Stress Fields Around Multiple Inclusions,” Monsanto/Washington University ONR/ARPA Association, HPC 68-60 (Jan. 1969).
Post, D., “Analysis of Moiré Fringe Multiplication Phenomena,”Applied Optics,6 (11),1938 (1967)
Post, Daniel, “New Optical Methods of Moiré-fringe Multiplication,”Experimental Mechanics,8 (2),63–68 (1968).
Post, D. andMacLaughlin, T. F., “Strain Analysis by Moiré Fringe Multiplication,”Experimental Mechanics,11 (9),408–413 (1971).
Sampson, R. C. andCampbell, D. M., “The Grid-shift Technique for Moiré Analysis of Strain in Solid Propellants,”Experimental Mechanics,7 (11),449 (1967).
Chiang, F., Parks, V. J. andDurelli, A. J., “Moiré-fringe Interpolation and Multiplication by Fringe Shifting,”Experimental Mechanics,8 (12),554–560 (1968).
Barker, R. M. and MacLaughlin, T. F., “Stress Concentrations Near a Discontinuity in Fibrous Composites,” Jnl. of Comp. Matlt., to be published.
MacLaughlin, T. F., “A Photoelastic Analysis of Fiber Discontinuities in Composite Materials,”Jnl. of Comp. Matls.,2 (1) (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacLaughlin, T.F., Barker, R.M. Effect of modulus ratio on stress near a discontinuous fiber. Experimental Mechanics 12, 178–183 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02330270
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02330270