Abstract
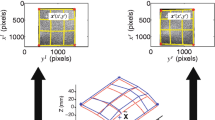
Stereo vision is used to measure the strain field of a round tension test specimen in a cylindrical coordinate system. Initially, the displacement fields of the specimen are measured relative to a world coordinate system erected by the stereo vision. Through coordinate transformations, the measured displacement fields expressed in world coordinates are then converted to the displacement fields expressed in cylindrical coordinates. By differentiating the axial and circumferential displacements in the axial and circumferential directions, the axial, circumferential and shear strains are determined. Results indicate that the measured mean value of the axial strains is in good agreement with the measurements of the extensometer and the strain gage. The Poisson's ratio obtained by the circumferential and axial strains is close to .33 in the elastic state. The mean error of the computed shear strain is approximately .03 percent in the smaller elastic deformation and .08 percent in the larger plastic deformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiang, F.P. andKin, C.C., “Three-beam Interferometric Technique for Determination of Strain of Curved Surfaces,”Opt. Eng.,23,766–768 (1984).
Steinchen, W., Schuth, M., andYang, L.X., “Strains Measured on Plane and Curved Surfaces by Means of the Shearographic Method—Part 1,”Strain,30 (3),105–108 (1984).
Steinchen, W., Schuth, M., andYang, L.X., “Strains Measured on Plane and Curved Surfaces by Means of the Shearographic Method—Part 2,”Strain,30 (4),139–141 (1994).
Steinchen, W., Schuth, M., andYang, L.X., “Strains Measured on Plane and Curved Surfaces by Means of the Shearographic Method—Part 3,”Strain,30 (5),25–29 (1995).
Lucia, A.C., Franchi, M., Marozzi, C.A., andFontana, R., “Three-dimensional Strain Field Measurement on Cylindrical Vessels by Computer Analysis of Laser Interferograms,” EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,29,132–137 (1989).
Goldberg, J.L., “A Method of Three-dimensional Strain Measurement on Non-ideal Objects Using Holographic Interferometry,” EEXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,23,59–73 (1983).
Morimoto, Y. andFujigaki, M., “Automated Analysis of 3-D Shape and Surface Strain Distributions of a Moving Object Using Stereo Vision,”Opt. Lasers Eng.,18,195–212 (1993).
Peters, W.H., Sutton, M.A., Ranson, W.F., Poplin, W.P., andWalker, D.M., “Whole-field Displacement Analysis of Composite Cylinders,” EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,29,58–62 (1989).
Lu, H., Vendroux, G., andKnauss, W.G., “Surface Deformation Measurements of a Cylindrical Specimen by Digital Image Correlation, EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,37,433–439 (1997).
Luo, P.F., Chao, Y.J., Sutton, M.A., andPeters, W.H., “Accurate Measurement of Three-dimensional Displacement in Deformable Bodies Using Computer Vision,” EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,33,123–132 (1993).
Luo, P.F., Chao, Y.J., andSutton, M.A., “Application of Stereo Vision to Three-dimensional Deformation Analyses in Fracture Experiments,”Opt. Eng.,33,981–990 (1994).
Luo, P.F. andLiou, S.S., “Measurement of Curved Surface by Stereo Vision and Error Analysis,”Opt. Lasers Eng.,30,471–486 (1998).
Peters, W.H. andRanson, W.F., “Digital Image Techniques in Experimental Stress Analysis,”Opt. Eng.,23,427–431 (1982).
Chu, T.C., Ranson, W.F., Sutton, M.A., andPeters, W.H., “Application of Digital-image-correlation Techniques to Experimental Mechanics,” EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICS,25,232–244 (1985).
Sutton, M.A., Wolters, W.J., Peters, W.H., Ranson, W.F., andMcNeill, S.R., “Determination of Displacements Using an Improved Digital Correlation Method,”Image Vision Comput.,1 (3),133–139 (1983).
International Mathematical and Statistical Libraries, Program Solving Software System for Mathematical and Statistical Fortran Programming (Subroutine DQD2DR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, P.F., Chen, J.N. Measurement of curved-surface deformation in cylindrical coordinates. Experimental Mechanics 40, 345–350 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02326479
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02326479