Abstract
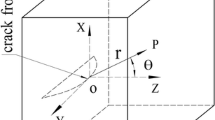
A loading effect on a-c potential difference measured for two-dimensional stationary surface crack is examined under opening load without shear. An increment of potential difference caused by a load change is revealed to have a proportional relationship with an increment of the stress-intensity factor,K I. Also, the constant of proportionality of the relationship is found to be independent of the crack length. Based on this relationship, a procedure is developed for measurement ofK Iby means of the a-c potential drop technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Measurement of Crack Length and Shape During Fracture and Fatigue, ed. C.J. Beevers, Engineering Materials Advisory Services, West Midlands (1980).
Tada, H., Paris, P. andIrwin, G., The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research Corporation, 2, 13 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saka, M., Nakayama, M., Kaneko, T. et al. Measurement of stress-intensity factor by means of a-c potential drop technique. Experimental Mechanics 31, 209–212 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02326061
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02326061