Summary
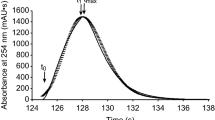
The influence of the alcohol content of the mobile phase and water, acetic acid and aniline as mobile phase additives on the generation and shape of two additional changes of the streaming current, generated inside the liquid chromatography column by injection of any sample and recorded before the responses of retained solutes, was studied in a normal-phase system using silica gel as the stationary phase. The mobile phases were based on a n-heptane-1-propanol mixtures. Under the same conditions the relationships between the column interparticle volume, the column void volume and the total liquid volume in the column and the retention volumes of these two streaming current responses, having the form of chromatographic peaks, were studied. The column void volume was identified with the retention volume of n-octane. The total liquid volume in the column (column hold-up) was calculated from the weight loss of the column wetted with water at first and then dried in nitrogen stream.
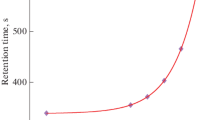
The retention volume of the first streaming current response equals the column interparticle volume disregarding the mobile phase composition. If the 95∶5 n-heptane-1-propanol mobile phase contains water up to 80% of its saturated concentration (up to 0.114% by vol.), the retention volume of the second response agrees with the total volume of the liquid in the silica gel column, with a precision better than 2%. At a higher relative water saturation the retention volume of the second response increases, while the column void volume decreases. Both changes are explained by the spontaneous formation of a highly polar stagnant liquid in the pores of the silica gel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.J. Hunter, Zeta Potential in Colloid Science, Academic Press, London (1981).
J. Neča, R. Vespalec, to be published.
R.M. Hurd, H. Hackerman, J. Electrochem. Soc.102, 594 (1955).
N. Ando, Y. Tanizaki, F. Hasegawa, U.S. Pat. 3352643 (1967).
M. Krejčí, K. Šlais andK. Tesařík, J. Chromatogr.149, 645 (1978).
J. Neča, R. Vespalec, J. Chromatogr.514, 161 (1990).
R. Vespalec, M. Ciganková, J. Chromatogr.364, 233 (1986).
R. Vespalec, M. Ciganková, J. Víška, in:H. Kalász andL. S. Ettre (Eds.), chromatography' 84, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest 1986, p. 145.
M. Krejčí, D. Kouřilová, R. Vespalec, K. Šlais, J. Chromatogr.191, 3 (1980).
W.R. Melander, J.F. Erard, Cs. Horváth, J. Chromatogr.282, 211 (1983).
J. Neča, F. Stehlík, R. Vespalec, J. Chromatogr.447, 177 (1988).
R.P.W. Scott, P. Kucera, J. Chromatogr.149, 93 (1978).
L.R. Snyder, Principles of Adsorption Chromatography, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1968, pp. 43 and 131.
R. Vespalec, J. Chromatogr.,118, 47 (1976).
J.P. Crombeen, S. Heemstra, J.C. Kraak, J. Chromatogr.282, 95 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vespalec, R., Šimek, Z. Dependence of the retention volumes of additional streaming current responses and of the column void volume on mobile phase composition. Chromatographia 32, 130–136 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02325015
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02325015