Abstract
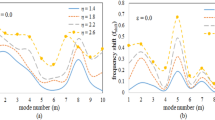
The influence of eccentricity of loading on the vibrations and buckling of stringer-stiffened shells is studied. An established nonlinear theory, which takes into account nonlinear prebuckling, is applied and the predictions are compared with experimental results. Two families of shells, one ‘heavily’ stiffened and the other ‘moderately’ stiffened, were tested but detailed results are presented only for the ‘heavily’ stiffened shells. In each family there are three identical shells, each with different eccentricity of loading. In all cases, different in-plane-boundary conditions are considered and correlated with experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A 1 :
-
cross-sectional area of stringers
- b 1 :
-
stringer spacing (distance between centers of stringers)
- c 1 :
-
width of stringer
- d 1 :
-
height of stringer
- E :
-
elastic modulus
- e 1 :
-
stringer eccentricity (distance from shell middle surface to stiffener centroid)
- e i :
-
eccentricity of loading at one stringer at one end (distance from shell middle surface to the point of load application)
- ē:
-
average eccentricity of loading (distance from shell middle surface to the point of load application)
- f :
-
frequency
- h :
-
thickness of shell
- I 11 :
-
moment of inertia of stringer cross section about its centroidal axis
- L :
-
length of shell
- M x :
-
moment resultant in axial direction
- m :
-
number of longitudinal half waves
- N x :
-
axial membrane force resultant
- n :
-
number of circumferential waves
- P :
-
axial load
- P cr :
-
buckling load
- R :
-
radius-to-shell middle surface
- SS3:
-
simple-support boundary condition,M x=w=v=Nx=0
- SS4:
-
simple-support boundary condition,M x=w=v=ux=0
- u, v, w :
-
displacements in axial, circumferential and radial directions, respectively (radial direction positive inward)
- Z :
-
(1-ν) 1/2(L/R)2(R/h), Batdorf shell parameter
- ν:
-
Poisson's ratio
- ηt1:
-
torsional stiffness parameter of stringer
- ɛ m :
-
axial bending strain
- σ.001:
-
0.1 percent offset yield stress
References
DeLuzio, A., Stuhlman, C. E. andAlmroth, B., “Influence of Stiffener Eccentricity and End Moment on Stability of Cylinders in Compression,”AIAA Journal 4 (5),872–877 (May1966).
Seggelke, P. andGeier, B., “Das Beulverhalten versteifter Zylinderschalen,”Zeitschrift fuer Flugwissenschaften No. 15, Helft 12, 477–490 (December1967).
Block, D. L., “Influence of Discrete Ring Stiffeners and Prebuckling Deformations on the Buckling of Eccentrically Stiffened Orthotropic Cylinders,” NASA TN D-4283 (January 1968).
Almroth, B. O., Bushnell, D. and Sobel, L. H., “Buckling of Shells of Revolution with various Wall Constructions,” NASA CR-1049,1,Numerical Resuts (May 1968).
Almroth, B. O. andBushnell, D., “Computer Analysis for Various Shells of Revolution,”AIAA Journal,6 (10),1848–1855 (October 1968).
Stein, M., “Some Recent Advances in the Investigation of Shell Bucking,”AIAA Journal,6 (12),2339–2345 (December,1968).
Hutchinson, J. W. andFrauenthal, J. C., “Elastic Post-Buckling Behaviour of Stiffened and Barreled Cylinders,”J. Appl. Mech.,36,Series E, (4),784–790 (December1969).
Chang, L. K. and Card, M. F., “Thermal Buckling Analysis for Stiffened Orthotropic Cylindrical Shells,” NASA TN-D-6332 (April 1971).
Weller, T., Singer, J. andBatterman, S. C., “Influence of Eccentricity of Loading on Buckling of Stringer-Stiffened Cylindrical Shells,”Thin-Shell Structures, Theory, Experiment and Design, ed. by Fung Y. C. andSechler, E. E., Prentice-Hall, Englewood-Cliffs, NJ, 305–324 (1974).
Bushnell, D., “Stress, Stability and Vibration of Complex Shells of Revolution: Analysis and User's Manual for BOSOR 3, Lockheed Missiles and Space Co., Report N-5J-69-1, Samso TR-69-375 (Sept. 1969).
Rosen, A. andSinger, J., “Vibrations of Axially Loaded Stiffened Cylindrical Shells: Part I—Theoretical Analysis,”TAE Report No. 162, Technion Research and Development Foundation Ltd., Haifa, Israel (February1974).
Singer, J., Baruch, M. andHarari, O., “On the Stability of Eccentrically Stiffened Cylindrical Shells under Axial Compression,”Int. J. of Solids and Structures,2,445–470 (1967).Also TAE Report No. 44, Technion Research and Development Foundation, Haifa, Israel (December, 1965).
Baruch, M., andSinger, J., “Effect of Eccentricity of Stiffeners on the General Instability of Stiffened Cylindrical Shells under Hydrostatic Pressure,”J. of Mech. Eng. Sci.,5 (1),23–27 (March1963).
Rosen, A. andSinger, J., “Vibrations of Axially Loaded Stiffened Cylindrical Shells: Part II—Experimental Analysis,”TAE Report No. 163, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel (August1973).
Weller, T. andSinger, J., “Experimental Studies on the Buckling of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Integrally Stringer-Stiffened Shells,”TAE Report No. 135 Technion Research and Development Foundation, Haifa Israel (November1971).
Singer, J., “The Influence of Stiffener Geometry and Spacing on the Buckling of Axially Compressed Cylindrical and Conical Shells,”Theory of Thin Shells, Proc. of 2nd IUTAM Symp. on Theory of Thin Shells, Copenhagen, (September 1967),234–263, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1969).
Weller, T., Singer, J. andNachmani, S., “Recent Experimental Studies on Buckling of Integrally Stiffened Cylindrical Shells under Axial Compression,”TAE Report 100, Technion Research and Development Foundation, Haifa, Israel (February,1970).
Rosen, A. andSinger, J., “Vibrations and Buckling of Eccentrically Loaded Stiffened Cylindrical Shells,”TAE Report No. 205, Technion Research and Development Foundation, Haifa, Israel (June1974).
Singer, J. and Rosen, A., “The Influence of Boundary Conditions on the Buckling of Stiffened Cylindrical Shells,” pressented at IUTAM Symp. on Buckling of Structures, Harvard University, June 17–21, 1974, to be published in the Proceedings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The research reported has been sponsored in part by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, through the European Office of Aerospace Research United States Air Force, under Grant 72-2394.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosen, A., Singer, J. Vibrations and buckling of eccentrically loaded stiffened cylindrical shells. Experimental Mechanics 16, 88–94 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02324891
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02324891