Abstract
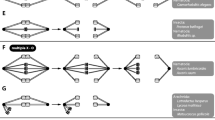
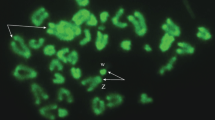
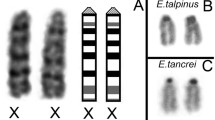
An improved technique for the study of meiosis is described. The principle is based on the use of Ca- and Mg- free isotonic salt solution buffered with phosphates and of hypotonic medium without citrate. Thousands of meiotic randomly dispersed prophases may be observed in good conditions regarding not only the preservation and spreading of autosomic bivalents but also the mode of association between the X and Y inside the sex vesicle. In the Rat, it seems clear that inside the sex vesicle in pachytene the Y (heterochromatic) and the X (not heterochromatic) chromosomes are already associated “end to end” and that there is no chiasmatic relation between them. In diplotene, the Y chromosome has been seen associated by its non-centromeric end, the X, apparently by its short-arms end. The question to know whether this kind of association is peculiar to the Rat or may be generalized to all placental mammals is still under investigation. In the Sloth (Choloepus hoffmanni), the normal translocation of the Y on an autosome is cleary, demonstrable during meiosis as a peculiar type of association (trivalent).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corin-Frederic, J. (1968). L'assortiment chromosomique du paresseuxCholoepus hoffmanni Peters. I. Etablissement et étude détaillée du caryotype. II. Mise en évidence d'une formule gonosomique particulière et ses implications dans le mécanisme général de “dosage-compensation” chez les mammifères. Thèse de Doctorat en Sciences Zoologiques, Université de Liège-144 pp., 42 fig.
Evans, E. P., G. Breckon & C. E. Ford (1964). An air-drying method for meiotic preparations from Mammalian testes.Cytogenetics 3: 289–294.
Hulten, M., J. Lindsten, Pen-Ming L. Ming & M. Fraccaro (1966). The XY bivalent in human male meiosis.Ann. Hum. Genet. 30: 119–124.
Moorhead, P. S., P. C. Nowell, W. J. Mellman, D. M. Battips & D. A. Hungerford (1960). Chromosome preparations of leucocytes cultivated from human peripheral blood.Exp. Cell Res. 20: 613–616.
Ohno, S., W. D. Kaplan & R. Kinosita (1959). On the end-to-end association of the X and Y chromosomes ofMus musculus.Exp. Cell. Res. 18: 282–290.
Puck, T. T., S. J. Cieciura & A. Robinson (1958). Genetics of somatic mammalian cells. III. Long term cultivation of euploid cells from human and animal subjects.J. Exp. Med. 108: 945–956.
Sasaki, M. & S. Makino (1965). The meiotic chromosomes of man.Chromosoma 16: 637–651.
Solari, A. J. (1964). The morphology and ultrastructure of the sex vesicle in the mouse.Exp. Cell Res. 36: 160–168.
Solari, A. J. & L. L. Tres (1967). The ultrastructure of the human sex vesicle.Chromosoma 22: 16–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corin-Frederic, J. Technique amelioree pour l'etude des meioses males et en particulier du mode d'association des gonosomes. Genetica 39, 345–350 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02324473
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02324473