Abstract
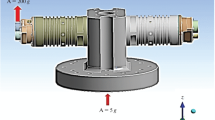
The mission of the ULLAGE motor is to maintain a positive acceleration of the Saturn rocket during the period between burnout of the first stage and ignitiion of the second stage. The eight ULLAGE motors attached to the Saturn second stage are fired during separation from the first stage. They must withstand intense sound levels and vibrations transferred through the first stage and the interstage structures.
Vibration tests were performed on an inert ULLAGE motor to safely educe the approximate response of the design configuration. The results served as a basis for improved definitions of the control parameters in subsequent vibration tests performed during the development program. The motor was tested while subjected to harmonic (sinusoidal) displacing excitation, as well as to a Gaussian distribution of random vibration. The transmissibilities and power spectral densities were obtained for forcing functionals in the longitudinal, radial and tangenital directions. Summaries of all the vibration tests were prepared and the critical frequencies were enumerated and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Procurement Specification MC901-0089 for ULLAGE Motors, S&ID, NAA, 12214 Lakewood Blvd., Downey, Calif., (July 25, 1964).
File No. 5777-6901-T0-S-1, ULLAGE, Inert Vibration, Data Reduction Group, Engineering Test Section, Eng. Dept., Rocketdyne, McGregor, Tex. (March and April, 1965).
Crandall, S. H., Random Vibration, MIT Press, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Mass. (Vol. I, 1958 and Vol. II, 1963).
Crandall, S. H. andMark, W. D., Random Vibration in Mechanical Systems, Academic Press, New York (1963).
Morrow, C. T., Shock and Vibration Engineering, I, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York (1963).
Harris, C. M. andCrede, C. E., Shock and Vibration Handbook, I, II, III, McGraw Hill, New York (1961).
Gottlieb, P., “Expanded Vibration Test Facility, Its Function and Use as an Engineering Tool”, EMT 65-1, Rocketdyne, McGregor, Tex. (April 22, 1965).
Bynum, D., Jr., “Vibration Test Evaluation of an Inert ULLAGE Motor”, DDM 65–43, Rocketdyne, McGregor, Tex. (June 18, 1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Douglas Bynum, Jr. was Senior Design Engineer at Rocketdyne, a Division of North American Rockwell Corp., McGregor, Texas at the time paper was prepared
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bynum, D. Vibration-test evaluation of an ULLAGE solid-propellant rocket motor. Experimental Mechanics 10, 57–63 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320133
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320133