Abstract
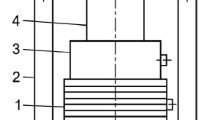
Force transducers directly interact with their environment. In this study, a force transducer is attached to the midpoint of a free-free beam and is used to measure the force on a rigid mass that vibrates with the beam. The ratio of force to mass times acceleration is measured for several different masses over a frequency range that includes the first four odd natural frequencies of the beam. Then the force transducer is mounted so that the beam's strain is isolated from the transducer. The tests are repeated. The results dramatically illustrate the effects of base strain on the force measurements. A simple theoretical model is developed that explains the vertical axis shift in the calibration curve.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a:
-
acceleration
- A:
-
a constant [see eq. (9)]
- b:
-
beam width
- B:
-
a constant [see eq.(13)]
- BS:
-
base strain test cases
- C:
-
charge amplifier feedback capacitance
- d:
-
depth of beam
- Ea :
-
accelerometer output voltage
- Ef :
-
force transducer output voltage
- F:
-
force
- EI:
-
beam's bending stiffness
- Kn :
-
constant dependent on nth mode of vibration
- g:
-
acceleration due to gravity
- h:
-
beam depth d/2
- IS:
-
isolated test cases (by using isolation a mass)
- l:
-
beam length
- m:
-
calibration mass
- man :
-
apparent seismic mass of nth mode
- mb :
-
beam mass
- men :
-
excess seismic mass for nth mode
- ms :
-
transducer's seismic mass
- NI:
-
isolated test cases (by using isolation a mass and a nut)
- S:
-
straight-line slope through data of voltage ratio vs calibration mass
- Sa :
-
accelerometer's voltage sensitivity (V/g)
- Sf :
-
force transducer's voltage sensitivity (V/unit force)
- Sq :
-
force transducer's charge sensitivity (pC/unit force)
- Sɛ :
-
force transducer's base strain sensitivity
- Yo :
-
vertical axis intercept
- Yon :
-
vertical intercept for nth mode
- βn1:
-
nth eigenvalue multiplying factor
- ɛ:
-
base strain
- φn :
-
second spatial derivative of nth mode shape at transducer's location
- φn :
-
nth mode shape at transducer's location
References
McConnell, K.G., “The Interaction of Force Transducers with Their Test Environment,”Modal Analysis: Internat. J. Analytical and Experimental Modal Analysis,8 (2),137–150 (1993).
Dally, J.W., Riley, W.F. andMcConnell, K.G. Instrumentation for Engineering Measurements, 2d ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 323–325 (1993).
McConnell, K.G. and Varoto, P., “Force Transducer Bending Moment Sensitivity Can Affect the Measured Frequency Response Functions,” Proc. 11th Internat. Modal Analysis Conference, Kissimmee, FL (Feb. 1993).
Rao, S.S. Mechanical Vibrations, 2d ed., Reading, MA, 394–408 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappa, P., McConnell, K.G. Base strain effects on force measurements. Experimental Mechanics 36, 284–289 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318020