Synopsis
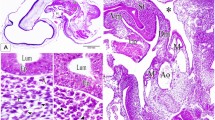
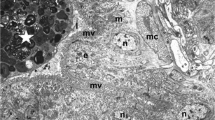
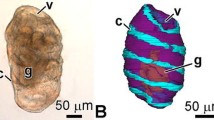
Ultrastructural features of the epidermis and rectum were studied inSebastes schlegeli andS. melanops during the late stages of embryonic development, to confirm uptake of maternal substances. Ruthenium red (RR) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) were used at fixation and in live embryos, respectively. Epidermal tissue of embryos after developmental stage 24 comprised two squamous cell layers. The outer, thinner cells and their intercellular spaces were easily infiltrated with RR, but the inner cells had no RR deposition. The HRP was not incorporated into the epidermis except in a few outer cells, which had well-developed microvillous projections of cytoplasm. Sacciform cells, chloride cells, and mucous cells distributed in the inner layer but protruding to the epidermal surface had no intracellular RR and HRP depositions. The rectal cells of embryos at about developmental stage 28 had many globular inclusions containing electron-dense substances. The rectal cells were found to take up and digest HRP actively. It is suggested that the embryonic epidermis is structurally loose and takes up low weight molecules, while rectal cells, after the opening of the mouth, actively ingest exogenous, high weight molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Aso, N., H. Saito & T. Takagi. 1977. Microridge formation of epidermal cells of the developing salmon (Oncorhynchus keta Walbaum): scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. Zool. Mag. 86: 208–221 (In Japanese.)
Boehlert, G.W., M. Kusakari, M. Shimizu & J. Yamada. 1986. Energetics during embryonic development in kurosoi,Sebastes schlegeli Hilgendorf. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 101: 239–256.
Boehlert, G.W. & M.M. Yoklavich. 1984. Reproduction, embryonic energetics, and the maternal-fetal relationship in the viviparous genusSebastes (Pisces: Scorpaenidae). Biol. Bull. 167: 354–370.
Brooks, R. E. 1969. Ruthenium red stainable surface layer of lung alveolar cells: electron microscopic interpretation. Stain Tech. 44: 173–177.
Iwai, T. 1969. Fine structure of gut epithelial cells of larvae and juvenile carp during absorption of fat and protein. Arch. Histol. Jap. 30: 183–199.
Jones, M.P., F.G.T. Holliday & A.G.E. Dunn. 1966. The ultrastructure of the epidermis of larvae of the herring (Clupea harengus) in relation to the rearing salinity. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 46: 235–239.
Karnovsky, M.J. 1965. A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 27: 137A.
Mendoza, G. 1958. The fin fold ofGoodea luitpoldii, a viviparous cyprinodont teleost. J. Morph. 103: 539–560.
Mendoza, G. 1972. The fine structure of an absorptive epithelium in a viviparous teleost. J. Morph. 136: 109–130.
Shimizu, M. & J. Yamada. 1980. Ultrastructural aspects of yolk absorption in the vitelline syncytium of the embryonic rockfish,Sebastes schlegeli. Jap. J. Ichthyol. 27: 56–63.
Tanaka, M. 1969. Studies on the structure and function of the digestive system in teleost larvae-2. Characteristics of the digestive system in larvae at the stage of first feeding. Jap. J. Ichthyol. 16: 41–49 (In Japanese).
Turner, C.L. 1947. Viviparity in teleost fishes. Sci. Mon. 65: 508–518.
Veith, W.J. 1979. The chemical composition of the follicular fluid of the viviparous teleostClinus superciliosus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 63A: 37–40.
Veith, W.J. 1980. Viviparity and embryonic adaptations in the teleostClinus superciliosus. Can. J. Zool. 58: 1–12.
Watanabe, Y. 1982. Intracellular digestion of horseradish peroxidase by the intestinal cells of teleost larvae and juveniles. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 48: 37–42.
Watanabe, Y. 1984. An ultrastructural study of intracellular digestion of horseradish peroxidase by the rectal epithelium cells in larvae of a freshwater cottid fishCottus nozawae. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 50: 409–416.
Wourms, J.P., G.D. Bryon & J. Lombardi. 1988. The maternalembryonic relationship in viviparous fishes. pp. 1–134.In: W.S. Hoar & D.J. Randall (ed.) Fish Physiology, Vol. 11B, Academic Press, New York.
Yamada, J. 1968. A study on the structure of surface cell layers in the epidermis of some teleosts. Annot. Zool. Jap. 41: 1–8.
Yamada, J. & M. Kusakari. 1991. Staging and the time course of embryonic development in kurosoi,Sebastes schlegeli. Env. Biol. Fish. 30: 103–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, M., Kusakari, M., Yoklavich, M.M. et al. Ultrastructure of the epidermis and digestive tract inSebastes embryos, with special reference to the uptake of exogenous nutrients. Environ Biol Fish 30, 155–163 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296886
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02296886