Summary
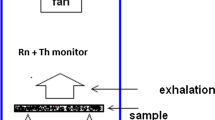
People who live in industrial countries receive a radioactive dose of 2.4 mSv/y: the most important contribution to this dose is given by radon decay products. Radon is a noble gas generated from the disintegration of radium, which is found in soils and building materials. Owing to a bad air circulation, radon and its daughters may accumulate in a house. By using a mathematical model it may be shown that radon concentration is inversely proportional to the ventilation rate. Measurements of radon concentration through the method of activated carbon canisters, show that in a room with a double-pane window, kept continuously closed, the mean radon concentration can exceed the concentration of a similar room with a single-pane window of 190%. However, the radon concentration inside the energy-saving room may be decreased up to values slightly higher than those measured in the conventional window room, by simply opening the double-pane window a few minutes a day. A set of measurements carried out in a group of house in Reggio Emilia validates the effectiveness of that practice: radon concentrations in rooms with double-pane window closely approximated to those of rooms with ordinary window.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen B.L., Cohen E.S., (1983) —Theory and practice of radon monitoring with charcoal adsorption. Health Phys.,45:501–508.
George A.C., (1984) —Passive, integrated measurement of indoor radon using activated carbon. Health Phys.,46:867–872.
Malanca A., Orlandini R., Pessina V., Dallara G., (1991) —Il radon nelle abitazioni di Reggio Emilia. Acqua Aria (in press) (with abstract in English).
Malanca A., Pessina V., Dallara G., (1991a) —Metodi per la riduzione del radon nelle abitazioni. Ing. Amb. (in press) (with abstract in English).
Porstendorfer et al., (1980) —Method for a continuous registration of radon, thoron and their decay products indoors and outdoors. In: Nat. Radiat. Envir. III, Gesell & Lowder E., CONF 780422:1293–1307.
Stranden E., Berteig L., (1980) —Radon in dwellings and influencing factors. Health. Phys.,39:275–284.
UNSCEAR, (1977) —Sources and effects of atomic radiation-1977 Report to the General Assembly with annexes. New York: United Nations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malanca, A., Cassoni, F., Dallara, G. et al. Radon in dwellings: The importance of ventilation. Aerobiologia 8, 57–61 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291330
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291330