Summary
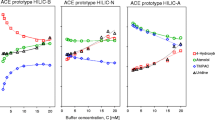
It is shown theoretically that when the concentration of organic solvent in the mobile phase increases, or solute size decreases, log k′ values of small solutes in reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) will tend to have a minimum value called the convergence point. A theoretical model for evaluating the convergent coordinates of small solutes is presented by using a stoichiometric displacement model for retention (SMDR). The physical meaning of the coordinates of each kind of convergence are also elucidated. The convergence points have either two-dimensional coordinates with a common ordinate (the logarithm of the phase ratio of the column, log φ) or threedimensional corrdinates with two common axes: — log φ and the logarithm of the molar concentration of the pure displacing agent in mobile phase, log aD. The other axis relates to the nature of the solutes, such as carbon number of a homolog, van der Waal's surface area, hydrophobic fragment constant etc. for the latter and those and/or concentration axis for the former. The model was tested with published data and found to give a good fit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. E. Berendsen, L. de Galan, J. Chromatogr.196, 21 (1980).
B. A. Bidlingmeyer, S. N. Deming, W. P. Price, Jr., B. Sachok, M. Petrusek, J. Chromatogr.186, 419 (1980).
H. Colin, A. M. Krustulovic, M. F. Gonnord, G. Guiochon, Z. Yun, P. Jandera, Chromatographia,17, 9 (1983).
XD. Geng, Fred E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.,296, 15 (1984).
XD. Geng, Fred E. Regnier, J. Chromatogr.332, 147 (1985).
XD. Geng, L. Guo, J. Chang, J. Chromatogr.507, 1 (1990).
XD. Geng, Guide to Theory of Separation Science, Northwest University Publisher, Xi'an, 1990.
A. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem.68, 441 (1964).
R. F. Rekker, The Hydrophobic Fragmental Constant, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co., Amsterdam, 1977, p. 350.
N. A. Katsanos, G. Karaiskakis, P. Agathonos, J. Chromatogr.218, 409 (1981).
P. Dufek, J. Chromatogr.281, 49 (1983).
XD. Geng, Xibei Daxue Xuebao (Natural Sci. Pub.)21, 25 (1991).
N. Tanaka, E. R. Thornton, J. Am. Chem. Soc.,99, 7300 (1977).
P. J. Schoenmakers, H. A. H. Billiet, R. Tijseen, L. de Galan, J. Chromatogr.149, 519 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, X.D., Regnier, F.E. Convergence of retention for small solutes in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Chromatographia 38, 158–162 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02290329
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02290329