Abstract
Tree decline has been observed recently in 25–30 year old pine stands inCladina andCalluna-type heath forests in the Hämeenkangas and Pohjankangas areas of southwestern Finland. The trees had grown more or less normally for 15 years. During the following 7 to 8 years increased growth occurred. From 1982 to 1984, however, the trees revealed a sudden reduction in height increment. Additionally, some trees were marked by poor apical shoot dominance. Occasionally complete crown dieback was observed. The trees retained only one to three years' needles. These needles often were characterized by a brownish yellow discoloration.
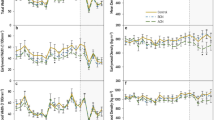
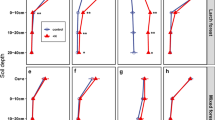
Chemical foliar and soil analysis indicate both a nitrogen deficiency and a deficiency in calcium and magnesium related to the relatively high aluminium levels in the soil. In the needles of affected trees phosphorus and especially potassium concentrations were higher than normally.
The low content of nitrogen, calcium and magnesium in the soil is related to the acidic, nutrient-poor bedrock, and the low cation exchange capacity. Also the leaching of nutrients, the shallow and poor quality of the humus layer, and the removal of nutrients by tree harvesting may have effected on the nutritional disturbances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsen G 1983 Sulphur pollution: Ca, Mg and Al in soils and soil water and possible effects on forest trees.In Effects of Accumulation of Air Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems Eds. B Ulrich and J Pankrath. pp 207–218. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht.
Ahrens E 1964 Untersuchungen über den Gehalt von Blättern und Nadeln verschiedener Baumarten an Kupfer, Zink, Bor Molybdän und Mangan. Allg. Forst- u. Jagdz. 135, 8–16.
Baule H and Fricker C 1967 Die Düngung von Waldbäumen. BLV Bayerischer Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH, München. 259 p.
Bergmann W 1983 Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen: Entstehung und Diagnose. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart. 591 p.
Bosch C, Pfannkuch E, Baum U and Rehfuess K E 1983 Über die Erkrankung der Fichte (Picea abies Karst.) in den Hochlagen des Bayerischen Waldes. Forstw. Cbl. 102, 167–181.
Clarkson D T and Sanderson J 1971 Inhibition of the uptake and long-distance transport of calcium by aluminium and other polyvalent cations. J. Exp. Bot. 22, 837–851.
Comerford N B 1981 Distributional gradients and variability of macroelement concentrations in the crowns of plantation grownPinus resinosa (Ait.) Plant and Soil 63, 345–353.
Elonen P 1971 Particle-size analysis of soil. Acta Agr. Fenn. 122, 1–122.
Evers F H 1983 Ein Versuch zur Aluminium-Toxizität bei Fichte: Ergebnisse eines Gefäßkulturversuchs mit bewurzelten Fichtenstecklingen. Forst- u. Holzwirt, 12, 305–307.
Foy C D 1974 Effects of aluminium on plant growth.In The Plant Root and its Environment. Ed. E W Carson. pp 601–642. University Press of Virginiana, Charlottesville.
Gomes M M S, Cambraia J, Sant'anna R and Esteväo M M 1985 Aluminium effects on uptake and translocation of nitrogen in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor, L. Moench). J. Plant Nutr. 8, 457–465.
Gosz J R 1984 Biological factors influencing nutrient supply in forest soils.In Nutrition of Plantation Forests. Eds. G D Bowen and E K S Nambiar. pp 119–146. Academic Press, New York.
Halonen O, Tulkki H and Derome J 1983 Nutrient analysis methods. Metsäntutkimuslaitoksen tiedonantoja 121, 28 p.
Hartikainen H 1981 Uptake of soil P, Al, Fe, Mn, Mg and Ca by Italian rye grass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) induced by synthetic chelating agent. J. Sci. Agric. Soc. Finl. 53, 152–160.
Heanes D L 1984 Determination of total organic-C in soils by an improved chromic acid digestion and spectrophotometric procedure. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 15, 1191–1213.
Hüttermann A 1985 The effects of acid deposition on the physiology of the forest ecosystem. Experientia 41, 584–590.
Ilvessalo Y 1920 Kasvu- ja tuottotaulukot Suomen eteläpuoliskon mänty-, kuusi- ja koivumetsille. Referat: Ertragstafeln für die Kiefern-, Fichten- und Birkenbestände in der Südhälfte von Finnland. Acta For. Fenn. 15, 1–94.
Kangas E 1931 Siikakankaan mäntytaimiston tuhoista. Referat: Über die Schädigungen der Kieferpflanzenbestände in Siikakangas. Silva Fenn. 17, 1–107.
Kangas E 1937 Tutkimuksia mäntytaimistotuhoista ja niiden merkityksestä. Referat; Untersuchungen über die in Kiefernpflanzbestände auftretenden Schäden und ihre Bedeutung. Commun. Inst. For. Fenn. 24(1), 1–238.
Kangas E 1940 Tuloksia Pohjankankaan ja Hämeenkankaan metsänviljelyksistä. Referat: Ergebnisse der Waldkulturen auf den Heiden Pohjankangas und Hämeenkangas. Acta For. Fenn. 49, 1–64.
Matisto A 1961 On the relation between stones of the eskers and the local bedrock in the area northwest of Tampere, south-western Finland. Bulletin de la Comission geologique de Finlande 193, 1–53.
Matzner E and Ulrich B 1985 Implications of the chemical soil conditions for forest decline. Experientia 41, 578–584.
Mengel K and Kirkby E A 1982 Principles of Plant Nutrition. Third edition. International Potash Institute, Bern. 655 p.
Miller H G 1984 Dynamics of nutrient cycling in plantation ecosystems.In Nutrition of Plantation Forests. Eds. G D Bowen and E K S Nambiar pp 51–78. Academic Press, New York
Mälkönen E 1974 Annual primary production and nutrient cycle in some Scots pine stands. Commun. Inst. For. Fenn. 84, 1–87.
Paarlahti K, Reinikainen A and Veijalainen H 1971 Nutritional diagnosis of Scots pine stands by needle and peat analysis. Commun. Inst. For. Fenn. 74, 1–58.
Raitio H 1987 Site elevation differences in frost damage to Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) For. Ecol. Management 20, 299–306..
Rajakorpi A 1984 Microclimate and soils of the central part of the Hämeenkangas interlobate complex in western Finland. Fennia 162, 237–337.
Rebel 1921 Heidekrankheit reiner Föhrenbestockung. Z. Forstu. Jagdw. 53, 321–348.
Rechcigl J E and Sparks D L 1985 Effect of acid rain on the soil environment: A review. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 16, 653–680.
Reigber E and Braun G 1985 Forstliche Bioindikatoruntersuchungen in Bayern: Methodik und erste Ergebnisse 1981/82. Forstl. Forsch. ber. München 68, 1–179.
Rost-Siebert K 1983 Aluminium-Toxizität und- Toleranz an Keimpflanzen von Fichte (Picea abies Karst.) und Buche (Fagus silvatica L.). Allg. Forstz. 38, 686–689.
Ryan D G and Bormann F H 1982 Nutrient resorption in northern hardwood forests. BioScience 32, 29–32.
Schulze E D and Küppers M 1985 Responses ofPinus silvestris to magnesium deciency.In Establishment and Tending of Subalpine Forest: Research and Management. Eds. H Turner and W Tranquillini. pp 193–196. Berichte, Eidgenössische Anstalt für das Forstliche Versuchswesen, Switzerland 270.
Stone E L 1968 Microelement nutrition of forest trees: A review.In Forest Fertilization — Theory and Practise. Symp. For. Fert. April, 1967. Knoxville, USA. pp 132–175. Tennessee Valley Authority, Nat. Fert. Develop. Cent., Muscle Shoals, Alabama.
Tamminen P and Mälkönen E 1986 Kangasmaiden herkkyys happamoitumiselle. Metsäntutkimuslaitoksen tiedonantoja 210, 25 p.
Ulrich B 1981 Ökologische Gruppierung von Böden nach ihrem chemischen Bodenzustand. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 144, 289–305.
Ulrich B 1983 Soil acidity and its relations to acid deposition.In Effects of Accumulation of Air Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems. Eds. B Ulrich and J Pankrath. pp 127–146. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht.
Urvas L and Erviö R 1974 Metsätyypin määräytyminen maalajin ja maaperän kemiallisten ominaisuuksien perusteella. Summary: Influence of the soil type and the chemical properties of soil on the determining of the forest type. J. Sci. Agric. Soc. Finl. 46, 307–319.
Viro P J 1969 Prescribed burning in forestry. Commun. Inst. For. Fenn. 67, 1–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raitio, H., Tikkanen, E. Nutritional disturbances of young pines in a dry heath forest. Plant Soil 113, 229–235 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02280185
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02280185