Summary
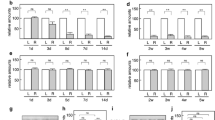
The abundance of muscarinic receptors and m2 muscarinic receptor mRNA in the facial nuclei of rats was evaluated by autoradiographic procedures at various times up to 14 days after transection of the right facial nerve. Receptors were labelled byin vitro incubation of brain sections with L-[3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate, whilein situ hybridization with a35S-labelled oligonucleotide was used to identify m2 muscarinic receptor mRNA in neighbouring sections. The right and left facial nuclei of non-operated control rats appeared equivalent in abundance of muscarinic receptors (359±8 versus 376±9 fmol per mg tissue,n=5) and the presence of m2 mRNA. Axotomy had no effect on the concentration of receptors in the contralateral facial nucleus but caused a gradual loss of receptors from the ipsilateral side. No change was detected at 1 day after nerve transection, but a 23% decrease relative to the contralateral facial nucleus had occurred by 3 days. A maximum decrease of 51% was achieved by 1 week after nerve transection. By comparison, m2 mRNA was nearly eliminated from the ipsilateral facial nucleus at 1 day post-taxonomy and remained depleted for the duration of study. Previous work has established that no significant loss of motoneurons occurs within this period. Accordingly, it is postulated that axonal injury inhibits transcription of the m2 muscarinic receptor gene, resulting in a later decrease in muscarinic receptor protein expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blinzinger, K. &Kreutzberg, G. (1968) Displacement of synaptic terminals from regenerating motoneurons by microglial cells.Z. Zellforsch. 85, 145–57.
Borke, R. C., Curtis, M. &Ginsberg, C. (1993) Choline acetyltransferase and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in motoneurons after different types of nerve injury.J. Neurocytol. 22, 141–53.
Buckley, N. J., Bonner, T. I. &Brann, M. R. (1988) Localization of a family of muscarinic receptor mRNAs in rat brain.J. Neurosci,8, 4646–52.
Chen, E. W., Loera, S. &Chiu, A. Y. (1995) Target regulation of a motor neuron-specific epitope.J. Neurosci. 15, 1556–66.
Fort, P., Sakai, K., Luppi, P.-H., Salvert, D. &Jouvet, M. (1989) Monoaminergic, peptidergic, and cholinergic afferents to the cat facial nucleus as evidenced by a double immunostaining method with unconjugated cholera toxin as a retrograde tracer.J. Comp. Neurol. 283, 285–302.
Fukamauchi, F., Saunders, P. A., Hough, C. &Chuang, D.-M. (1993) Agonist-induced down-regulation and antagonist-induced up-regulation of m2- and m3-muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mRNA and protein in cultured cerebellar granule cells.Mol. Pharmacol. 44, 940–9.
Graeber, M. B. &Kreutzberg, G. W. (1988) Delayed astrocyte reaction following facial nerve axotomy.J. Neurocytol. 17, 209–20.
Haas, C. A., Donath, C. &Kreutzberg, G. W. (1993) Differential expression of immediate early genes after transection of the facial nerve.Neuroscience 53, 91–9.
Habecker, B. A. &Nathanson, N. M. (1992) Regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mRNA expression by activation of homologous and heterologous receptors.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5035–8.
Hermanson, M., Olsson, T., Westermark, B. &Funa, K. (1995) PDGF and its receptors following facial nerve axotomy in rats: expression in neurons and surrounding glia.Exp. Brain Res. 102, 415–22.
Hoover, D. B. &Hancock, J. C. (1985) Effect of facial nerve transection on acetylcholinesterase, choline acetyltransferase and [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding in rat facial nuclei.Neuroscience 15, 481–7.
Hoover, D. B., Baisden, R. H. &Xi-Moy, S. X. (1994) Localization of muscarinic receptor mRNAs in rat heart and intrinsic cardiac ganglia by in situ hybridization.Circ. Res. 75, 813–20.
Houser, C. R., Crawford, G. D., Barber, R. P., Salvaterra, P. M. &Vaughn, J. E. (1983) Organization and morphological characteristics of cholinergic neurons: an immunocytochemical study with a monoclonal antibody to choline acetyltransferase.Brain Res. 266, 97–119.
Kitahara, T., Kiryu, S., Ohno, K., Morita, N., Kubo, T. &Kiyama, H. (1994) Up-regulation of ERK (MAP kinase) and MEK (MAP kinase kinase) transcription after rat facial nerve transection.Neurosci. Res. 20, 275–80.
Kou, S.-Y., Chiu, A. Y. &Patterson, P. H. (1995) Differential regulation of motor neuron survival and choline acetyltransferase expression following axotomy.J. Neurobiol. 27, 561–72.
Levey, A. I., Kitt, C. A., Simonds, W. F., Price, D. L. &Brann, M. R. (1991) Identification and localization of muscarini acetylcholine receptor proteins in brain with subtype-specific antibodies.J. Neurosci. 11, 3218–26.
Lewis, J. V., Baisden, R. H. &Hoover, D. B. (1995) Fate of muscarinic receptors and m2 mRNA in the facial motor nucleus after nerve transection.Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 21 (Part 1), 96.
Mei, L., Roeske, W. R. &Yamamura, H. I. (1989) Molecular pharmacology of muscarinic receptor heterogeneity.Life Sci. 45, 1831–51.
Quirion, R., Aubert, I., Araujo, D. M., Hersi, A. &Gaudreau, P. (1993) Autoradiographic distribution of putative muscarinic receptor sub-types in mammalian brain.Prog. Brain Res. 98, 85–93.
Rousell, J., Haddad, E.-B., Mak, J. C. W. &Barnes, P. J. (1995) Transcriptional down-regulation of m2 muscarinic receptor gene expression in human embryonic lung (HEL 299) cells by protein kinase C.J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7213–18.
Saika, T., Senba, E., Noguchi, K., Sato, M., Kubo, T., Matsunaga, T. &Tohyama, M. (1991a) Changes in expression of peptides in rat facial motoneurons after facial nerve crushing and resection.Mol. Brain. Res. 11, 187–96.
Saika, T., Senba, E., Noguchi, K., Sato, M., Yoshida, S., Kubo, T., Matsunaga, T. &Tohyama, M. (1991b) Effects of nerve crush and transection on mRNA levels for nerve growth factor receptor in the rat facial motoneurons.Mol. Brain. Res. 9, 157–60.
Saika, T., Kiyama, H., Matsunaga, T. &Tohyama, M. (1994) Differential regulation of phospholipase C isozymes in the rat facial nucleus following axotomy.Neuroscience 59, 121–9.
Semba, K. &Egger, M. D. (1986) The facial ‘motor’ nerve of the rat: control of vibrissal movement and examination of motor and sensory components.J. Comp. Neurol. 247, 144–58.
Villaró, M. T., Wiederhold, K.-H., Palacios, J. M. &Mengod, G. (1992) Muscarinic M2 receptor mRNA expression and receptor binding in cholinergic and non-cholinergic cells in the rat brain: a correlative study usingin situ hybridization histochemistry and receptor autoradiography.Neuroscience 47, 367–93.
Vilaró, M. T., Palacios, J. M. &Mengod, G. (1994) Multiplicity of muscarinic autoreceptor subtypes? Comparison of the distribution of cholinergic cells and cells containing mRNA for five subtypes of muscarinic receptors in the rat brain.Mol. Brain Res. 21, 30–46.
Wooten, G. F., Park, D. H., Joh, T. H. &Reis, D. J. (1978) Immunochemical demonstration of reversible reduction in choline acetyltransferase concentration in rat hypoglossal nucleus after hypoglossal nerve transection.Nature 275, 324–5.
Yan, Q., Matheson, C., Lopez, O. T. &Miller, J. A. (1994) The biological responses of axotomized adult motoneurons to brain-derived neurotrophic factor.J. Neurosci. 14, 5281–91.
Young, W. S. III, Bonner, T. I. &Brann, M. R. (1986) Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 9827–31.
Yuguchi, T., Kohmura, E., Yamada, K., Sakaki, T., Yamashita, T., Otsuki, H., Wanaka, A., Tohyama, M., Tsuji, S. &Hayakawa, T. (1995) Changes in growth inhibitory factor mRNA expression compared with those in c-jun mRNA expression following facial nerve transection.Mol. Brain Res. 28, 181–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoover, D.B., Baisden, R.H. & Lewis, J.V. Axotomy-induced loss of m2 muscarinic receptor mRNA in the rat facial motor nucleus precedes a decrease in concentration of muscarinic receptors. Histochem J 28, 771–778 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02272150
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02272150