Abstract
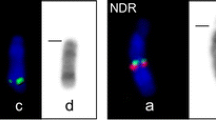
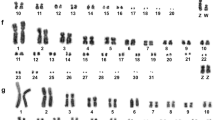
Chevrotains are small forest-dwelling ruminants of the family Tragulidae. The chromosome number of the lesser Malay chevrotain was determined to be 2n=32, NF=64. G- and Q-banding allowed the identification of homologous chromosomes, and C-banding demonstrated the presence of pericentromeric, telomeric and interstitial constitutive heterochromatin. Q-band comparisons with domestic cattle revealed relatively few monobrachial chromosome band homologies. However, the smallest biarmed autosome of the chevrotain, chromosome 15, was determined to be cytogenetically homologus with the acrocentric chromosome 19 of cattle. A molecular cytogenetic analysis confirmed this putative chromosomal homology. In fact, molecular cytogenetic analyses indicate complete conservation of synteny among mouse deer chromosome 15, domestic cattle chromosome 19, domestic pig chromosome 12 and human chromosome 17. In the light of these molecular cytogenetic data and since mouse deer chromosome 15 is submetacentric and appears homologous in banding to submetacentric chromosome 12 of the domestic pig, these outgroup comparisons indicate that the acrocentric condition of cattle chromosome 19 has been derived by inversion. Since this derivative condition is present in the Antilocapridae, Bovidae, Cervidae and Giraffidae, it is a chromosomal synapomorphy that unites these advance ruminant families within the Artiodactyla.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckland RA, Evans HJ (1978a) Cytogenetic aspects of phylogeny in the Bovidae I. G-banding.Cytogenet Cell Genet 21: 42–63.
Buckland RA, Evan HJ (1978b) Cytogenetic aspects of phylogeny in the Bovidae II. C-banding.Cytogenet Cell Genet 21: 64–71.
Cai L, Taylor JF, Wing RA, Gallagher DS, Woo S-S, Davis SK (1995) Construction and characterization of a bovine bacterial artificial chromosome library.Genomics 29: 413–425.
Carpio CM, Ponce de Leon FA (1995) Generation of bovine chromosome-specific DNA libraries for autosomes 1,4,14, 20 and 29. Proc 9th N A Colloq Domestic Animal Cytogenetics and Gene Mapping, p. 18. Texas: Texas A & M University.
Effron M, Bogart MH, Kumamoto AT, Benirschke K (1976) Chromosome studies in the mammalian subfamily Antilopinae.Genetica 46: 419–444.
Evans HJ, Buckland RA, Sumner AT (1973) Chromosome homology of heterochromatin in goat, sheep, and ox studied by banding techniques.Chromosoma 42: 383–402.
Fontana F, Rubini M (1990) Chromosomal evolution in Cervidae.Biosystems 24: 157–174.
Gallagher DS Jr, Womack JE (1992) Chromosome conservation in the Bovidae.J Hered 83: 287–298.
Gallagher DS Jr, Derr JN, Womack JE (1994) Chromosome conservation among the advanced pecorans and determination of the primitive bovid karyotype.J Hered 85: 204–210.
Grubb P (1993) Order Artiodactyla. In: Wilson DE & Reeder DM, eds.Mammal Species of the World. 2nd ed. Washington DC, Smithsonian Institution Press, pp. 377–413.
Gustavsson I (1988) Standard karyotype of the domestic pig: committee for the standardized karyotype of the domestic pig.Hereditas 109: 151–157.
Hansen KM (1973) Heterochromatin (C-bands) in bovine chromosomes.Hereditas 73: 65–70.
Iannuzzi L, Di Meo GP (1995) Chromosomal evolution in bovids: a comparison of cattle, sheep and goat G-and R-banded chromosomes and cytogenetic divergences among cattle, goat and river buffalo sex chromosomes.Chrom Res 3: 291–299.
Iannuzzi L, Di Berardino D, Gustavsson I, Ferrara L, Di Meo GP (1987) Centromeric loss in translocations of centric fusion type in cattle and river buffalo.Hereditas 106: 73–81.
ISCNDA 1989 (1990) International system for cytogenetic nomenclature of domestic animals Di Berardino D, Hayes H, Fries R, Long S (eds).Cytogenet Cell Genet 53: 65–79.
Janis JM, Scott KM (1988) The interrelationships of higher ruminant families with special emphasis on the members of the Cervoidae.novitates 2893: 1–85.
Liming S, Yuze C (1989) The karyotype analysis of the Yunnan mouse deer (Tragulus javanicus williamsoni); ACTAZoological Sinica 35: 41–44.
Mendiola JR, Amady S, Buoen LC, Paszek AA, Schook LB, Ponce de Leon FA, Louis CF (1995) Generation of a swine chromosome 6 specific library by microisolation. Proc 9th N A Colloq Domestic Animal Cytogenetics and Gene Mapping, p. 56. Texas: Texas A & M University.
Nash WG, O'Brien SJ (1982) Conserved regions of homologous G-banded chromosomes between orders in mammalian evolution: carnivores and primates.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 6631–6635.
Petit P, De Meurichy W (1992) Comparative standardized cytogenertic studies in family Giraffidae. Proc 10th Eur Colloq Cytogenetics Domestic Animals, Utrecht University, The Netherlands, pp. 171–177. Utrecht: Utrecht University.
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative high sensitivity fluourescence hybridization.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2934–2938.
Reading Conference 1976 (1980) Proceedings of the first international conference for the standardization of banded karyotypes of domestic animals.Hereditas 92: 145–162.
Rettenberger G, Klett C, Zechner U, Kunz J, Vogel W, Hameister H (1995) Visualization of the conservation of synteny between humans and pigs by heterologous chromosomal painting.Genomics 26: 372–378.
Sawyer JR, Hozier JC (1986) High resolution banding of mouse chromosomes: banding conservation between man and mouse.Science 232: 1632–1635.
Solinas-Toldo S, Lengauer C, Fries R (1995) Comparative genome map of human and cattle.Genomics 27: 489–496.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin.Exp Cell Res 75: 304–306.
Vaughan TA (1986)Mammalogy. Philadelphia: Saunders College Publishing.
Verma and Babu, 1989.Human Chromsomes—Manual of Basic Techniques. Pergamon Press, New York.
Von Kiel K, Hameister H, Somissich IE, Adolph S (1985) Early replication banding reveals a strongly conserved functional pattern in mammalian chromosomes.Chromosoma 93: 69–76.
Wurster DH, Benirschke K (1967a) The chromosomes of twenty-three species of the Cervoidea and Bovoidea.Mammal Chrom Newslett 8: 226–229.
Wurster DH, Benirschke K (1967b) Chromosome studies in some deer, the springbok, and the pronghorn, with notes on the placentation in deer.Cytologia 32: 273–285.
Wurster DH, Benirschke K (1968) Chromosome studies in the superfamily Bovid.Chromosoma 25: 152–171.
Yong HS (1973) Complete Robertsonian fusion in the Malayan lesser mouse deer (Tragulus javanicus).Experentia 29: 366–367.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
accepted for publication by David C. Ward
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallagher, D.S., Houck, M.L., Ryan, A.M. et al. A karyotypic analysis of the lesser Malay chevrotain,Tragulus javanicus (Artiodactyla: Tragulidae). Chromosome Res 4, 545–551 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261783
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261783