Abstract
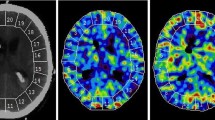
Regional hypoperfusion is a very frequent complication of subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH), being related to vasospasm in the majority of cases. Twenty-six patients who were admitted for SAH underwent follow-up with technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime single photon emission tomography (SPECT) 3 and 8 days after surgery. Fifteen patients of these had one more examination 15 days after surgery. The degree of hypoperfusion was quantified using an index of asymmetry which allow the comparison of two symmetrical regions of interest (ROIs) on the transaxial slice which presented the greatest perfusion defect. Comparison of CT data, transcranial Doppler data and clinical signs with the perfusion as quantified by99mTc-HMPAO SPECT indicates that a difference in counts of less than 10% between the two symmetrical ROIs is of no diagnostic value. Follow-up of the brain perfusion clearly shows that the most pronounced hypoperfusion was observed just after surgery, with progressive normalization at 8 and 15 days after surgery.99mTc-HMPAO SPECT performed 8 days after surgery allows prediction of the clinical outcome. For these reasons,99mTc-HMPAO SPECT, which is the only method for follow-up of cerebral perfusion in routine clinical practice, should be the first examination to be performed after surgery in patients with SAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ades PE, Groussin P, Arbeille P, Rieant JF (1989) Apport de la tomoscintigraphie à l'HMPAO Tc99 dans la surveillance des ischémies post-hémorragies méningées. Cite Métab Cerveau 6:262–264
Chakeves D, Bryan RN (1986) Acute subarachnoid hemorrhage: in vitro comparison of magnetic resonance and computed tomography. AJNR 7:223–228
Davis S, Andrews J, Lichtenstein M et al. (1990) A single photon emission computed tomography study of hypoperfusion after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 21:252–259
Deruyty R, Patet JD, Mottolese C, Honorato D (1986) Outcome of ruptured intra-cranial aneurysm treated by a deferred operation. Neurol Res 8:183–188
Geraud G, Tremoulet M, Guell A, Bes A (1984) The prognostic value of noninvasive CBF measurement in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 15:301–305
Heilbrun MP, Olesen J, Lassen N (1972) Regional cerebral blood flow studies in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 37:36–44
Heiss WD, Herholz K, Podreka I et al. (1990) Comparison of99mTc HMPAO SPECT with18F fluoromethane PET in cerebrovascular disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:687–697
Hellman RS, Tikofsky RS (1990) An overview of the contribution of regional cerebral blood flow studies in cerebrovascular disease; is there a role for single photon emission computed tomography? Semin Nucl Med 10:303–324
Holmes RA, Chaplin SB, Royston KG et al. (1985) Cerebral uptake and retention of99mTc hexamethyl propyleneamine (99Tc-HMPAO). Nucl Med Commun 6:443–447
Hunt WE, Hess RM (1968) Surgical risks as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 28:14–20
Jenkins A, Hadley D, Teasdale G et al. (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 68:731–736
Lassen NA, Andersen AR, Neirinckx RD et al. (1987) Validation of Ceretec. In: rCBF Atlas. Amersham, pp 14–18
Le Scao Y, Baulieu JL, Robier A et al. (1991) Increment of brain temporal perfusion during auditory stimulation. Eur J Nucl Med 18:981–983
Neirinckx RD, Canning LR, Piper IM et al. (1987) Technetium-99md,l-HM-PAO: a new radiopharmaceutical for SPECT imaging of regional cerebral blood perfusion. J Nucl Med 28:191–202
Pasqualin A, Rosta L, Da Pian R et al. (1984) Role of computed tomography in the management of vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 353:343–353
Powers WJ, Grubb RL, Baker RP et al. (1985) Regional cerebral blood flow and metabolism in reversible ischemia due to vasospasm. J Neurosurg 62:539–546
Rawluk D, Smith FW, Deans HE et al. (1988) Technetium-99mHMPAO scanning in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a preliminary study. Br J Radiol 61:26–29
Seiler RW, Grolimund P, Aaslid R wet al. (1986) Cerebral vasospasm evaluated by transcranial ultrasound correlated with clinical grade and CT-scan visualised subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 64:594–600
Sekhar LN, Wechsler LR, Yonas H et al. (1988) Value of transcranial Doppler examination in the diagnosis of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 22:813–821
Soucy JP, McNamara D, Mohr G et al. (1990) Evaluation of vasospasm secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage with technetium 99m-hexamethyl-propyleneamine oxime (HMPAO) tomoscintigraphy. J Nucl Med 31:972–977
Steinling M, Mazingue A, Kassiotis P et al. (1988) Le HMPAO comme indicateur de débit sanguin cérébral local: Étude quantifiée comparée à la méthode par inhalation au Xénon 133. Ann Radiol 31:229–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tranquart, F., Ades, P.E., Groussin, P. et al. Postoperative assessment of cerebral blood flow in subarachnoid haemorrhage by means of99mTc-HMPAO tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 20, 53–58 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261246
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261246