Summary
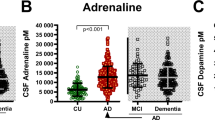
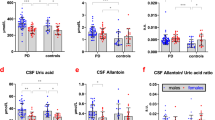
Neuropeptide Y, one of the most abundant polypeptides within the nervous system, is co-stored with catecholamines, especially norepinephrine (NE), thus suggesting its possible involvement in pathologies characterized by a noradrenergic impairment. In Parkinson's disease (PD), as well as in multiple system atrophy (MSA), a central noradrenergic deficit has been demonstrated, and in the dementia of Alzheimer type (DAT) an impaired noradrenergic transmission has been postulated. In this study we determined CSF NE and MHPG levels in 29 PD, 15 MSA, 22 DAT patients and in 36 controls, while CSF NPY-immunoreactivity (NPY-ir) levels were measured in 10 PD, 7 MSA, 10 DAT patients and 20 controls. PD, MSA, and DAT patients showed a significant reduction in CSF NPY-ir and NE levels compared with controls, while CSF MHPG levels resulted in a reduction in only the MSA group.
Furthermore, an inverse correlation between either NE or MHPG levels and the duration of the orthostatic hypotension was found in MSA patients while for DAT patients the MHPG levels were directly correlated to the severity of cognitive impairment, and inversely to the duration of illness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolfsson R, Gottfries CG, Roos BE, Winblad B (1979) Changes in the brain catecholamines in patients with dementia of Alzheimer type. Br J Psychiatry 135: 216–223
Adolfsson R, Gottfries CG, Oreland L, Widberg A, Winblad B (1980) Increased activity of brain and platelet monoamine oxidase in dementia of Alzheimer type. Life Sci 27: 1029–1034
Adrian TE, Allen JM, Bloom SR, Ghatei MA, Rossor MN, Roberts GW, Crow TJ, Tatemoto K, Polak JM (1983) Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature 306: 584–586
Allen JM, Ferrier IN, Roberts GE, Gross AJ, Adrian TE, Crow TJ, Bloom SR (1984) Elevation of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in substantia innominata in Alzheimer type dementia. J Neurol Sci 64: 325–331
Allen JM, Cross AJ, Crow TJ, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Bloom SR (1985) Dissociation of neuropeptide Y and somatostatin in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 377: 197–200
Alom J, Galard R, Catalan R, Castellanos JM, Schwartz S, Tolosa E (1990) Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y in Alzheimer's disease. Eur Neurol 30: 207–210
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3 rd ed revised. Washington DC
Anton AH, Sayre DF (1962) A study of the factor affecting the aluminium oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of the catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 138: 360–375
Arai H, Moroii T, Kosaka K (1984) Somatostatin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in postmortem brains from patients with Alzheimer's type dementia. Neurosci Lett 52: 73–78
Atack JR, Beal MF, May C, Kaye JA, Mazurek MF, Kay AD, Rapoport SI (1988) Cerebrospinal fluid somatostatin and neuropeptide Y. Concentrations in aging and dementia of the Alzheimer's type with and without extrapyramidal signs. Arch Neurol 45: 269–274
Beal MF, Mazurek MF, Chattha GK, Svendsen CM, Bird ED, Martin JB (1986) Neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity is reduced in cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 20: 282–288
Bondareff W, Mountjoy CQ, Roth M (1981) Selective loss of neurones of origin of adrenergic projection to cerebral cortex (nucleus locus caeruleus) in senile dementia. Lancet i: 1247–1249
Chan-Palay V, Lang W, Allen YS, Lang W, Haesler V, Polak JM (1985) Cortical neurons immunoreactive with antisera against neuropeptide Y are altered in Alzheimer's type dementia. J Comp Neurol 238: 390–400
Chan-Palay V, Lang W, Haesler U, Köhler C, Yasargil G (1986) Distribution of altered hippocampal neurons and axons immunoreactive with antisera against neuropeptide Y in Alzheimer's type dementia. J Comp Neurol 248: 376–394
Chan-Palay V, Jentsch B, Lang W, Höchli, Asan E (1990) Distribution of neuropeptide Y, c-terminal flanking peptide of NPY and galanin coexistence with catecholamine in the locus coeruleus of normal humans, Alzheimer's dementia and Parkinson's disease brains. Dementia 1: 18–31
Chronwall BM, Chase TN, O'Donohue TL (1984) Coexistence of neuropeptide Y and somatostatin in rat and in human cortical and rat hypothalamic neurons. Neurosci Lett 52: 213–217
Cross AJ, Crow TJ, Perry EK, Blessed G, Tomlinson BE (1981) Reduced dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in Alzheimer's disease. Br Med J 1: 93–94
Davies P, Katzman R, Terry RD (1980) Reduced somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex from cases of Alzheimer's disease and Alzheimer senile dementia. Nature 288: 279–280
Everitt BJ, Hökfelt T (1989) The coexistence of neuropeptide Y with other peptides and amines in the central nervous system. In: Mutt V, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM (eds) Neuropeptide Y. New York, Raven Press, pp 61–71
Everitt BJ, Hökfelt T, Terenius T, Tatemoto K, Mutt V, Goldstein M (1984) Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience 11: 443–462
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, Mc Hugh PR (1975) Mini-Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12: 189–198
Forster NL, Tamminga CA, O'Donohue T, Tanimoto K, Bird ED, Chase TN (1986) Brain choline acetyltransferase activity and neuropeptide Y concentrations in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 63: 71–75
Freed DM, Corkin S, Growdon JH, Nissen MJ (1988) Selective attention in Alzheimer's disease: CSF correlates of behavioural impairments. Neuropsychologia 26: 895–902
Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Härfstrand A, Zini I, Tatemoto K, Merlo Pich E, Hökfelt T, Mutt V, Terenius L (1983) Central administration of neuropeptide Y induces hypotension bradypnea and EEG synchronization in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 118: 189–192
Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Härfstrand A, Janson AM, Neumeyer A, Andersson K, Ruggeri M, Zoli M, Goldstein M (1986) Morphofunctional studies on the neuropeptide Y/adrenaline costoring terminal systems in the dorsal cardiovascular region of the medulla oblongata. Focus on the receptor-receptor interactions in cotransmission. In: Hökfelt T, Fuxe K, Pernow B (eds) Progress in brain research, vol 68. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 303–320
Gottfries CG, Adolfsson R, Aquilonius SM, Carlsson A, Eckernas SA, Nordberg A, Oreland L, Svennerholm L, Widberg A, Winblad B (1983) Biochemical changes in dementia disorders of Alzheimer type (AD/SDAT). Neurobiol Aging 4: 262–271
Hamilton MA (1959) The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 32: 50–55
Hamilton MA (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23: 56–62
Härfstrand A, Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Benfenati F, Goldstein M (1986) Receptor autoradiographical evidence for high densities of 125 I-neuropeptide Y binding sites in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the normal male rat. Acta Physiol Scand 128: 195–200
Härfstrand A, Fuxe K, Agnati LF and Fredholm B (1989) Reciprocal interactions between 2-adrenoreceptor agonist and neuropeptide Y binding sites in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. J Neural Transm 75: 83–99
Hendry SHC, Jones EG, Emson PC (1984) Morphology, distribution and synaptic relations of somatostatin and neuropeptide Y immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey neocortex. J Neurosci 4: 2497–2517
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17: 427–442
Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM, Lagercrantz H, Tatemoto K, Mutt V, Lindberg J, Terenius L, Everitt BJ, Fuxe K, Agnati L, Goldstein M (1983) Occurence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in catecholamine neurons in the human medulla oblongata. Neurosci Lett 36: 217–222
Hornykiewicz O, Kish S (1986) Biochemical pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. In: Yahr MD, Bergman KJ (eds) Advances in neurology, vol 45. Raven Press, New York, pp 19–34
Hurst HJ, Lewitt PA, Burns RS, Foster NL, Lovenberg W (1985) CSF dopamine-β-hydroxylase activity in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 35: 565–568
Köhler C, Eriksson L, Davies S, Chan-Palay V (1986) Neuropeptide Y innervation of the hippocampal region in the rat and monkey brain. J Comp Neurol 244: 284–400
Lesser PR, Fahn S, Snider SR, Cote LJ, Isgreen WP, Barett RE (1979) Analysis of the clinical problems in parkinsonism and the complications of long-term levodopa therapy. Neurology 2: 1253–1260
Lundberg JM, Terenius T, Hökfelt T Goldstein M (1983) High levels of neuropeptide Y in peripheral noradrenergic neurons in various mammals including man. Neurosci Lett 42: 167–172
Mann JJ, Stanley M, Kaplan RD, Sweeney J, Neophytides A (1983) Central catecholamine metabolism in vivo and the cognitive and motor deficits in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46: 905–910
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Melzi d'Eril GV (1986) A rapid and simple method for determining catecholamines in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Funct Neurol 1: 182–190
Minthon L, Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Gustafson L (1990a) Neuropeptide levels in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with frontotemporal degeneration. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 30: 57–67
Minthon L, Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Gustafson L (1990b) Cerebrospinal fluid neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactive levels in dementia of Alzheimer type and dementia with frontotemporal degeneration of non-Alzheimer type. Dementia 1: 262–266
Polinsky RJ, Jimerson DC, Kopin IJ (1984) Chronic autonomic failure: CSF and plasma 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol. Neurology 34: 979–983
Quinn N (1989) Multiple system atrophy: the nature of the beast. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry [Special Suppl]: 78–89
Raskind MA, Peskind ER, Halter JB, Jimerson DC (1984) Norepinephrine and MHPG levels in CSF and plasma in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41: 343–346
Reinikaininen J, Paljärvi L, Halonen T, Malminen O, Kosma VM, Laakso M, Riekkinen PJ (1988) Dopaminergic system and monoamine oxidase-B activity in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 9: 245–252
Reisberg B, Ferris SH, De Leon MJ, Crook T (1982) The global deterioration scale for assessment of primary degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry 139: 1136–1139
Riederer P, Birkmayer W, Seemann D, Wuketich S (1977) Brain noradrenaline and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol in Parkinson's syndrome. J Neural Transm 41: 241–251
Rinne UK, Sonninen V (1973) Brain catecholamines and their metabolites in Parkinsonian patients. Arch Neurol 28: 107–110
Rizzo V, Melzi d'Eril GV (1987) Determination of free 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethy-leneglycol in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid by liquid chromatography with coulometric detection. Clin Chem 33: 844–845
Rossor MN, Emson PC, Mountjoy CQ, Roth M, Iversen LL (1980) Reduced amounts of immunoreactive somatostatin in the temporal cortex in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neurosci Lett 20: 373–377
Rubenstein AE, Yahr MD, Mytilineou C (1978) Peripheral adrenergic hypersensitivity in orthostatic hypotension: the effect of denervation versus decentralization. Neurology 28: 376
Sasek CA, Elde RP (1985) Distribution of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity and its relationship to FMRF-amide-like immunoreactivity in the sixth lumbar and first sacral spinal cord segments of the rat. J Neurosci 5: 1729–1739
Soininen H, Joskkonen JT, Reinikainen KJ, Halonew PO, Riekkinen PJ (1984) Reduced cholinesterase activity and somatostatin like immunoreactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neurol Sci 63: 167–172
Spokes E, Bannister R, Oppenheimer DR (1979) Multiple system atrophy with autonomic failure. Clinical, histological and neurochemical observations on four cases. J Neurol Sci 43: 59–82
Stern Y, Mayeux R, Cote L (1984) Reaction time and vigilance in Parkinson's disease. Possible role of altered norepinephrine metabolism. Arch Neurol 41: 1086–1089
Tatemoto K (1982) Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79: 5485–5489
Teychenne PF, Lake CR, Ziegler MG, Plotkin C, Wood JH, Calne DB (1977) Central and peripheral deficiency of norepinephrine in Parkinson's disease and the effects of L-dopa therapy. Neurosci Abs 3: 47
Teychenne PF, Feuerstein G, Lake CR, Ziegler MG (1985) Central catecholamine systems: interactions with neurotransmitters in normal subjects and in patients with selected neurologic diseases. In: Lake CR, Ziegler MG (eds) The catecholamines in psychiatric and neurologic disorders. Butterworth, Stoneham, pp 91–119
Whitehouse PJ (1989) Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease: new neurochemical parallels. Mov Disord 4: 57–62
Widerlöw E, Lindström LH, Wahlestedt C, Ekman R (1988) Neuropeptide Y and peptide YY as possible cerebrospinal fluid markers for major depression and schizophrenia, respectively. J Psychiatr Res 22: 69–79
Williams A (1981) CSF biochemical studies on some extrapyramidal diseases. In: Rose FC, Capildeo R (eds) Research progress in Parkinson's disease. Pitman, London, pp 170–180
Wood PL Etienne P, Lal S, Gauthier S, Cajal S, Nair NPV (1982) Reduced lumbar CSF somatostatin levels in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci 31: 2073–2079
Yaksh TL, Carmichael SW, Stoddard SL, Tyce G, Kelly PJ, Lucas D, Van Heerden JA, Ahlskog JE, Byer DE (1990) Measurement of lumbar CSF levels of met-enkephalin, encrypted met-enkephalin, and neuropeptide Y in normal patients and in patients with Parkinson's disease before and after autologous transplantation of adrenal medulla into the caudate nucleus. J Lab Clin Med 115: 346–351
Ziegler MG, Lake CR, Kopin IJ (1977) The sympathetic nervous system defect in primary orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med 296: 293–297
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martignoni, E., Blandini, F., Petraglia, F. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid norepinephrine, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol and neuropeptide Y levels in Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy and dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 4, 191–205 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260903
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02260903