Abstract
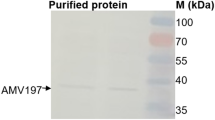
Protein kinases play an important role in the signaling pathway of growth factors in most of the higher organisms. During the study of protein kinase profiles of mosquitoes using RT-PCR and degenerate primers for consensus catalytic domain motifs to amplify protein kinase genes, we have noticed that a novel mosquito kinase, AaPK-38, shares a stretch of amino acids identical to the corresponding domain in Tousled gene ofArabidopsis thaliana that is required for leaf and flower development. A 2.1-kb cDNA encoding human HsHPK gene, which is a homolog of AaPK-38, was isolated from human testis cDNA library. This cDNA contains an open reading frame of 563 amino acids, with a complete kinase domain in its carboxyl terminus. The expressed Flag-tagged HsHPK was shown to have kinase activity based on in vitro autophosphorylation. Northern blot analysis revealed that human HsHPK mRNA is most abundant in testes, much less in heart and skeletal muscle and almost undetectable in liver and lung. Finally, we found that the expression of HsHPK in 4 out of 6 human hepatoma tissues is much higher than that in the adjacent normal counterpart. This result suggests HsHPK may play a role in the development of human hepatoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beasley RP, Hwang Ly, Lin CC, Chien CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22707 men in Taiwan. Lancet ii:1129–1133;1981.
Brechot C, Pourcel C, Louis A, Rain B, Tiollais P. Presence of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in cellular DNA of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature 286:533–535;1980.
Brechot C, Hadchouel M, Scotto J, Fonck M, Potet F, Vyas GS, Tiollais P. State of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes of patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive and -negative liver diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3906–3910;1981.
Chakraborty PR, Ruiz-Opazo N, Shouval D, Shafritz SA. Identification of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and expression of viral RNA in an HBsAg-producing human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Nature 286:531–533;1980.
Duffy JB, Perrimon N. The torso pathway in Drosophila: Lessons on receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and pattern formation. Dev Biol 166:380–395;1996.
Edelman AM, Blumenthal DK, Krebs EG. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 56:567–613;1987.
Glisin V, Crkvenjakov R, Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry 13:2633–2637;1974.
Graham F, Van der Eb A. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology 52:456–457;1973.
Hammerschmidt M, Bitgood MJ, McMahon AP. Protein kinase A is a common negative regulator of hedgehog signaling in the vertebrate embryo. Genes Dev 10:647–658;1996.
Hanks SK. Homology probing: Identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:388–392;1987.
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T. The protein kinase family: Conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 241:42–52;1988.
Hengartner MO. Programmed cell death in invertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:34–38;1996.
Hunter TA. Thousand and one protein kinase. Cell 50:823–829;1987.
Kumar S, Harvey NL. Role of multiple cellular proteases in the execution of programmed cell death. FEBS Lett 375:169–173;1995.
Lai C, Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron 6:691–704;1991.
Robinsons D, He F, Pretlow T, Kung H-J. A tyrosine kinase profile of prostate carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5958–5962;1996.
Roe J, Rivin CJ, Sessions RA, Feldmann KA, Zambryski PC. The Tousled gene inA. thaliana encodes a protein kinase homolog that is required for leaf and flower development. Cell 75:939–950;1993.
Roe JL, Durfee T, Zupan JR, Repetti PP, McLean BG, Zambryski PC. TOUSLED is a nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase that requires a coiled-coil region for oligomerization and catalytic activity. J Biol Chem 272:5838–5845;1997.
Roe JL, Nemhauser JL, Zambryski PC. Tousled participates in apical tissue formation during gynoecium development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 9:335–353;1997.
Sanger F, Coulson AR. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol 94:441–448;1975.
Shafritz DA, Kew MC. Identification of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology 1:1–8;1981.
Shafritz DA, Shouval D, Sherman HI, Hadziyannis SJ, Kew MC. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue. N Engl J Med 305:1067–1073;1981.
Siegfried E, Perrimon N. Drosophila wingless: A paradigm for the function and mechanism of Wnt signaling. Bioessays 16:395–404;1994.
Sundaram M, Han M. Control and integration of cell signaling pathways duringC. elegans vulval development. Bioessays 18:473–480;1996.
Thomas PS. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:5201–5204;1980.
Tiollais P, Pourcel C, Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature 317:489–495;1985.
Wilks AF. Two putative protein-tyrosine kinases identified by application of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1603–1607;1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, AM., Chang, TJ., Cho, WL. et al. From mosquito to man: Identification of a novel protein kinase, HsHPK, which is highly expressed in human hepatoma tissues. J Biomed Sci 5, 135–140 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02258367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02258367