Summary
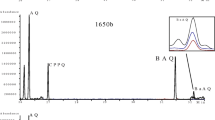
Samples of suspended particulate matter collected in Duisburg were investigated for phenolic compounds. The loaded filters were extracted with dichloromethane for 10 hours in a soxhlet apparatus. The concentrated extract was resolved in cyclohexane and separated into a non polar and a polar fraction on alumina. The polar fraction was taken up in dichloromethane and steam-distilled. The distillate was extracted with ether. After the evaporation of the ether, the residue was resolved in dichloromethane and allowed to react with benzoyl chloride. After adding toluene the solution was reduced in volume and analyzed in a GC-MS system. For the separation of phenols by means of HPLC the enrichment of the phenols was performed without benzoylization. Six phenols were detected: hydroxibenzene, methylhydroxibenzene, hydroxibiphenyl, hydroxifluorene, benzylhydroxibenzene and dihydroxibiphenyl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Sawicki Analysis for aerotoxicants. Table of contents. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem.1, 275–333 (1970).
F. Pott, R. Tomingas, A. Brockhaus, F. Huth, Untersuchungen zur tumorerzeugenden Wirkung von Extrakten und Extraktfraktionen aus Schwebstoffen im Subkutantest bei der Maus. Zbl. Bakt., I. Abt. Orig. B170, 17–34 (1980).
N. Seemayer, N. Manojlovic, Cytotoxic effects of air pollutants on mammalian cells in vitro. Toxicology17, 177–182 (1980).
W. Dehnen, N. Pitz, R. Tomingas, The mutagenicity of airborne particulate pollutants. Cancer Letters4, 5–12 (1977).
P. Bogovski, A. Kueng, F. Winkmann, Phenole, andere Bestandteile des Brennschieferteers und Asbest als modifizierende Faktoren der karzinogenen Wirkung. Arch. Geschwulstforsch.52, 49–55 (1982).
E. Barber, E. Sawicki, S. McPherson, Separation and identification of phenols in automobile exhaust by paper and gas liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem.36, 2442–2445 (1964).
D. Hoffmann, E. Wynder, Nat. Cancer Inst. Monograph9, 91–116 (1962).
P. Roumeliotis, W. Liebald, K. Unger, Determination of phenols from automobile exhaust by means of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Internat. J. Environ. Anal. Chem.9, 27–43 (1981).
E. Wauters, F. Vangaever, P. Sandra, M. Verzele, Polar organic fraction of air particulate matter. J. Chromatogr.170, 133–138 (1979).
R. Knights Analysis of particulate organic air pollutants by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Advances Environ. Science Technol.10, 237–251 (1980).
D. Schuetzle, F. Lee, T. Prater, S. Tejeda, The identification of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) derivatives in mutagenic fractions of diesel particulate extracts. Intern. J. Environ. Anal. Chem.9, 93–144 (1981).
E. Wauters, P. Sandra, M. Verzele, Qualitative and semiquantitative analysis of the nonpolar organic fraction of air particulate matter. J. Chromatogr.170, 125–131 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomingas, R., Mönch, W. & Matthiesen, U. Remarks on the detection of phenols in airborne particulate matter. Chromatographia 22, 191–193 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257326
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257326