Abstract
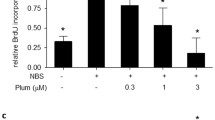
Excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) in the intima is an important etiologic factor in vascular proliferative disorders such as atherosclerosis and restenosis after balloon angioplasty. Therefore, control of VSMC growth may be a suitable therapeutic intervention in vascular proliferative disorders. In the present work, we have studied the 2-benzyloxybenzaldehyde (CCY1a)-mediated antiproliferative effect and its mechanisms of action. CCY1a inhibited serum-induced VSMC proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner, as demonstrated using [3H]thymidine incorporation and MTT assays; the IC50 values were calculated to be 7.0 × 10−6 and 1.2 × 10−5 M, respectively. Furthermore, it also significantly suppressed serum-induced progression of the cell cycle, as shown by flow cytometric analysis. CCY1a as well as PD98059 almost completely abolished serum-induced activation of p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), the downstream effectors of c-fos and c-jun mRNA expression and activator protein-1 (AP-1) DNA binding activity, suggesting the central roles of these signaling cascades. Interestingly, CCY1a also effectively blocked serum-induced IκB-α phosphorylation, IκB-α degradation and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) binding activity. Based on these observations, we examined the effect of CCY1a on serum-mediated Ras activity, an upstream regulator of the above signaling events. The data demonstrated a marked inhibition of Ras activation by CCY1a. We conclude that CCY1a blocks cell proliferation via inhibition of the upstream effector of Ras and downstream events, including p42/44 MAPK activation and c-fos and c-jun mRNA expression, as well as NF-κB and AP-1 DNA binding activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham E. NF-kappaB activation. Crit Care Med 28:100–104;2000.
Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1072:129–157;1991.
Ayllon V, Rebollo A. Ras-induced cellular events (review). Mol Membr Biol 17:65–73;2000.
Bellas RE, Lee JS, Sonenshein GE. Expression of a constitutive NF-kappa B-like activity is essential for proliferation of cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 96:2521–2527;1995.
Cercek B, Yamashita M, Dimayuga P, Zhu J, Fishbein MC, Kaul S, Shah PK, Nilsson J, Regnstrom J. Nuclear factor-kappaB activity and arterial response to balloon injury. Atherosclerosis 131:59–66;1997.
Chang CY, Kuo SC, Lin YL, Wang JP, Huang LJ. Benzyloxybenzaldehyde analogues as novel adenylyl cyclase activators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1971–1974;2001.
Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X. New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB in cell growth regulation. Am J Pathol 159:387–397;2001.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159;1987.
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:225–260;1998.
Gorski DH, Walsh K. Mitogen-responsive nuclear factors that mediate growth control signals in vascular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 30:585–592;1995.
Graves JD, Campbell JS, Krebs EG. Protein serine/threonine kinases of the MAPK cascade. Ann NY Acad Sci 766:320–343;1995.
Guh JH, Hwang TL, Ko FN, Chueh SC, Lai MK, Teng CM. Antiproliferative effect in human prostatic smooth muscle cells by nitric oxide donor. Mol Pharmacol 53:467–474;1998.
Hall A. G proteins and small GTPases: Distant relatives keep in touch. Science 280:2074–2075;1998.
Hanna AN, Chan EY, Xu J, Stone JC, Brindley DN. A novel pathway for tumor necrosis factor-alpha and ceramide signaling involving sequential activation of tyrosine kinase, p21(ras), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 274:12722–127299;1999.
Hoshi S, Goto M, Koyama N, Nomoto KI, Tanaka H. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by nuclear factor-κB and its inhibitor, I-κB. J Biol Chem 275:883–889;2000.
Janssen-Heininger YM, Macara I, Mossman BT. Cooperativity between oxidants and tumor necrosis factor in the activation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB: Requirement of Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the activation of NF-kappaB by oxidants. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20:942–952;1999.
Karin M. Signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus through the phosphorylation of transcription factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:415–424;1994.
Landry DB, Couper LL, Bryant SR, Lindner V. Activation of the NF-kappa B and I kappa B system in smooth muscle cells after rat arterial injury. Induction of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Am J Pathol 151:1085–1095;1997.
Lawrence R, Chang LJ, Siebenlist U, Bressler P, Sonenshein GE. Vascular smooth muscle cells express a constitutive NF-kappa B-like activity. J Biol Chem 269:28913–28918;1994.
Libby P, Tanaka H. The molecular basis of restenosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 40:97–106;1997.
Obata H, Biro S, Arima N, Kaieda H, Kihara T, Eto H, Miyata M, Tanaka H. NF-kappa B is induced in the nuclei of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells by stimulation of various growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 224:27–32;1996.
Porter AC, Vaillancourt RR. Tyrosine kinase receptor-activated signal transduction pathways which lead to oncogenesis. Oncogene 17:1343–1352;1998.
Radler-Pohl A, Gebel S, Sachsenmaier C, Konig H, Kramer M, Oehler T, Streile M, Ponta H, Rapp U, Rahmsdorf HJ. The activation and activity control of AP-1 (fos/jun). Ann NY Acad Sci 684:127–148;1993.
Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature 362:801–809;1993.
Rothman A, Wolner B, Button D, Taylor P. Immediate-early gene expression in response to hypertrophic and proliferative stimuli in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 269:6399–6404;1994.
Schlesinger TK, Demali KA, Johnson GL, Kazlauskas A. Platelet-derived growth factor-dependent association of the GTPase-activating protein of Ras and Src. Biochem J 344:519–526;1999.
Sebti SM, Hamilton AD. Farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I inhibitors and cancer therapy: Lessons from mechanism and bench-to-bedside translational studies. Oncogene 19:6584–6593;2000.
Seto M, Kim S, Yoshifusa H, Nakamura Y, Masuda T, Hamaguchi A, Yamanaka S, Iwao H. Effects of prednisolone on glomerular signal transduction cascades in experimental glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1367–1376;1998.
Shields JM, Pruitt K, McFall A, Shaub A, Der CJ. Understanding Ras: ‘It ain't over 'til it's over’. Trends Cell Biol 10:147–154;2000.
Treisman R. Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:205–215;1996.
Tuyt LM, Dokter WH, Birkenkamp K, Koopmans SB, Lummen C, Kruijer W, Vellenga E. Extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2, Jun N-terminal kinase, and c-Jun are involved in NF-kappa B-dependent IL-6 expression in human monocytes. J Immunol 162:4893–4902;1999.
Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ. Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med 74:589–607;1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, SL., Guh, JH., Huang, YW. et al. Inhibition of ras-mediated cell proliferation by benzyloxybenzaldehyde. J Biomed Sci 9, 622–630 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02254990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02254990