Summary
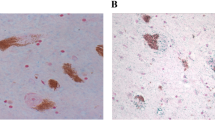
Semiquantitative histological evaluation of brain iron and ferritin in Parkinson's (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (DAT) have been performed in paraffin sections of brain regions which included frontal cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia and brain stem. The results indicate a significant selective increase of Fe3+ and ferritin in substantia nigra zona compacta but not in zona reticulata of Parkinsonian brains, confirming the biochemical estimation of iron. No such changes were observed in the same regions of DAT brains. The increase of iron is evident in astrocytes, macrophages, reactive microglia and non-pigmented neurons, and in damaged areas devoid of pigmented neurons. In substantia nigra of PD and PD/DAT, strong ferritin reactivity was also associated with proliferated microglia. A faint iron staining was seen occasionally in peripheral halo of Lewy bodies. By contrast, in DAT and PD/DAT, strong ferritin immunoreactivity was observed in and around senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. The interrelationship between selective increase of iron and ferritin in PD requires further investigation, because both changes could participate in the induction of oxidative stress and neuronal dath, due to their ability to promote formation of oxygen radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambani LM, van Woert MH, Murphy S (1975) Brain peroxidase and catalase in Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol 32: 114–118
Adolfsson R, Gottfries CG, Roos BE, Winblad B (1979) Post mortem distribution of dopamine and homovanillic acid in human brain. Variations related to age, and a review of the literature. J Neural Transm 45: 81–105
Ben-Shachar D, Ashkenazi R, Youdim MBH (1986) Long term consequences of early irondeficiency on dopaminergic neurotransmission Int J Dev Neurosci 4: 81–88
Burns SR, Markey SP, Philips JM, Chuang CC (1984) The neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in the monkey and man. Can J Neurol Sci 11: 166–169
Casey JL, Hentze MW, Koeller DM, Caughman SW, Rounault TA, Klausner RD, Harford JB (1988) Iron responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science 240: 924–928
Chen JC, Hardy PA, Clauberg M, et al (1989) T2 values in the human brain: comparison with quantitative assays of iron and ferritin. Radiology 173: 521–526
Davis GC, Williams AC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Caine ED, Reichert CM, Kopin IJ (1979) Chronic parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiatry Res 1: 249–254
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Agid F, Agid Y, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1987) Increased nigral iron content in postmortem parkinsonian brain Lancet ii: 1219–1220
Dexter DT, Carter CJ, Wells FR, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Lees A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989a) Basal lipid peroxidation substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 52: 381–389
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ, Agid F, Agid Y, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989b) Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal irons occurring in brains in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 52: 1830–1836
Dexter DT, Carayon A, Vidailhet M, Ruberg M, Agid F, et al (1990) Decreased ferritin levels in brain in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 55: 16–20
Drayer BP, Burger P, Darwin R, et al (1986a) Magnetic resonance imaging of brain iron. AJNR 7: 373–380
Brayer BP, Olanow W, Burger P, et al (1986b) Parkinson plus syndrome diagnosis using high field MR imaging of brain iron. Radiology 159: 493–498
Dwork AJ, Lawler G, Zybert PA, Durkin W, Osman M, Wilson N, Barkai AI (1990) An autoradiographic study of the uptake and distribution of iron by the brain of young rat. Brain Res (in press)
Earle KM (1968) Studies on Parkinson's disease including X-ray fluorescent spectroscopy of formalin fixed brain tissue. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 27: 1–14
Fischer P, Gatterer G, Simanyi M, Jellinger K, Marterer A, Danielczyk K, Danielzcyk W (1990) Memory deficits in advanced Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (PD-Sect) 2: 59–70
Forno LS (1983) Pathology of Parkinson's disease. In: Marsden CD, Fahn ST (eds) Movement disorders I. Butterworths, London, pp 25–40
Fleming J, Joshi JP (1987) Ferritin: isolation of aluminium-ferritin complex from brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 7866–7870
Gerber MR, Connor JR (1989) Do oligodendrocytes mediate iron regulation in human brain? Neurology 26: 95–98
Gomori G (1936) Microtechnical demonstration of iron. Am J Pathol 12: 655–663
Grundke-Iqbal I, Fleming J, Tung YC, Lassmann H, Iqbal K, Joshi JG (1990) Ferritin as a component of the neurotic (senile) plaque in Alzheimer dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 81 (in press)
Gutteridge JMC, Halliwell B, Treffry A, Harrison PM, Blake D (1983) Effect of ferritin containing fractions with different iron loading on lipid peroxidation. Biochem J 209: 557–560
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3: 41–51
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1986) Iron and free radical reactions: two aspects of antioxidant protection. Trends Biochem Sci 11: 1372–1375
Heikkila RE, Nicklas WJ, Duvoisin RC (1986) Studies on the mechanism of MPTP-MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in rodents. In: Markey, SP, Castagnoli N Jr, Trevor A, Kopin IJ (eds) MPTP: a neurotoxin producing a parkinsonian syndrome. Academic Press, Orlando San Diego New York Austin Boston London Sidney Tokyo Toronto, pp 69–83
Hentze MW, Caugham SW, Rouault TA, Barriolanal JG, Dancis A, Harford JB, Klausner RD (1987) Identification of the iron-responsive element for the translational regulation of human ferritin mRNA. Science 238: 1570–1573
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17: 427–443
Iacopino AM, Christakos S (1990) Specific reduction of calcium-binding protein (28-kilo-dalton calbindin-D) gene expression in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 4078–4082
Jellinger K, Danielczyk W, Fischer P, Gabriel E (1990a) Clinico-pathological analysis of dementia disorders in the elderly. J Neurol Sci 95: 239–258
Jellinger K, Lassmann H, Fischer P, Danielczyk W (1990b) Validation of diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 11: 126
Joshi JC, Clauberg M (1988) Ferritin; an iron storage protein with diverse functions. BioFactors 1: 207–212
Joshi JG, Fleming J, Lassmann H, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1990) Accumulation of ferritin in Alzheimer disease (AD) brain. Neurobiol Aging 11: 216–217
Kaneko Y, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, Yamaguchi K (1989) Ferritin immunohistochemistry as a marker for microglia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 79: 129–136
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42: 1097–1105
Kish SJ, Morito C, Hornykiewicz O (1985) Glutathione peroxidase activity in Parkinson's disease brain. Neurosci Lett 58: 343–346
Langston JW, Forno LS, Rebert CD, Irwin I (1984) Selective nigra toxicity after systemic administration of MPTP in the squirrel monkey. Brain Res 292: 390–394
McKhann G, Drachman D, Fostein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan E (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Report of the NINCDS/ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Akiyama H, McGeer EG (1988a) Rate of cell death in parkinsonism indicates active neuropathological process. Ann Neurol 24: 574–576
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988b) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology 38: 1285–1291
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163: 1450–1455
Octave JN, Schneider YJ, Trouet A, Crichton RR (1983) Iron uptake and utilization by mammalian cells. I. Cellular uptake of transferrin and iron. Trends Biochem Sci 8: 217–220
Reichmann H, Riederer P (1989) Biochemische Analyse des Atmungskettenkomplexes verschiedener Hirnregionen von Patienten mit M. Parkinson. In: Oertel H (Hrsg) Morbus Parkinson und andere Basalganglienerkrankungen. BMFT Symposium Bad Kissingen, S 44
Riederer P, Jellinger K, Seemann D (1984) Monoamine oxidase and parkinsonism. In: Tipton KF, Dostert P, Strolin-Benedetti (eds) Monoamine oxidase and disease. Academic Press, London Orlando San Diego New York Toronto Montreal Sidney Tokyo, pp 403–415
Riederer P, Sofic E, Rausch WD, Schmidt B, Reynolds GP, Jellinger K, Youdim MBH (1989) Transition metals, ferritin, glutathione, and ascorbic acid in parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52: 515–520
Rozemuller JM, Eikelenboom P, Pals ST, Stam FC (1989) Microglia cells around amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease express leucocyte adhesion molecules of the LFA-1 family. Neurosci Lett 101: 288–292
Rutledge JN (1988) Magnetic resonance of movement disorders. In: Jankovic J, Tolosa E (eds) Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 441–459
Schapira AHV, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Jenner P, Jenner P, Clark JB, Marsden CD (1989) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease. Lancet i: 1269
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heinsen H, Beckmann H, Reynolds GP, Hebenstreit G, Youdim MBH (1988) Increased iron (III) and total iron content in post mortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural Transm 74: 199–205
Sofic E, Paulus W, Jellinger K, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1991) Selective increase of iron in substantia nigra zona compacta of Parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem (in press)
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradisch peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18: 315–333
Theil EC (1987) Ferritin; structure, gene regulation, and cellular function in animals, plants and microorganisms. Annu Rev Biochem 56: 289–315
Tierney MC, Fisher RH, Lewis AJ, et al (1988) The NINDCS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease. A clinicopathologic study of 57 cases. Neurology 38: 359–364
White K, Munro HN (1988) Induction of ferritin subunit synthesis by iron is regulated at both the transcriptional and translational levels. J Biol Chem 263: 8938–8942
Youdim MBH, Ben-Shachar D, Riederer P (1989) Is Parkinson's disease a progressive siderosis of substantia nigra resulting in iron and melanin induced neurodegeneration? Acta Neurol Scand 126: 47–54
Youdim MBH, Ben-Schachar D, Yehuda S, Riederer P (1990) The role of iron in the basal ganglia. Adv Neurol 53: 153–216
Zaleska MH, Nagy K, Floyd RA (1989) Iron-induced lipid peroxidation and inhibition of dopamine synthesis in striatum synaptosomes. Neurochem Res 14: 597–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Ferritin antisera were kindly provided by Dr. J. G. Joshi, Department of Biochemistry, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellinger, K., Paulus, W., Grundke-Iqbal, I. et al. Brain iron and ferritin in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 2, 327–340 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02252926
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02252926