Summary
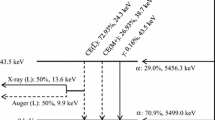
To measure atmospheric radon-220 (thoron) a device has been developed which uses alpha-alpha coincidences from the decay of radon-220 and its very shortlived decay product polonium-216 (half-life 0.16 sec). The alpha decays are detected in a scintillation chamber of 1340 cm3 effective volume and 2600 cm2 sensitive inner surface. The equipment records all alpha-alpha coincidences with time delays up to 0.32 sec. This time constant has been chosen as an optimal compromise with regard to the half-life of polonium-216 and the rate of chance coincidences for atmospheric air free of aerosol particles flowing through the chamber.
Atmospheric thoron concentrations were measured at 0.5 and 1 meter as well as 1 and 6 meters above the ground in Mannheim at the station of the Deutsche Forschungs-Gemeinschaft where the important meteorological parameters are recorded regularly. Correlation and regression calculations were carried out for various parameters. The change of radon-220 content with wind speed in various heights is particularly interesting. A maximum is found for a certain wind speed in each altitude. This result has some consequences for the determination of diffusion coefficients from the ratios of radon-220 concentrations in every two different heights respectively.
Zusammenfassung
Für die Messung des atmosphärischen Radon-220 (Thoron) wurde eine Apparatur entwickelt, bei der von den α-α-Koinzidenzen beim Zerfall des Radon-220 und seines sehr kurzlebigen Folgeprodukts Polonium-216 (Halbwertszeit 0,16 sec) Gebrauch gemacht wird. Der Nachweis der α-Teilchen erfolgt mittels einer Szintillationskammer, deren effektives Volumen 1340 cm2 und deren empfindliche innere Oberfläche 2600 cm2 beträgt. Registriert werden alle α-α-Koinzidenzen innerhalb einer Zeit von 0,32 sec. Diese Zeitkonstante bedeutet einen optimalen Kompromiß bezüglich der Halbwertszeit des Polonium-216 und der Zahl der Zufalls-Koinzidenzen, wenn von Aerosolen gereinigte Luft durch die Kammer strömt.
Gemessen wurde die Konzentration des Radon-220 in 0,5 und 1 m bzw. 1 und 6 m Höhe auf der Meßstelle der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft in Mannheim, wo laufend die wesentlichen meteorologischen Parameter registriert werden. Mit den einzelnen Parametern und den Radon-220-Aktivitäten wurden Korrelations-und Regressions-Rechnungen durchgeführt. Besonders interessant ist die Änderung der Radon-220-Konzentration mit der Windgeschwindigkeit für die verschiedenen Höhen. Für jede Höhe ergab sich jeweils ein Maximum für eine bestimmte windgeschwindigkeit. Dieses Ergebnis hat gewisse Konsequenzen für die Bestimmung der turbulenten Diffusionskoeffizienten aus den Radon-220-Konzentrationsverhältnissen in je zwei verschiedenen Höhen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Israël, H., and G. W. Israël: Measurements of the Thoron Content of the Atmosphere and Their Application in Meteorology, Rep. Contr. DA-91-591-EUC-3483, U.S. Army — Europ. Res. Off. 1965.—H. Israël, M. Horbert, and C. de la Riva: The Thoron Content of the Atmosphere and Its Relation to the Exchange Conditions. Rep. Contr. DA-91-591-EUC-3761, U.S. Army — Europ. Res. Off. 1967, and following annual reports as well as further publications.
Israël, H.: Natürliche Radioaktivität. Nuclear Radiation in Geophysics, p. 81 (ed. H. Israël and A. Krebs). Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag 1962.
Blanc, D., J. Fontan et G. Vedrenne: Un procédé de dosage continu du radon dans l'air atmosphérique. J. Phys. Radium21, 176A-180A (1960). —Fontan, J., D. Blanc, M. Bonnafous et A. Bouville: Dosage du radon et du thoron contenus dans l'air atmosphérique, application à l'étude de l'équilibre radioactif entre ces gaz et leurs descendants. J. Phys. Radium 22, 179A–181A (1961). — Une méthode de dosage direct du radon et du thoron contenus dans l'atmosphère. Nuovo Cim. (X)23 Suppl., 132–143 (1962).
Jacobi, W.: A New Method to Measure Radon and Thoron in Streaming Gases and Its Use to Determine the Tn-Content of Atmospheric Air. Coll. Internat. Pollution Radioactive des Milieux Gazeux, Saclay 1963, p. 509–515.
Israël, G. W.: Neues Verfahren zur Direktmessung des atmosphärischen Thoron-Gehalts. Naturwiss.51, 134–135 (1964).
Israël, H.: Das Emanationsdosimeter, ein Gerät zur Dauerkontrolle mäßig hoher Emanationskonzentrationen in Luft. Wiss. Abh. Reichsamt Wetterdienst, Berlin 2, Nr. 10 (1937).
Israël, G. W.: Thoron (Rn-220) Measurements in the Atmosphere and Their Application in Meteorology. Tellus17, 383–388 (1965).
Föhlisch, W.: Messung des Thoron in bodennaher Luft mit Hilfe einer Gitterionisationskammer als Detektor. Dipl.-Arbeit, II. Physik. Inst. Univ. Heidelberg 1965.—Hoffmann, G.: Alpha-Spektroskopie zur gleichzeitigen quantitativen Bestimmung der Radonisotope Rn-220 und Rn-222. Dipl.-Arbeit, II. Phys. Inst. Univ. Heidelberg 1970.—Schumann, G.: Measurement of Individual Alpha Emitters in the Environment. Coll. Electronique Nucléaire et Radioprotection, Toulouse 1968, Tome 4.
Giffin, C., A. Kaufman, and W. Broecker: Delayed Coincidence Counter for the Assay of Actinon and Thoron. J. Geophys. Res.68, 1749–1757 (1963).
Bogen, J.: Verzögerte Koinzidenz zwischen Tn (Rn-220) und ThA (Po-216) zur kontinuierlichen Messung von atmosphärischem Thoron. Dipl.-Arbeit, II. Phys. Inst. Univ. Heidelberg 1966.
Sappok, M.: Der Einfluß meteorologischer Meßgrößen auf die Aktivität des Thoron in der Atmosphäre. Dipl.-Arbeit, II. Phys. Inst. Univ. Heidelberg 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Prof. Hans Israël.
With 6 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogen, J., Sappok, M. & Schumann, G. Measurements of atmospheric radon-220 using delayed alpha-particle coincidences. Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. A. 21, 171–182 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247970
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247970