Abstract
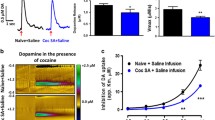
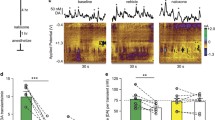
Chronic daily injections of cocaine induce behavioral sensitization to subsequent cocaine challenge, while continuous infusion induces tolerance. Following a 7-day withdrawal period, we examined the effects of these two dosing regimens on: (1) baseline dopamine efflux and uptake following single-pulse electrical stimulation, (2) inhibition of uptake by cocaine; and (3) inhibition of efflux by autoreceptor activation. Cocaine (40 mg/kg per day) was administered to rats for 14 days either continuously by osmotic minipumps or intermittently by once-a-day injections. Minipumps containing saline were implanted in the control group. After 7 days of withdrawal, dopamine kinetics in the caudate was examined using in vitro fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. This technique provides very rapid measurements of dopamine in the extracellular space. Thus, when combined with endogenous dopamine efflux evoked by single-pulse, electrical stimulations, it was possible directly to measure the release and uptake components of the efflux. In the absence of pharmacological agents, no group differences were found in the amount of baseline dopamine released or in the uptake kinetics; the potency of bath-applied cocaine (0.03–60 µM) in inhibiting the uptake was also unaltered in either group. In contrast, the potency of quinpirole (an autoreceptor agonist, 5–250 nM) was significantly decreased and increased in the cocaine injection and pump groups, respectively. Thus, the cocaine administration regimen which produces sensitization results in a functional subsensitivity of release-modulating autoreceptors, while the tolerance-producing regimen results in autoreceptor supersensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baur JE, Kristensen EW, May LJ, Wiedemann DJ, Wightman RM (1988) Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry of biogenic amines. Anal Chem 60:1268–1272
Calligaro DO, Eldefrawi ME (1988) High affinity stereospecific binding of [3H]cocaine in striatum and its relationship to the dopamine transporter. Membr Biochem 7:87–106
Cass WA, Gerhardt GA, Gillespie K, Curella P, Mayfield RD, Zahniser NR (1993) Reduced clearance of exogenous dopamine in rat nucleus accumbens, but not in dorsal striatum, following cocaine challenge in rats withdrawn from repeated cocaine administration. J Neurochem 61:273–283
Chen N-H, Reith EA (1993) Dopamine and serotonin release-regulating autoreceptor sensitivity in A9/A10 cell body and terminal areas after withdrawal of rats from continuous infusion of cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1445–1453
Cubeddu LX, Hoffman IS (1983) Frequency-dependent release of acetylcholine and dopamine from rabbit striatum: its modulation by dopaminergic receptors. J Neurochem 41:94–101
Desban M, Kemel ML, Glowinski J, Gauchy C (1993) Spatial organization of patch and matrix compartments in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 57:661–671
Dwoskin LP, Peris J, Yasuda RP, Philpott K, Zahniser NR (1988) Repeated cocaine administration results in supersensitivity of striatal D2 dopamine autoreceptors to pergolide. Life Sci 42:255–262
Ellinwood EH Jr, Lee T (1983) Effect of continuous systemic infusion ofd-amphetamine on the sensitivity of nigral dopamine cells to apomorphine inhibition of firing rates. Brain Res 273:379–383
Fitzgerald JL, Reid JJ (1991) Chronic treatment does not alter striatal D2 autoreceptor sensitivity to pergolide. Brain Res 541:327–333
Garris PA, Ciolkowski EL, Wightman RM (1994) Heterogeneity of evoked dopamine overflow within the striatal and striatoamygdaloid regions. Neuroscience 59:417–427
Gerhardt GA, Gratton A, Rose GM (1988) In vivo electrochemical studies of the effects of cocaine on dopamine nerve terminals in the rat neostriatum. Psychol Behemoslov 37:249–257
Gifford AN, Johnson KM (1992) Effect of chronic cocaine treatment on D2 receptors regulating the release of dopamine and acetylcholine in the nucleus accumbens and striatum. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:841–846
Izenwasser S, Cox BM (1990) Daily cocaine treatment produces a persistent reduction of [3H] dopamine uptake in vitro in rat nucleus accumbens but not in striatum. Brain Res 531:338–341
Izenwasser S, Cox BM (1992) Inhibition of dopamine uptake by cocaine and nicotine: tolerance to chronic treatments. Brain Res 573:119–125
Jones SR, Garris PA, Kilts CD, Wightman RM (1995a) Comparison of dopamine uptake in the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 64:2581–2589
Jones SR, Garris PA, Wightman RM (1995b) Different effects of cocaine and nomifensine on dopamine uptake in the caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:396–403
Joyner C, King G, Lee TH, Ellinwood EH Jr (1993) A technique for the continuous infusion of high doses of cocaine by osmotic minipump. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:971–973
Kalivas PW (1995) Neural basis of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. In: Hammer Jr RP (ed) The neurobiology of cocaine: cellular and molecular mechanisms. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 81–98
Kalivas PW, Duffy P (1990) Effect of acute and daily cocaine treatment on extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. Synapse 5:48–58
Kawagoe K, Zimmerman JB, Wightman RM (1993) Principles of voltammetry and microelectrode surface states. J Neurosci Methods 48:225–240
Kennedy RT, Jones SR, Wightman RM (1992) Dynamic observation of dopamine autoreceptor effects in rat striatal slices. J Neurochem 59:449–455
King GR, Joyner C, Lee T, Kuhn C, Ellinwood EH (1992) Intermittent and continuous cocaine administration: residual behavioral states during withdrawal. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:243–248
King GR, Kuhn C, Ellinwood EH (1993) Dopamine efflux during withdrawal from continuous or intermittent cocaine. Psychopharmacology 111:179–184
King GR, Joyner C, Ellinwood EH Jr (1994) Continuous or intermittent cocaine administration: effects of flupenthixol treatment during withdrawal. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:883–889
Krueger BK (1990) Kinetics and block of dopamine uptake in synaptosomes form rat caudate nucleus. J Neurochem 55:260–267
Lee T, Ellinwood EH (1989) Time-dependent changes in the sensitivity of dopamine neurons to low doses of apomorphine following amphetamine infusion: electrophysiological and biochemical studies. Brain Res 483:17–29
Lee TH, Ellinwood EH Jr, Zhang H (1993) In vitro extracellular recording from nigral dopamine neurons following continuousd-amphetamine infusion. Eur J Pharmacol 232:125–129
Limberger N, Trout SJ, Kruk ZL, Starke K (1991) “Real-time” measurement of endogenous dopamine release during short trains of impulses in slices of rat neostriatum and nucleus accumbens: role of autoinhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:623–629
Little KY, Kirkman JA, Carroll FI, Clark TB, Duncan GE (1993) Cocaine use increases [3H]WIN 35428 binding sites in human striatum. Brain Res 628:17–25
Marshall JF, O'Dell SJ, Navarrete R, Rosenstein AJ (1990) Dopamine high-affinity transport site topography in rat brain: major differences between dorsal and ventral striatum. Neuroscience 37:11–21
May LJ, Wightman RM (1989) Heterogeneity of stimulated dopamine overflow within rat striatum as observed with in vivo voltammetry. Brain Res 487:311–320
McElvain JS, Schenk JO (1992) A multisubstrate mechanism of striatal dopamine uptake and its inhibition by cocaine. Biochem Pharmacol 43:2189–2199
Meiergerd SM, Patterson TA, Schenk JO (1993) D2 receptors may modulate the function of the striatal transporter for dopamine: kinetic evidence from studies in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 61:764–767
Millar J, Stamford JA, Kruk ZL, Wightman RM (1985) Electrochemical, pharmacological, and electrophysiological evidence of rapid dopamine release and removal in the rat caudate nucleus following electrical stimulation of the median forebrain bundle. Eur J Pharmacol 109:341–348
Missale C, Castelletti L, Govoni S, Spano PF, Trabucchi M, Hanbauer I (1985) Dopamine is differentially regulated in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 45:51–56
Ng JP, Hubert GW, Justice JB (1991) Increased stimulated release and uptake of dopamine in nucleus accumbens after repeated cocaine administration as measured by in vivo voltammetry. J Neurochem 56:1485–1492
Parsons LH, Schad CA, Justice JB Jr (1993) Co-administration of the D2 antagonist pimozide inhibits up-regulation of dopamine release and uptake induced by repeated cocaine. J Neurochem 60:376–379
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Pettit HO, Pan H-T, Parsons LH, Justice JB Jr (1990) Extracellular concentrations of cocaine and dopamine are enhanced during chronic cocaine administration. J Neurochem 55:798–804
Post RM, Rose H (1976) Increasing effects of repetitive cocaine administration in the rat. Nature 260:731–732
Reith MEA, Benuck M, Lajtha A (1987) Cocaine disposition in the brain after continuous or intermittent treatment and locomotor stimulation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:281–287
Richelson I, Pfenning M (1984) Blockade by antidepressants and related compounds of biogenic amine uptake into rat brain synaptosomes: most antidepressants selectively block norepinephrine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 104:277–286
Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR and Kuhar MJ (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-admi nistration of cocaine. Science 237:1219–1223
Segal DS, Kuczenski R (1992) Repeated cocaine administration induces behavioral sensitization and corresponding decreased extracellular dopamine responses in caudate and accumbens. Brain Res 577:351–355
Sharpe LG, Pilotte NX, Mitchell WM, DeSouza EB (1991) Withdrawal of repeated cocaine decreases autoradiographic [3H]mazindol labeling of dopamine transporter in rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 203:141–144
Silvia CP, King GR, Lee TH, Xue Z-Y, Caron MG (1994) Intranigral administration of D2 dopamine receptor antisense oligodeoxynucleotides establishes a role for nigrostriatal D2 autoreceptors in the motor actions of cocaine. Mol Pharmacol 46:51–57
Stamford JA, Kruk ZL, Millar J (1988) Stimulated limbic and striatal dopamine release measured by fast cyclic voltammetry: anatomical, electrochemical, and pharmacological characterization. Brain Res 454:282–288
Stryer L (1981) Biochemistry, 2nd edn. W.H. Freeman San Francisco
Wightman RM, Zimmerman JB (1990) Control of dopamine extracellular concentration in rat striatum by impulse flow and uptake. Brain Res Rev 15:135–144
Wise RA (1980) Action of drugs of abuse on brain reward systems. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:213–223
Yi S, Johnson KM (1990) Chronic cocaine treatment impairs the regulation of synaptosomal3H-DA release by D2 autoreceptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:841–846
Zhang H, Lee TH, Ellinwood EH Jr (1992) The progressive changes of neuronal activities of the nigral dopaminergic neurons upon withdrawal from continuous infusion of cocaine. Brain Res 594:315–318
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, S.R., Wightman, R.M., Lee, T.H. et al. Effects of intermittent and continuous cocaine administration on dopamine release and uptake regulation in the striatum: in vitro voltammetric assessment. Psychopharmacology 126, 331–338 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247384
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247384