Abstract
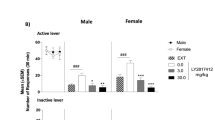
The selective serotonin(5-HT)1A receptor agonists 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone were tested in selectively inbred Wistar rats, with high preference [70–90%: defined as the ratio of ethanol (EtOH) to total fluid intake] for EtOH (10% v/v) over water in a two-bottle free choice situation. Rats were injected shortly before the overnight test session (8:00p.m.–8:00a.m.). EtOH and water consumption were determined in 20-min intervals; food consumption after the session. 8-OH-DPAT (ED50: 2.4 mg/kg, SC) and ipsapirone (ED50: 12.5 mg/kg, SC) reduced EtOH preference in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, 8-OH-DPAT increased total fluid intake, whereas ipsapirone enhanced total food intake. The EtOH preference reduction was time-dependent and reached a maximum within the second 4 h after application of 8-OH-DPAT (−73%) and ipsapirone (−72%). The preference reducing effect of ipsapirone (20 mg/kg, PO) was completely blocked by the nonselective 5-HT1A antagonist spiperone (0.05 mg/kg, SC). Local application of 8-OH-DPAT (10 µg, 0.5 µl) into the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN, a brain area rich in somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors), reduced the EtOH preference significantly as compared to the saline injection in the same animal (−12%, 8:00–12:00p.m.). Only marginal effects on ingestion behavior were observed after micro-injection into the nucleus accumbens. Reduction of brain 5-HT levels by pretreatment with the 5-HT synthesis inhibitor pCPA (2×150 mg/kg, IP) resulted in a short lasting, marked reduction (−54%) and a long lasting, small attenuation of the EtOH preference. Total food consumption was strongly decreased but returned soon to normal; total fluid intake was only slightly decreased. The EtOH preference reducing effect of ipsapirone (5 and 20 mg/kg, SC) was attenuated in pCPA-pretreated rats. The present data suggest that 5-HT1A receptor ligands reduce EtOH preference via stimulation of 5-HT1A receptors in the DRN. The possibility of additional mechanism(s) is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blokland A, Prickaerts J, Raaijmakers W (1992) Reduced level of anxiety in adult Lewis rats after chronic ethanol consumption. Physiology and Behavior 51:245–248
Chaput Y, Lesieur P, De Montigny C (1990) Effects of short-term depletion on the efficacy of serotonin neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. Synapse 6:328–337
Collins DM, Myers RD (1987) Buspirone attenuates volitional alcohol intake in the chronically drinking monkey. Alcohol 4:49–56
Contreras S, Alvarado R, Mardones J (1990) Effects of p-chlorophenylalanine on the voluntary consumption of ethanol water and solid food by UCHA and UCHB rats. Alcohol 7:403–407
De Vry J, Slangen J (1986) Effect of training dose on discrimination and crossgeneralization of chlordiazepoxide, pentobarbital and ethanol in the rat. Psychopharmacology 88:341–345
De Vry J, Glaser T, Schuurman T, Schreiber R, Traber J (1991) 5-HT1A receptors in anxiety. In: Briley M, File SE (eds) New concepts in anxiety. MacMillan, London, pp 94–129
De Vry J, Schreiber R, Glaser T, Traber J (1992) Behavioral pharmacology of 5-HT1A agonists: animal models of anxiety and depression. In: Stahl SM, et al. (eds) Serotonin1A receptors in depression and anxiety. Raven, New York, pp 55–81
Engel JA, Fahlke C, Hard E, Svensson L (1990) Effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on ethanol preference in the rat. Pharmacol Toxicol 67 [suppl 1]:21
Fallon D (1965) Eatometer: a device for continuous recording of free-feeding behavior. Science 148:977–978
Fornal CA, Marrosu F, Tada K, Metzler CW, Jacobs BL (1991) Effects of putative 5-HT1A antagonists on dorsal raphe unit activity in behaving cats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17:569.13
Geller I (1973) Effects of para-chlorophenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophan on alcohol intake in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1:361–365
Gill K, Amit Z (1987) Effects of serotonin uptake blockade on food, water, and ethanol consumption in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 11:444–449
Gill K, Filion Y, Amit Z (1988a) Treatment with sertraline, a new serotonin uptake inhibitor, reduces voluntary ethanol consumption in rats. Alcohol 5:349–354
Gill K, Fillion Y, Amit Z (1988b) A further examination of the effects of sertraline on voluntary ethanol consumption. Alcohol 5:355–358
Glaser T, Rath M, Traber J, Zilles K, Schleicher A (1985) Autoradiographic identification and topographical analysis of high affinity serotonin receptor subtypes as a target for the novel putative anxiolytic TVX Q7821. Brain Res 358:129–136
Glaser T, Greuel JM, Horvath E, Schreiber R, De Vry J (1991) Differentiation of 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone in rat models of 5-HT1A receptor function. In: Fozard JR, Saxena PR (eds) Serotonin: molecular biology receptors and functional effects. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 460–470
Glennon R (1990) Serotonin receptors: clinical implications. Neurosci Bio Behav Rev 14:35–47
Gonzales-Heydrich J, Peroutka SJ (1990) Serotonin receptors reuptake sites: pharmacological significance. J Clin Psychiatry (suppl) 5:13
Griffiths RR, Lamb RJ, Sannerud CA, Ator NA, Brady JV (1991) Self-injection of barbiturates, benzodiazepines and other sedativ-e-anxiolytics in baboons. Psychopharmacology 103:154–161
Haraguchi M, Samson HH, Tolliver GA (1990) Reduction in oral ethanol self-administration in the rat by the 5-HT uptake blocker fluoxetine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:259–262
Hjorth S, Magnusson T (1988) The 5-HT1A agonist 8-OH-DPAT preferentially activates cell-body 5-HT autoreceptors in the rat brain in vivo. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 338:463–471
Katz JL, Winger GD, Woods JH (1991) Abuse liability of benzodiazepines and 5-HT1A agonists. In: Rodgers RJ, Cooper SJ (eds) 5-HT1A agonists, 5-HT3 antagonists and benzodiazepines. Their comparative behavioural pharmacology. Wiley, New York, pp 317–342
Knapp DJ, Benjamin D, Pohorecky LA (1992) Effects of gepirone on ethanol consumption, exploratory behavior, and motor performance in rats. Drug Dev Res 26:319–341
Kostowski W, Dyr W (1992) Effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on ethanol preference in the rat. Alcohol 9:283–286
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Lumeng L, Li TK (1989) Spiroxatrine augments fluoxetine-induced reduction of ethanol intake by the P line of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:381–386
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Lumeng L, Li TK (1990) Serotonin, dopamine and GABA involvement in alcohol drinking of selectively bred rats. Alcohol 7:199–205
Murphy JM, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK (1987) Contents of monamines in forebrain regions of alcohol-preferring (P) and -nonpreferring (NP) lines of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:389–393
Murphy JM, Waller MB, Gatto GJ, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK (1988) Effects of fluoxetine on the intragastric self-administration of ethanol in the alcohol preferring P line of rats. Alcohol 5:283–286
Myers RD, Melchior CL (1978) Alcohol and alcoholism: role of serotonin. In: Essman WB (ed) Serotonin in health and disease volume 2: physiological regulation and pharmacological action. Spectrum Publications Inc, NY, London, pp 373–430
Naranjo CA, Sellers EM, Sullivan JT, Woodley DV, Kadlec K, Sykora K (1987) The serotonin uptake inhibitor citalopram attenuates ethanol intake. Clin Pharmacol Ther 41:266–274
Naranjo CA, Sullivan JT, Kadlec K, Woodley-Remus DV, Kennedy G, Sellers EM (1989) Differential effects of viqualine on alcohol intake and other consummatory behaviors. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46:301–309
Neisewander JL, McDougall SA, Bowling SL, Bardo MT (1990) Conditioned taste aversion and place preference with buspirone and gepirone. Psychopharmacology 100:485–490
Opitz K (1969) Beobachtungen bei Alkohol trinkenden Ratten — Einfluss von Fenfluramin. In: Coper H, Engelmeier MP, Heinrich K, Herz A, Hippius H (eds) Pharmakopsychiatrie Neuropharmakologie, Fortschritte in Theorie, Klinik und Praxis 3:202–205
Opitz K, Weischer ML (1988) Volitional oral intake of nicotine in tupaias: drug induced alterations. Drug Alcohol Depend 21:99–104
Papp M, Willner P (1991) 8-OH-DPAT-induced place preference and place aversion: effects of PCPA and dopamine antagonists. Psychopharmacology 103:99–102
Parvez H, Nevo I, Elisabeth P, Parvez S, Burov Y, Nagatsu T (1989) Role of central 5-HT neurons upon predisposition to alcohol intake. Neuroendocrinol Lett 11:83–89
Paxinons G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Pazos A, Palacios JM (1985) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the brain. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res 346:205–230
Peltier R, Schenk S (1991) The effects of serotonergic manipulations on cocaine self-administration in rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17:348.20
Privette TH, Hornsby RL, Myers RD (1988) Buspirone alters alcohol drinking induced in rats by tetrahydropapaveroline injected into brain monoaminergic pathways. Alcohol 5:147–152
Rezvani AH, Overstreet DH, Janowsky DS (1991) Drug-induced reductions in ethanol intake in alcohol preferring and Fawn-Hooded rats. Alcohol [suppl 1]:433–437
Rowan MJ, Anwyl R (1987) Neurophysiological effects of buspirone in the hippocampus: comparison with 5-hydroxytryptamine. Eur J Pharmacol 132:93–96
Schreiber R, De Vry J (1991a) Involvement of pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms in the anxiolytic effects of the 5-HT1A receptor ligands 8-OH-DPAT, ipsapirone and buspirone in the rat. Proceedings of the 12th Low Countries Meeting, Cologne, p 32
Schreiber R, De Vry J (1991b) Involvement of pre- and postsynaptic mechanisms in the antidepressive effects of the 5-HT1A receptor ligands 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone in the rat forced swimming test. Proceedings of the 12th Low Countries Meeting, Cologne, p 79
Schreiber R, De Vry J (1993) 5-HT1A receptor ligands in animal models of anxiety impulsivity and depression: multiple mechanisms of action? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:87–104
Schweizer E and Rickels K (1991) Serotonergic anxiolytics: a review of their clinical efficacy. In: Briley M, File SE (eds) New concepts in anxiety. MacMillan Press, London, pp 94–129
Sellers EM, Kaplan HL, Higgens GA (1991) Dexfenfluramine and sertraline effects on ethanol consumption and drinking microstructure in rats. Proceedings of Serotonin 1991: 5-hydroxytryptamine-CNS receptors and brain function. Birmingham, p 125
Sellers EM, Higgins GA, Sobell MB (1992) 5-HT and alcohol abuse. TIPS 13:69–75
Seppälä T, Aranko K, Mattila MJ, Shrotriya RL (1982) Effects of alcohol on buspirone and lorazepam actions. Clin Pharmacol Ther 32:201–207
Sharp T, Hjorth S (1990) Application of brain microdialysis to study the pharmacology of the 5-HT1A autoreceptor. J Neurosci Methods 34:83–90
Shippenberg T (1991) Conditioned reinforcing effects of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin: involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A and D1 dopamine receptors. Neurosci Lett 121:136–138
Soubrie P (1986) Reconciling the role of central serotonin neurons in human and animal behavior. Behav Brain Sci. 9:319–364
Sprouse JC, Aghajanian GK (1988) Responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to putative serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists: a comparative study with dorsal raphe neurons. Neuropharmacology 27:707–715
Svensson L, Engel J, Hard E (1989) Effects of the 5-HT receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, on ethanol preference in the rat. Alcohol 6:17–21
Thiebot MH, Martin P (1991) Effects of benzodiazepines, 5-HT1A agonists and 5-HT3 antagonists in animal models sensitive to antidepressant drugs. In: Rodgers RJ, Cooper SJ (eds) 5-HT1A agonists, 5-HT3 antagonists and benzodiazepines. Their comparative pharmacology. Wiley, New York, pp 159–195
Tollefson GD (1989) Serotonin and alcohol: interrelationships. Psychopathology 22 [suppl]:37–48
Tollefson GD (1991) Anxiety and alcoholism: a serotonin link. Br J Psychiatry 159:34–39
Tomkins DM, Higgens GA, Sellers EM (1991) Biphasic effects of 8-OH-DPAT on ethanol intake measured in rats using a continue access paradigm. Proceedings of: Serotonin 1991. 5-hydroxy-tryptamine-CNS receptors and brain function. Birmingham, p 101
Traber J, Glaser T (1987) 5-HT1A receptor related anxiolytics. TIPS 8:432–437
West R, Hajek P, McNeill A (1991) Effect of buspirone on cigarette withdrawal symptoms and short-term abstinence rates in a smokers clinic. Psychopharmacology 104:91–96
Wong DT, Murphy JM (1989) Serotonergic mechanisms in alcohol intake. In: Sun GY et al. (eds) Molecular mechanisms of alcohol, pp 133–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreiber, R., Opitz, K., Glaser, T. et al. Ipsapirone and 8-OH-DPAT reduce ethanol preference in rats: involvement of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 112, 100–110 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247369
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247369