Abstract
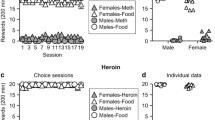
The alcohol-preferring AA rats have previously been shown to drink more solution containing the opioid etonitazene than the alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. The present experiments were initiated to see whether the line difference in opioid and alcohol intake would persist if an intravenous (IV) route of self-administration is used. Following establishment of stable heroin responding (0.03 mg/kg per infusion), AA and ANA rats were first subjected to three within-session dose-response determinations during which they were allowed to respond for ascending heroin doses (0.0075, 0.015, 0.03, and 0.06 mg/kg per infusion) and then to one progressive-ratio schedule session. AA rats obtained more heroin infusions than ANAs during the first acquisition sessions but there were no significant differences between the lines either in their baseline heroin responding, across the ascending within-session doses, or on the progressive ratio probe. When, after additional heroin baseline sessions, ethanol (1.0 mg/kg per infusion) was substituted for heroin, AA rats initially increased their responding and showed stable rates for responding across ascending ethanol doses (2.0 and 4.0 mg/kg), whereas ANAs declined below their heroin baseline. These findings give evidence for only an initial line difference in IV opiate self-administration but for a sustained difference in IV ethanol self-administration, thus suggesting that the differential alcohol drinking of the AA and ANA rats is dependent at least partly on non-oral factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler HL, Phillips PE, Feinhandler DA (1980) Alteration of ethanol self-administration by naltrexone. Life Sci 26:679–688
Caine SB, Lintz R, Koob GF (1993) Intravenous drug self-administration techniques in animals. In: Sahgal A (ed) Behavioral neuroscience: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 117–143
Collins RJ, Weeks JR, Cooper MM, Good PI, Russell RR (1984) Prediction of abuse liability of drugs using IV self-administration by rats. Psychopharmacology 82:6–13
de Waele JP, Kiianmaa K, Gianoulakis C (1994) Spontaneous and ethanol-stimulated in vitro release of β-endorphin by the hypothalamus of AA and ANA rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 18:1468–1473
de Waele JP, Kiianmaa K, Gianoulakis C (1995) Distribution of the μ-and δ-opioid binding sites in the brain of the alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA lines of rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:518–527
Deneau G, Yanagita T, Seevers MH (1969) Self-administration of psychoactive substances by the monkey. Psychopharmacologia 16:30–48
Eriksson K (1968) Genetic selection for voluntary alcohol consumption in the albino rat. Science 159:739–741
Eriksson K, Rusi M (1981) Finnish selection studies on alcohol related behaviors. General outline. In: McClearn GE, Dietrich RA, Erwin EG (eds) Development of animal models as pharmacogenetic tools. NIAAA Research Monograph 6, Rockville, MD, NIAAA, pp 87–117
Gatto GJ, McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Lumeng L, Li TK (1994) Ethanol self-infusion into the ventral tegmental area by alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol 11:557–564
Gianoulakis C, de Waele JP, Kiianmaa K (1992) Differences in the brain and pituitary β-endorphin system between the alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16:453–459
Grupp LA (1982) An investigation of intravenous ethanol self-administration in rats using a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement. Physiol Psychol 9:359–363
Honkanen A, Ovaska T, Korpi ER (1995a) Defective habituation to nociceptive stimulation in alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. Psychopharmacology 120:21–27
Honkanen A, Korpi ER, Holopainen I, Ahtee L (1995b) Repeated alcohol and morphine treatment differently affect locomotor activity in rats selectively bred for different alcohol preference. Soc Neurosci Abstr 21:729
Hubner CB, Koob GF (1990) The ventral pallidum plays a role in mediating cocaine and heroin self-administration in the rat. Brain Res 508:20–29
Hyytiä P, Sinclair JD (1993) Oral etonitazene and cocaine consumption by AA, ANA and Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 111:409–414
Karoly AJ, Winger G, Ikomi F, Woods JH (1978) The reinforcing property of ethanol in the rhesus monkey. II. Some variables related to the maintenance of intravenous ethanol-reinforced responding. Psychopharmacology 58:19–25
Koob GF, Bloom FE (1988) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science 242:715–723
Li TK, Lumeng L, McBride WJ, Waller BM (1981) Indiana selection studies on alcohol-related behaviors. In: McClearn GE, Dietrich RA, Erwin EG (eds) Development of animal models as pharmacogenetic tools. NIAAA Research Monograph 6, Rockville, MD, NIAAA, pp 171–191
Lyness WH, Smith FL (1992) Influence of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons on intravenous ethanol self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42:187–192
Martin TJ, Dworkin SI, Smith JE (1995) Alkylation of mu opioid receptors by β-funaltrexamine in vivo: comparison of the effects on in situ binding and heroin self-administration in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:1135–1140
Numan R (1981) Multiple exposures to ethanol facilitate intravenous self-administration of ethanol by rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:101–108
Numan R, Naparzewska AM, Adler CM (1984) Absence of reinforcement with low dose intravenous ethanol self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:609–615
Nylander I, Hyytiä P, Forsander O, Terenius L (1994) Differences between alcohol-preferring (AA) and alcohol-avoiding (ANA) rats in the prodynorphin and proenkephalin systems. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 18:1272–1279
Samson HH (1986) Initiation of ethanol reinforcement using a sucrose-substitution procedure in food- and water-sated rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 10:436–442
Sinclair JD, Le AD, Kiianmaa K (1989) The AA and ANA rat lines, selected for differences in voluntary alcohol consumption. Experientia 45:798–805
Sinclair JD, Hyytiä P, Nurmi M (1992a) The limited access paradigm: description of one method. Alcohol 9:441–444
Sinclair JD, Kampov-Polevoy A, Stewart R, Li TK (1992b) Taste preferences in rat lines selected for low and high alcohol consumption. Alcohol 9:55–60
Sinden JD, Le Magnen J (1982) Parameters of low-dose ethanol intravenous self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16:181–183
Smith SG, Davis WM (1974) Intravenous alcohol self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Res Commun 6:397–402
Smith SG, Werner TE, Davis WM (1976) Comparison between intravenous and intragastric alcohol self-administration. Physiol Psychol 4:91–93
Waller MB, WJ McBride, Gatto GJ, Lumeng L, Li TK (1984) Intragastric self-infusion of ethanol by ethanol-preferring and -nonpreferring lines of rats. Science 225:78–80
Winger GD, Woods JH (1973) The reinforcing property of ethanol in the rhesus monkey: I. Initiation, maintenance and termination of intravenous ethanol-reinforced responding. Ann NY Acad Sci 215:162–175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyytiä, P., Schulteis, G. & Koob, G.F. Intravenous heroin and ethanol self-administration by alcohol-preferring AA and alcohol-avoiding ANA rats. Psychopharmacology 125, 248–254 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247335
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247335