Abstract
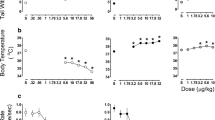
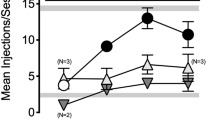
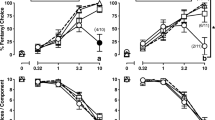
The present study was designed to explore the nature of the interaction between mu and kappa opioid agonists in the rat drug discrimination procedure. In rats trained to discriminate the kappa agonist U50,488 (5.6 mg/kg) from water, the other kappa agonist bremazocine substituted completely for the U50,488 training stimulus, and the additional kappa agonist tifluadom substituted in three of five of rats tested. In contrast, the mu agonists morphine, fentanyl, and buprenorphine produced primarily vehicle-appropriate responding. When morphine, fentanyl, and buprenorphine were combined with the training dose of U50,488, all three mu agonists reduced U50,488-appropriate responding. In rats trained to discriminate the mu agonist morphine (10.0 mg/kg) from saline, the other mu agonists morphine and buprenorphine all substituted in a dose-dependent manner for the morphine training stimulus, whereas U50,488, bremazocine, and tifluadom produced primarily vehicle-appropriate responding. When combined with the training dose of morphine, bremazocine antagonized morphine's discriminative stimulus effects, whereas U50,488 and tifluadom had no effect. The barbiturate pentobarbital neither substituted for, nor antagonized, the discriminative stimulus effects of either U50,488 or morphine. These results suggest that mu agonists and kappa agonists produce interacting effects in the drug discrimination procedure in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry H (1974) Classification of drugs according to their discriminable effects in rats. Fed Proc 33:1814–1824
Bryant RM, Olley JE, Tyers MB (1983) Antinociceptive actions of morphine and buprenorphine given intrathecally in the conscious rat. Br J Pharmacol 78:659–663
Chang KJ, Cuatrecasas P (1981) Heterogeneity and properties of opiate receptors. Fed Proc 40:2729–2734
Colpaert FC, Janssen PAJ (1984) Agonist and antagonist effects of prototype opiate drugs in rats discriminating fentanyl from saline: characteristics of partial generalization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:193–199
Cooper SJ, Moores WR, Jackson A, Barber DJ (1985) Effects of tifluadom on food consumption compared with chlordiazepoxide and kappa agonists in the rat. Neuropharmacology 24:877–883
Corbett AD, Kosterlitz HW (1986) Bremazocine is an agonist at k-opioid receptors and an antagonist at μ-opioid receptors in guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Br J Pharmacol 89:245–249
Cowan A, Lewis JW, MacFarlane IR (1977) Agonist and antagonist properties of buprenorphine, a new antinociceptive agent. Br J Pharmacol 60:537–545
Cowan A, Zhu XZ, Porecca F (1985) Studies in vivo with ICI174,864 and [D-Pen2, D-Pen5] enkephalin. Neuropeptides 5:311–314
Demoliou-Mason CD, Barnard EA (1986) Distinct subtypes of the opioid receptor with allosteric interactions in brain membranes. J Neurochem 46:1118–1128
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5274–5278
Doty P, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1989) Differential cross-tolerance to opioid agonists in morphine-tolerant squirrel monkeys responding under a schedule of food presentation. Eur J Pharmacol 174:171–180
Dum J, Blasig J, Herz A (1981) Buprenorphine: demonstration of physical dependence liability. Eur J Pharmacol 70:293–300
Dykstra LA (1985) Effects of buprenorphine on shock titration in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:20–25
Dykstra LA, Massie CA (1988) Antagonism of the analgesic effects of mu and kappa opioid agonists in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:813–821
France CP, Jacobson AE, Woods JH (1984) Discriminative stimulus effects of reversible and irreversible opiate agonists: morphine, oxymorphazone and buprenorphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:652–657
Gauvin DV, Young AM (1989a) Perceptual masking of drug stimuli. Drug Dev Res 16:151–162
Gauvin DV, Young AM (1989b) Evidence for perceptual masking of the discriminative morphine stimulus. Psychopharmacology 98:212–221
Genovese RF, Dykstra LA (1986) Tifluadom's effects under electric shock titration and tail-immersion procedures in squirrel monkeys. Life Sci 39:1713–1719
Hayes A, Kelly A (1985) Profile of activity of k receptor agonists in the rabbit vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 110:317–322
Hayes AG, Sheehan MJ, Tyers MB (1987) Differential sensitivity of models of antinociception in the rat, mouse and guinea-pig to mu- and kappa-opioid receptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol 91:823–832
Holaday JW, Long JB, Torella FC (1985) Evidence for κ, μ and δ opioid binding site interactions in vivo. Fed Proc 44:2860–2862
Holtzman SG (1985) Discriminative stimulus properties of opioids that interact with mu, kappa and PCP/Sigma receptors. In: Seiden LS, Balster RL (eds) Behavioral pharmacology: the current status. Liss, New York, pp 131–147
Howard AD, Sarne Y, Gioannini TJ, Hiller JM, Simon EJ (1986) Identification of distinct binding site subunits of mu and delta opioid receptors. Biochemistry 25:357–360
Huidobro-Toro JP, Parada S (1985) K-opiates and urination: pharmacological evidence for an endogenous role of the K-opiate receptor in fluid and electrolyte balance. Eur J Pharmacol 107:1–10
Jackson HC, Sewell RDE (1984) The role of opioid receptor sub-types in tifluadom-induced feeding. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:683–686
Kenakin TP (1987) Pharmacologic analysis of drug-receptor interaction. Raven Press, New York, pp 183–204
Kramer TH, Shook JE, Kazmierski W, Ayres EA, Wire WS, Hruby VJ, Burks TF (1989) Novel peptidic mu opioid antagonists: pharmacologic characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249:544–551
Leander DJ (1983a) A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:89–94
Leander DJ (1983b) Further study of kappa opioids on increased urination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:35–41
Leander DJ (1984) K-opioid diuretic effects of tifluadom, a benzodiazepine opioid agonist. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:555–556
Leander DJ (1985) Behavioral effects of agonist and antagonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. In: Seiden LS, Balster RL (ed) Behavioral pharmacology: the current status. Liss, New York, pp 93–110
Leander DJ (1987) Buprenorphine has potent kappa opioid receptor antagonist activity. Neuropharmacology. 26:1445–1447
Lord JAH, Waterfield AA, Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW (1977) Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature 267:495–499
Magnan J, Stewart JP, Tavani A, Kosterlitz HW (1982) The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 319:197–205
Mansour A, Khachaturian H, Lewis ME, Akil H, Watson SJ (1988) Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci 11:308–314
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine-like drugs in the non-dependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Mucha RF, Herz A (1985) Motivational properties of kappa- and mu- opioid receptor agonists studied with place and taste preference conditioning procedures. Psychopharmacology 86:274–280
Negus SS, and Dykstra LA (1988) Kappa antagonist properties of buprenorphine in the shock titration procedure. Eur J Pharmacol 156:77–86
Negus SS, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1989) Kappa antagonist properties of buprenorphine in non-tolerant and morphine-tolerant rats. Psychopharmacology 98:141–143
Nencini P, Woolverton WL (1988) Effects of nimodipine on the discriminative stimulus properties ofd-amphetamine in rats. Psychopharmacology 96:40–44
Overton DA (1988) Similarities and differences between behavioral control by drug-produced stimuli and by sensory stimuli. In: Corpert FC, Balster RL (ed) Transduction mechanisms of drug stimuli. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 176–198
Petrillo P, Gambino MC, Tavani A (1984) Bremazocine induces antinociception, but prevents opioid-induced constipation and catatonia in rats and precipitates withdrawal in morphine-dependent rats. Life Sci 35:917–927
Picker MJ, Doty P, Negus SS, Mattox SR, Dykstra LA (1990) Discriminative stimulus properties of U50,488 and morphine: effects of training dose on stimulus substitution patterns produced by mu and kappa opioid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:13–22
Ramarao P, Jablonski HI, Rehder KR, Bhargava NH (1988) Effect of k-opioid receptor agonists on morphine analgesia in morphine-naive and morphine-tolerant rats. Eur J Pharmacol 156:239–246
Richards ML, Sadee W (1985) Buprenorphine is an antagonist at the kappa opioid receptor. Pharmacol Res 2:178–181
Romer D, Buscher H, Hill RC, Maurer R, Petcher TJ, Welle HBA, Bakel HCCK, Akkerman AM (1980) Bremazocine: a potent, long-acting opiate kappa agonist. Life Sci 27:971–978
Rothman RB, Westfall TC (1982) Allosteric coupling between morphine and enkephalin receptors in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 21:548–557
Rothman RB, Bykov V, Long JB, Brady LS, Jacobson AE, Rice KC, Holaday JW (1989) Chronic administration of morphine and naltrexone up-regulate mu-opioid binding sites labeled by [3H]D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin: further evidence for two mu-opioid binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol 160:71–82
Shannon HE, Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW (1984) Morphine-like discriminative stimulus effects of buprenorphine and demethoxybuprenorphine in rats: quantitative antagonism by naloxone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 229:768–774
Sheldon RJ, Nunan L, Porreca F (1987) Mu antagonist properties of kappa agonists in a model of urinary bladder motility in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:234–240
Smith JR, Simon EJ (1980) Selective protection of stereospecific enkephalin and opiate binding against inactivation by N-ethylmaleimide: evidence for two classes of opiate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:281–284
Takemori AE, Ho BY, Naeseth JS, Portoghese PS (1988) Norbinaltorphimine, a highly selective kappa-opioid antagonist in analgesic and receptor-binding assays. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:255–258
Ureta H, Lopez LF, Perez A, Huidobro-Toro JP (1987) K-opiate-induced diuresis and changes in blood pressure: demonstration of receptor stereoselectivity using (+)- and (−)-tifluadom. Eur J Pharmacol 135:289–295
Von Voigtlander PF, Lahti RA, Ludens JH (1983) U50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:7–12
Wood PL, Charleson SE, Lane D, Hudgin RL (1981) Multiple opiate receptors: differential binding of mu, kappa and delta agonists. Neuropharmacology 20:1215–1220
Wood PL, Sanschagrin D, Richard JW, Thakur M (1983) Multiple opiate receptor affinities of kappa and agonist/antagonist analgesics: in vivo assessment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:545–550
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negus, S.S., Picker, M.J. & Dykstra, L.A. Interactions between mu and kappa opioid agonists in the rat drug discrimination procedure. Psychopharmacology 102, 465–473 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247126
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247126