Abstract
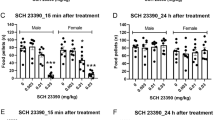
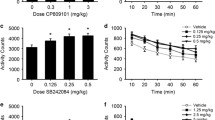
The locomotor stimulatory effects of the dopamine D1 receptor partial agonist SKF 38393 were examined in male C57B1/6J mice. Non-habituated mice showed marked dose-related (3–300 mg/kg, SC) locomotor stimulation. The time-course effect was biphasic at very high doses (100–300 mg/kg), with dose-related locomotor depression followed by dose-related long-term hyperlocomotion. For all doses, locomotor effects were detectable throughout the 4-h test period. To determine whether these effects were mediated by D1 receptor stimulation, effects of SKF 38393 were assessed in combination with behaviorally inactive and active doses (0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg, respectively) of the selective D1 receptor antagonist SCH 39166. Both doses of SCH 39166 attenuated the hyperlocomotion induced by 30 mg/kg of the agonist to a similar degree. However, neither dose was able to reverse either the depressant or the stimulatory effects of 300 mg/kg SKF 38393. These results demonstrate effects of the prototypical D1 agonist previously unobserved, and raise questions concerning the nature of agonist/antagonist interactions at the D1 receptor subtype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J (1985) Behavioral stimulation is induced by separate dopamine D1 and D2 receptor sites in reserpine-pretreated but not in normal rats. Eur J Pharmacol 113:79–88
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1988) Behavioral differentiation between effects elicited at dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rats with normosensitive DA receptors. Pharmacopsychiatry 21:24–27
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Perregaard J (1987) Dopamine D-1 receptor agonists combined with the selective D-2 agonist quinpirole facilitate the expression of oral stereotyped behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 133:137–145
Arnt J, Bogeso KP, Hyttel J, Meier E (1988) Relative dopamine D1 and D2 receptor affinity and efficacy determine whether dopamine agonists induce hyperactivity or oral stereotypy in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 62:121–130
Belcheva I, Bryer JB, Starkstein SE, Honig M, Moran TH, Robinson RG (1990) Hemispheric asymmetry in behavioral response to D1 and D2 receptor agonists in the nucleus accumbens. Brain Res 533:286–291
Braun AR, Chase TN (1986) Obligatory D-1/D-2 receptor interactions in the generation of dopamine agonist related behaviors. Eur J Pharmacol 131:301–306
Breese GR, Duncan GE, Napier TC, Bondy SC, Iorio LC, Mueller RA (1987) 6-Hydroxydopamine treatments enhance behavioral response to intracerebral microinjections of D1 and D2 agonists into the nucleus accumbens and striatum without changing dopamine antagonist binding. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:167–176
Brent PJ (1991) Behavioural effects of selective dopamine D-1 and D-2 agonists and antagonists in guinea pigs. Psychopharmacology 104:201–207
Bruhwyler J, Chleide E, Liegeois J-F, Delarge J, Mercier M (1991) Effects of specific dopaminergic agonists and antagonists in the open-field test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:367–371
Cameron DL, Crosbie J, Crocker AD (1988) A fixed interval momentary sampling method for assessing ongoing behaviors induced by dopamine receptor agonists. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 12:595–606
Chagraoui A, Vasse M, Protais P (1990) Effects of chronic treatments with amineptine and desipramine on motor responses involving dopaminergic systems. Psychopharmacology 102:201–206
Chandler CJ, Wohab W, Starr BS, Starr MS (1990) Motor depression: a new role for D1 receptors? Neuroscience 38:437–445
Chipkin RE, Iorio LC, Coffin VL, McQuade RD, Berger JG, Barnett A (1988) Pharmacological profile of SCH 39166: a dopamine D1 selective benzonaphthazepine with potential antipsychotic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:1093–1102
Clarke D, White FJ (1987) Review: D1 dopamine receptor — the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse 1:347–388
Collins P, Broekkamp CLE, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1991) Drugs acting at D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors induce identical purposeless chewing in rats which can be differentiated by cholinergic manipulation. Psychopharmacology 103:503–512
Darney KJ, Lewis MH, Brewster WK, Nichols DE, Mailman RB (1991) Behavioral effects in the rat of dihydrexidine, a high potency full efficacy D1 dopamine receptor agonist. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:187–195
DeNinno MP, Schoenleber R, MacKenzie R, Britton DR, Asin KE, Briggs C, Trugman JM, Ackerman M, Artman L, Bednarz L, Bhatt R, Curzon P, Gomez E, Kang CH, Stittsworth J, Kebabian JW (1991) A68930: a potent agonist selective for the D1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 199:209–219
Dreher JK, Jackson DM (1989) Role of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in mediating locomotor activity elicited from the nucleus accumbens of rats. Brain Res 487:267–277
Eilam D, Clements KVA, Szechtman H (1991) Differential effects of D1 and D2 dopamine agonists on stereotyped locomotion in rats. Behav Brain Res 45:117–124
Fletcher GH, Starr MS (1985) SKF 38393 and apomorphine modify locomotion and exploration in rats placed on a holeboard by separate actions at dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 117:381–385
Gandolfi O, Dall'olio R, Vaccheri A, Roncada P, Montanaro N (1988) Responses to selective D-1 and D-2 agonists after repeated treatment with selective D-1 and D-2 antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:463–469
Hoffman DC, Beninger RJ (1985) The D1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH 23390 reduces locomotor activity and rearing in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:341–342
Hoffman DC, Beninger RJ (1989) Preferential stimulation of D1 or D2 receptors disrupts food-rewarded operant responding in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:923–925
Johnsen PA, Hu X-T, White FJ (1991) Relationship between D1 receptors, adenylate cyclase, and the electrophysiological responses of rat nucleus accumbens neurons. J Neural Transm 86:97–113
Johansson P, Levin E, Gunne L, Ellison G (1987) Opposite effects of a D1 and a D2 agonist on oral movements in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 134:82–88
Kamien JB, Goldberg LI, Woolverton WL (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of D1 and D2 dopamine agonists in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:804–811
Kelley AE, Delfs JM, Chu B (1990) Neurotoxicity induced by the D-1 agonist SKF 38393 following microinjection into rat brain. Brain Res 532:342–346
Kirk RE (1982) Experimental design: procedures for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Brooks Cole, Monterey, CA
Mackintosh JH, Chance MRA, Silverman AP (1977) The contribution of ethological techniques to the study of drug effects. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 7. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3–34
Mazurski EJ, Beninger RJ (1991) Effects of selective drugs for dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors on conditioned locomotion in rats. Psychopharmacology 105:107–112
Molloy AG, O'Boyle KM, Pugh MT, Waddington JL (1986) Locomotor behaviors in response to new selective D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptor agonists, and the influence of selective antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:249–253
Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1984) Dopaminergic behavior stereospecifically promoted by the D-1 agonist R-SK&F 38393 and selectively blocked by the D-1 antagonist SCH 23390. Psychopharmacology 82:409–410
Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1985) Sniffing, rearing and locomotor responses to the D-1 dopamine agonist R-SK&F 38393 and to apomorphine: differential interactions with the selective D-1 and D-2 antagonists SCH 23390 and metoclopramide. Eur J Pharmacol 108:305–308
Molloy AG, Waddington JL (1987) Assessment of grooming and other behavioural responses to the D-1 receptor agonist SK&F 38393 and its R- and S-enantiomers in intact adult rats. Psychopharmacology 92:164–168
Monti JM, Fernandez M, Jantos H (1990) Sleep during acute dopamine D1 agonist or D1 antagonist SCH 23390 administration in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:153–162
Morelli M, DiChiara G (1985) Catalepsy induced by SCH 23390 in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 117:179–185
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1989) The induction of grooming and vacuous chewing by a series of selective D-1 dopamine receptor agonists: two directions of D-1:D-2 interaction. Eur J Pharmacol 160:377–384
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1990) New putative selective agonists at the dopamine D-1 receptor: behavioural and neurochemical comparison of CY 208–243 with SK&F 101384 and SK&F 103243. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:105–110
Rosengarten H, Schweitzer JW, Friedhoff AJ (1983) Induction of oral dyskinesias in naive rats by D-1 stimulation. Life Sci 33:2479–2482
Rosengarten H, Schweitzer JW, Friedhoff AJ (1986) Selective dopamine D2 receptor reduction enhances a D1 mediated oral dyskinesia in rats. Life Sci 39:29–35
Rusk IN, Cooper SJ (1989) The selective dopamine D1 agonist SK&F 38393: its effects on palatability- and deprivation-induced feeding, and operant responding for food. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:17–22
Serra G, Collu M, D'Aquila PS, De Montis GM, Gessa GL (1990) Possible role of the D1 receptor in the behavioural supersensitivity to dopamine agonists induced by chronic treatment with antidepressants. Brain Res 527:234–243
Setler PE, Sarau HM, Zirckle Cl, Saunders HJ (1978) The central effects of a novel dopamine agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 50:419–430
Shannon HE, Peters SC (1990) A comparison of the effects of cholinergic and dopaminergic agents on scopolamine-induced hyperactivity in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:549–553
Shannon HE, Bemis KG, Peters SC (1991) Potency and efficacy of dopamine agonists in mouse strains differing in dopamine cell and receptor number. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:103–107
Skrinskaya JA, Nikulina EM, Popova NK (1992) Role of genotype in brain dopamine metabolism and dopamine dependent behavior of mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42:261–267
Starr BS, Starr MS (1986a) Grooming in the mouse is stimulated by the dopamine D1 agonist SKF 38393 and by low doses of the D1 antagonist SCH 23390, but is inhibited by dopamine D2 agonists, D2 antagonists and high doses of SCH 23390. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:837–839
Starr BS, Starr MS (1986b) Differential effects of dopamine D1 agonists and antagonists on velocity of movement, rearing and grooming in the mouse. Neuropharmacology 25:455–463
Starr BS, Starr MS (1987) Behavioral interactions involving D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in non-habituated mice. Neuropharmacology 26:613–619
Starr BS, Starr MS, Kilpatrick JC (1987) Behavioural role of dopamine D1 receptors in the reserpine treated mouse. Neuroscience 22:179–188
Terry P, Katz JL (1992) Differential antagonism of the effects of dopamine D-1 receptor agonists on feeding behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Trampus M, Ferri N, Monopoli A, Ongini E (1991) The dopamine D1 receptor is involved in the regulation of REM sleep in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 194:189–194
Waddington JL, O'Boyle, KM (1989) Drugs acting on brain dopamine receptors: a conceptual re-evaluation five years after the first selective D-1 antagonist. Pharmacol Ther 43:1–52
Wamsley JK, Hunt ME, McQuade RD, Alburges MB (1991) [3H]SCH39166, a D1 dopamine receptor antagonist: binding characteristics and localization. Exp Neurol 111:145–151
White FJ, Bednarz LM, Wachtel SR, Hjorth S, Brooderson RJ (1988) Is stimulation of both D1 and D2 receptors necessary for the expression of dopamine mediated behaviors? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:189–193
Witkin JM, Schindler CW, Tella SR, Goldberg SR (1991) Interaction of haloperidol and SCH 23390 with cocaine and dopamine receptor subtype-selective agonists on schedule-controlled behavior of squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 104:425–431
Zarrindast MR, Elliasi A (1991) Differential effects of dopamine agonists on locomotion in intact and reserpine-treated mice. Gen Pharmacol 22:1027–1031
Zhou L-W, Qin Z-H, Weiss B (1991) Downregulation of stereo-typed behavior and production of latent locomotor behaviors in mice treated continuously with quinpirole. Neuropsychopharmacology 4:47–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tirelli, E., Terry, P. Biphasic locomotor effects of the dopamine D1 agonist SKF 38393 and their attenuation in non-habituated mice. Psychopharmacology 110, 69–75 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246952
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246952