Abstract
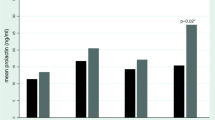
Roxindole is a potent autoreceptor-selective dopamine agonist with additional properties as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT1A agonist. In order to get more insight into its mode of action in various psychiatric populations, we evaluated the effects of subchronic roxindole treatment on pituitary and adrenal hormone secretion, i.e. release of prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and cortisol. Fifteen schizophrenic patients with positive and negative symptomatology, respectively, were treated with roxindole for 28 days. Both basal and thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) -induced prolactin secretion diminished significantly to 26.4% and 22.8% of baseline levels, respectively, under roxindole. Basal GH secretion was insignificantly elevated by 89%, whereas GH levels increased nearly 3-fold after stimulation by TRH. TSH levels decreased insignificantly to 57.5% of baseline levels, while TRH-induced TSH release was not affected by subchronic roxindole. Roxindole treatment influenced neither LH secretion nor cortisol release. Our results indicate that roxindole's dopaminergic actions might prevail over its serotonergic effects, at least as far as the regulation of anterior pituitary hormone secretion is concerned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Samra AB, Pugeat M, Dechaud H, Nachury L, Touriaire J (1984) Acute dopaminergic blockade by sulpiride stimulatesβ-endorphin secretion in pregnant women. Clin Endocrinol 21:583–588
Anderson MS, Bowers CY, Kastin AJ, Schalch DS, Schally AV, Snyder PJ, Utiger RD, Wilber JF, Wise AJ (1971) Synthetic thyrotropin-releasing hormone: a potent stimulator of thyrotropin secretion in man. N Engl J Med 285:1279–1283
Arnold MA, Fernstrom JD (1980) Administration of anti-somatostatin serum to rats reverses the inhibition of pulsatile growth hormone secretion produced by injection of metergoline but not yohimbine. Neuroendocrinology 31:194–99
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1984) Postsynaptic dopamine agonistic effects of 3-PPP enantiomers revealed by bilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions and by chronic reserpine treatment in rats. J Neural Transm 60:205–223
Bansal SA, Lee LA, Woolf PD (1981) Dopaminergic regulation of growth hormone (GH) secretion in normal men: correlation ofl-dopa and dopamine levels with the GH response. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53:301–306
Benkert O, Laakmann G, Souvatzoglou, von Werder K (1973) Missing indicator function of growth hormone and luteinizing hormone blood levels for dopamine and serotonin concentration in the human brain. J Neural Transm 34:291–299
Benkert O, Gründer G, Wetzel H (1992) Dopamine autoreceptor agonists in the treatment of schizophrenia and major depression. Pharmacopsychiatry 25:254–260
Besses GS, Burrow GN, Spaulding SW, Donabedian RK (1975) Dopamine infusion acutely inhibits the TSH and prolactin response to TRH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 41:983–987
Carlsson A (1988) The current status of the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 1:179–186
Davis KL, Kahn RS, Ko G, Davidson M (1991) Dopamine in schizophrenia: a review and reconceptualization. Am J Psychiatry 148:1474–1486
Demarest KT, Moore KE (1979) Comparison of dopamine synthesis regulation in terminals of nigrostriatal, mesolimbic, tuberoinfundibular, and tuberohypophyseal neurons. J Neural Transm 46:263–277
De Marinis L, Mancini A, Calabro F, Massari M, Torlontano M, Barbarino A (1983) Differential effects of a dopaminergic drug (piribedil) on pituitary hormone release in normal men and women. Acta Endocrinol 104:385–389
Eriksson E, Modigh K, Carlsson A, Wikström H (1983) Dopamine receptors involved in prolactin secretion pharmacologically characterized by means of 3-PPP enantiomers. Eur J Pharmacol 96:29–36
Gallo RV (1981) Further studies on dopamine-induced suppression of pulsatile LH release in ovariectomized rats. Neuroendocrinology 32:187–192
Gründer G, Wetzel H, Hammes E, Benkert O (1993) Roxindole, a dopamine autoreceptor agonist, in the treatment of major depression. Psychopharmacology 111:123–126
Hiemke C, Frohne D, Bruder D, Ghraf R (1983) Effects of oestradiol benzoate and progesterone on luteinizing hormone release and catecholamine turnover in the preoptic-hypothalamic brain area of ovariectomized rats. J Endocrinol 97:437–445
Hjorth S, Carlsson A (1987) Postsynaptic dopamine (DA) receptor stimulator properties of the putative DA autoreceptor-selective agonist B-HT 920 uncovered by co-treatment with the D-1 agonist SKF 38393. Psychopharmacology 93:534–537
Ishibashi M, Yamaji T (1984) Direct effects of catecholamines, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, and somatostatin on growth hormone and prolactin secretion from adenomatous and nonadenomatous human pituitary cells in culture. J Clin Invest 73:66–78
Jaspers C, Benker G, Reinhardt W, Cissewski K, Lederbogen S, Schröder H-G, Reinwein D (1992) A new non-ergot dopamine agonist (roxindol) for treatment of prolactinoma: first results. Acta Endocrinol 126 [Suppl 4]:131
Jezova-Repcekova D, Vigas M, Klimes J (1980) Decreased plasma cortisol response to pharmacological stimuli after glucose load in man. Endocrinol Exp 14:113–120
Lal S (1987) Growth hormone and schizophrenia. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology. The third generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 809–818
Lal S, De La Vega C, Sourkes TL, Friesen HG (1973) Effect of apomorphine on growth hormone, prolactin, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone levels in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 37:719–724
Lal S, Guyda H, Bikadoroff S (1977) Effect of methysergide and pimozide on apomorphine-induced growth hormone secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 44:766–770
Lawton NF, Evans AJ, Weller RO (1981) Dopaminergic inhibition of growth hormone and prolactin release during continous in vitro perifusion of normal and adenomatous human pituitary. J Neurol Sci 49:229–239
Lesch KP, Rupprecht R, Poten B, Müller U, Söhnle K, Fritze J, Schulte HM (1989) Endocrine responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A receptor activation by ipsapirone in humans. Biol Psychiatry 26:203–205
Maeda K, Kato Y, Ohgo S, Chihara K, Yoshimoto Y, Yamaguchi N, Kuromaru S, Imura H (1975) Growth hormone and prolactin release after injection of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in patients with depression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 40:501–503
Meller E, Helmer-Matyjek R, Bohmaker K, Adler CH, Friedhoff AJ, Goldstein M (1986) Receptor reserve at striatal dopamine autoreceptors: implications for selectivity of dopamine agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 123:311–314
Murakami Y, Kato Y, Kabayama Y, Tojo K, Inoue T, Imura H (1986) Involvement of growth hormone (GH)-releasing factor in GH secretion induced by serotoninergic mechanisms in conscious rats. Endocrinology 119:1089–1092
Pifl C, Hornykiewicz O (1988) Postsynaptic dopamine agonist properties of B-HT 920 as revealed by concomitant D-1 receptor stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol 146:189–191
Roth RH, Wolf ME, Deutch AY (1987) Neurochemistry of mid-brain dopamine systems. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology. The third generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 81–94
Rubin RT (1987) Prolactin and schizophrenia. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology. The third generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 803–808
Scanlon MF, Pourmand M, McGregor AM, Rodriguez-Arnao MD, Hall K, Gomez-Pan A, Hall R (1979) Some current aspects of clinical and experimental neuroendocrinology with particular reference to growth homone, thyrotropin and prolactin. J Endocrinol Invest 2:307–331
Scanlon MF, Lewis M, Weightman DR, Chan V, Hall R (1980) The neuroregulation of human thyrotropin secretion. Front Neuroendocrinol 6:333–380
Seyfried CA, Boettcher H (1990) Central D2-autoreceptor agonists, with special reference to indolylbutylamines. Drugs Future 15:819–832
Seyfried CA, Greiner HE, Haase AF (1989) Biochemical and functional studies on EMD 49980: a potent, selectively presynaptic D-2 dopamine agonist with actions on serotonin systems. Eur J Pharmacol 160:31–41
Seyfried CA, Haase AF, Böttcher H (1991) Presynaptic D2-receptor selectivity of roxindole (EMD 49 980). In: Tamminga CA, Schulz SC (eds) Advances in neuropsychiatry and psychopharmacology, vol I: schizophrenia research. Raven, New York, pp 317–322
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres M-P, Bouthenet M-L, Schwartz JC (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Sowers JR, Berg G, Tuck ML, Martin VI, Chandter DW, Mayes DM (1982) Dopaminergic modulation of 18-hydroxycorticosterone secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54:523–527
Tuomisto J, Männistö P (1985) Neurotransmitter regulation of anterior pituitary hormones. Pharmacol Rev 37:249–332
Van de Kar LD (1991) Neuroendocrine pharmacology of serotonergic (5-HT) neurons. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 31:289–320
Weinberger DR (1987) Implications of normal brain development for the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44:660–669
Wetzel H, Hillert A, Gründer G, Benkert O (1994a) Roxindole, a dopamine autoreceptor agonist, in the treatment of positive and negative schizophrenic symptoms. Am J Psychiatry 191:1499–1502
Wetzel H, Wiesner J, Hiemke C, Benkert O (1994b) Acute antagonism of D2-like receptors by amisulpride: effects on hormone secretion. J Psychiatric Res 28:461–473
Wiedemann K, Benkert O, Holsboer I (1990) B-HT 920 - a novel dopamine autoreceptor agonist in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. Pharamacopsychiatry 23:50–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gründer, G., Wetzel, H., Hillert, A. et al. The neuroendocrinological profile of roxindole, a dopamine autoreceptor agonist, in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 117, 472–478 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246221
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246221