Abstract
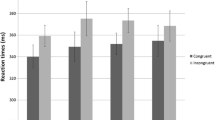
Effects of aging on ethyl alcohol (EtOH) pharmacodynamics were examined over progressive dosing schedules (0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 g/kg) in groups of young (25.0±2.9 years), middle-aged (41.1±6.6 years), and young-elderly adults (60.9±2.6 years) using three computerized cognitive-neuromotor tasks: digitsymbol substitution (DSS), keypad reaction time (KRT), and subcritical tracking (SCT). Hysteresis curves of performance impairment (adjusted for pre-drug baseline) as a function of blood alcohol concentration (BAC) were examined for time-course effects, and regression analyses were performed to assess the contribution of age beyond that accounted for by BAC. Results reflected differences in the patterning but not magnitude of impairment for elderly subjects, with earlier decrements and more rapid acute tolerance observed for DSS, in conjunction with less pharmacodynamic sensitivity for SCT. Regression analyses furthermore indicated that age and impairment were negatively related, arguing against synergistic intoxication effects as a function of aging. Analyses specifically comparing performance at baseline versus legally intoxicating BACs (>1.0 mg/ml) likewise reflected a lack of interactive effects involving the elderly. Elderly subjects nevertheless exhibited significantly lower baseline performance for DSS and KRT than young subjects and achieved higher BACs with equivalent doses. These latter findings support the exercise of caution by elderly individuals consuming EtOH prior to engaging in neuromotor pursuits such as driving.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum-Baicker C (1985) The psychological benefits of moderate alcohol consumption: a review of the literature. Drug Alcohol Depend 15:305–322
Bennett RH, Cherek DR, Spiga R (1993) Acute and chronic alcohol tolerance in humans: effects of dose and consecutive days of exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 17:740–745
Cohen MJ, Schandler SL, McArthur DL (1989) Spatial learning of visual ‘nonsense figures’ during experimental ethanol intoxication. Percept Motor Skills 68:599–606
Collins WE, Mertens HW (1988) Age, alcohol, and simulated altitude: effects on performance and breathalyzer scores. Aviat Space Environ Med 59:1026–1033
Ellinwood EH Jr, Linnoila M, Easler ME, Molter DW (1981) Onset of peak impairment after diazepam and after alcohol. Clin Pharmacol Ther 30:534–538
Ellinwood EH Jr, Linnoila M, Easler ME, Molter DW (1983) Profile of acute tolerance to three sedative anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology 79:137–141
Ellinwood EH Jr, Heatherly DG, Nikaido AM, Bjornsson TD, Kilts C (1985) Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam and diazepam. Psychopharmacology 86:392–399
Ellinwood EH Jr, Nikaido AM, Heatherly DG (1987) Comparative pharmacodynamics of benzodiazepines. In: Dahl SG, Gram LF, Paul SM, Potter WZ (eds) Clinical pharmacology in psychiatry (Psychopharmacology series, vol 3). Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 77–82
Ellinwood EH Jr, Nikaido AM, Gupta SK, Heatherly DG, Hege S (1993) Comparison of the relationship between structure and CNS effects for lorazepam, clonazepam and alprazolam. J Psychopharmacol 7:24–32
Franks HM, Hensley VR, Hensley WJ, Starmer GA, Teo RKC (1976) The relationship between alcohol dosage and performance decrement in humans. J Stud Alcohol 37:284–297
Gengo FM, Gabos C, Straley C, Manning C (1990) The pharmacodynamics of ethanol: effects on performance and judgment. J Clin Pharmacol 30:748–754
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York Basel
Hashtroudi S, Parker ES, DeLisi LE, Wyatt RJ (1983) On elaboration and alcohol. J Verb Learn Verb Behav 22:164–173
Heishman SJ, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE (1988) Alcohol and marijuana: comparative dose effect profiles in humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31:649–655
Houx PJ, Jolles J (1993) Age-related decline of psychomotor speed: effects of age, brain health, sex, and education. Percept Mot Skills 76:195–211
Huntley MS Jr (1974) Effects of alcohol, uncertainty and novelty upon response selection. Psychopharmacologia 39:259–266
Hurst PM, Bagley SK (1972) Acute adaptation to the effects of alcohol. Q J Stud Alcohol 33:358–378
Jones MK, Jones BM (1980) The relationship of age and drinking habits to the effects of alcohol on memory in women. J Stud Alcohol 41:179–186
Jones BM, Vega A (1972) Cognitive performance measured on the ascending and descending limb of the blood alcohol curve. Psychopharmacologia 23:99–114
Klein RH, Jex HR (1975) Effects of alcohol on a critical tracking task. J Stud Alcohol 36:11–20
Linnoila M, Mattila MJ (1973) Drug interaction on psychomotor skills related to driving: diazepam and alcohol. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 5:186–194
Linnoila M, Erwin CW, Ramm D, Cleveland WP (1980) Effects of age and alcohol on psychomotor performance of men. J Stud Alcohol 41:488–495
Linnoila M, Mattila MJ, Karhunen P, Nuotto E, Seppälä T (1981) Failure of TRH and ORG 2766 hexapeptide to counteract alcoholic inebriation in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21:27–32
Mattila MJ, Mattila ME, Konno K, Saarialho-Kere U (1988) Objective and subjective effects of remoxipride, alone and in combination with ethanol or diazepam, on performance in healthy subjects. J Psychopharmacol 2:138–149
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA (1987) Effects of alcohol and practice on choice reaction time. Percept Psychophys 42:465–475
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA, Kingstone A (1987) Effects of alcohol on word categorization and recognition memory. Br J Psychol 78:233–239
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA, James GH, Kerr SA (1990a) Comparing the effects of alcohol and intelligence on text recall and recognition. Br J Psychol 81:299–313
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA, James GH, Kerr SA (1990b) Effects of alcohol and extended practice on divided-attention performance. Percept Psychophys 48:445–452
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA, James GH, Kerr SA (1992) Effects of alcohol, practice, and task complexity on reaction time distributions. Q J Exp Psychol 44A:119–139
Morrow D, Leirer V, Yesavage J (1990) The influence of alcohol and aging on radio communication during flight. Aviat Space Environ Med 61:12–20
Morrow D, Yesavage J, Leirer V, Dolhert N, Taylor J, Tinklenberg J (1993) The time-course of alcohol impairment of general aviation pilot performance in a Frasca 141 simulator. Aviat Space Environ Med 64:697–705
Moskowitz H, Burns M (1971) Effect of alcohol on the psychological refractory period. Q J Stud Alcohol 32:782–790
Nelson TO, McSpadden M, Fromme K, Marlatt GA (1986) Effects of alcohol intoxication on metamemory and on retrieval from long-term memory. J Exp Psychol [Gen] 115:247–254
Nicholson ME, Wang M, Airhihenbuwa CO, Mahoney BS, Christina R, Maney DW (1992) Variability in behavioral impairment involved in the rising and falling BAC curve. J Stud Alcohol 53:349–356
Nikaido AM, Ellinwood EH Jr, Heatherly DG, Dubow D (1987) Differential CNS effects of diazepam in elderly adults. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27:273–281
Nilsson LG, Backman L, Karlsson T (1989) Priming and cued recall in elderly, alcohol intoxicated and sleep deprived subjects: a case of functionally similar memory deficits. Psychol Med 19:423–433
Poon LW (1985) Differences in human memory with aging: nature, causes, and clinical implications. In: Birren JE, Schaie KW (eds) Handbook of the psychology of aging, 2nd edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 427–462
Roe DA (1979) Alcohol and the diet. AVI Publishing, Westport, Conn.
Sahgal A, Wright C, Ferrier IN (1986) Desamino-d-arg8-vaso-pressin (DDAVP), unlike ethanol, has no effect on a boring visual vigilance task in humans. Psychopharmacology 90:58–63
Salthouse TA (1985) Speed of behavior and its implications for cognition. In: Birren JE, Schaie KW (eds) Handbook of the psychology of aging, 2nd edn. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 400–426
Salthouse TA (1992) What do adult age differences in the Digit Symbol Substitution Test reflect? J Gerontol 47:P121–128
Shillito ML, King LE, Cameron C (1974) Effects of alcohol on choice reaction time. Q J Stud Alcohol 35:1023–1034
Smith A (1982) Manual for the Symbol Digit Modalities Test. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
Solon J, Watkins J, Mikkelsen L (1972) Automated analysis of alcohols in blood. J Foren Sci 17:447–452
Swan GE, LaRue A, Carmelli D, Reed TE, Fabsitz RR (1992) Decline in cognitive performance in aging twins: heritability and biobehavioral predictors from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Twin Study. Arch Neurol 49:476–481
van Steveninck AL, Gieschke R, Schoemaker HC, Pieters MSM, Kroon JM, Breimer DD, Cohen AF (1993) Pharmacodynamic interactions of diazepam and intravenous alcohol at pseudo steady state. Psychopharmacology 110:471–478
Verhaeghen P, Marcoen A, Goossens L (1993) Facts and fiction about memory aging: quantitative integration of research findings. J Gerontol 48:P157–171
Vogel-Sprott MD (1979) Acute recovery and tolerance to low doses of alcohol: differences in cognitive and motor skill performance. Psychopharmacology 61:287–291
Vogel-Sprott M, Barrett P (1984) Age, drinking habits and the effects of alcohol. J Stud Alcohol 45:517–521
Wilson AS, Barboriak JJ, Kass WA (1970) Effects of alcoholic beverages and congeners on psychomotor skills in old and young subjects. Q J Stud Alcohol Supp 5:115–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIDA Grant 5 R01 DA01883
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tupler, L.A., Hege, S. & Ellinwood, E.H. Alcohol pharmacodynamics in young-elderly adults contrasted with young and middle-aged subjects. Psychopharmacology 118, 460–470 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245947
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245947