Abstract
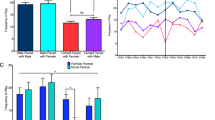
The effects of idazoxan, an alpha-2 noradrenergic antagonist, on play and open field behavior were assessed in juvenile rats. Play was assessed in two separate paradigms. Initially, juvenile rats were housed individually and given a daily 5 min opportunity to play with a responsive partner. Idazoxan (1–8 mg/kg) increased pinning, an indicator variable of play, but did not affect the frequency of dorsal contacts, an index of play solicitation. When rats were tested in a separate test for play solicitation using an unresponsive play partner, idazoxan increased all three measures of play solicitation. Idazoxan increased activity and exploration when rats were tested in an open field, suggesting that the effects of idazoxan on play may be due to an increase in behavioral arousal and/or attention. These data are consistent with a modulatory role for norepinephrine in the control of behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1984) The physiology of central α- and β-adrenoceptors. In: Catecholamines: neuropharmacology and central nervous system — theoretical aspects. Liss, New York
Beatty WW, Dodge AM, Dodge LJ, White K, Panksepp J (1982) Psychomotor stimulants, social deprivation and play in juvenile rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 16:417–422
Beatty WW, Costello KB, Berry SL (1984) Suppression of play fighting by amphetamine: effects of catecholamine antagonists, agonists and synthesis inhibitors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:747–755
Bell R, Hepper PG (1987) Catecholamines and aggression in animals. Behav Brain Res 23:1–21
Curet O, Dennis T, Scatton B (1987) Evidence for the involvement of presynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the regulation of norepinephrine metabolism in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:327–336
Dennis T, L'Heureux R, Carter C, Scatton B (1987) Presynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptors play a major role in the effects of idazoxan on cortical noradrenaline release (as measured by in vivo dialysis) in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:642–649
Dettmar PW, Lynn AG, Tulloch IF (1983) Neuropharmacological studies in rodents on the action of Rx 781094, a new selective α2-adrenoceptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 22:729–737
Dooley DJ, Bittiger H, Hauser KL, Bischoff SF, Waldmeier PC (1983) Alteration of central alpha2- and beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat after DSP-4, a selective noradrenergic neurotoxin. Neuroscience 9:889–898
Durcan MJ, Lister RG, Linnoila M (1989) Behavioral effects of alpha2 adrenoceptor antagonists and their interactions with ethanol in tests of locomotion, exploration and anxiety in mice. Psychopharmacology 97:189–194
Fagen R (1981) Animal play behavior. Oxford University Press, New York
File SE (1987) The contribution of behavioural studies to the neuropharmacology of anxiety. Neuropharmacology 26:877–886
Freedman JE, Aghajanian GK (1984) Idazoxan (RX 781094) selectively antagonizes α2-adrenoceptors on rat central neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 105:265–272
Langer SZ (1981) Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev 32:337–362
Leibowitz SF (1986) Brain monoamines and peptides: role in the control of eating behavior. Fed Proc 45:1396–1403
Mason ST (1984) Catecholamines and behaviour. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Meyerson BJ, Malmnas CO, Everitt BJ (1985) Neuropharmacology, neurotransmitters, and sexual behavior in mammals. In: Adler N, Pfaff D, Goy RW (eds) Handbook of behavioral neurobiology, vol 7, Reproduction. Plenum Press, New York
Mogilnicka E (1986) Increase in β- and α-adrenoceptor binding sites in the rat brain and in the α1-adrenoceptor functional sensitivity after the DSP-4 induced noradrenergic denervation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:743–746
Normansell L, Panksepp J (1985) Effects of clonidine and yohimbine on the social play of juvenile rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:881–883
Oades RD (1985) The role of noradrenaline in tuning and dopamine in switching between signals in the CNS. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 9:261–282
Panksepp J (1981) The ontogeny of play in rats. Dev Psychobiol 14:327–332
Panksepp J, Beatty WW (1980) Social deprivation and play in rats. Behav Neural Biol 30:197–206
Panksepp J, Siviy S, Normansell L (1984) The psychobiology of play: theoretical and methodological perspectives. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 8:465–492
Panksepp J, Normansell L, Cox JF, Crepeau LJ, Sacks DS (1987) Psychopharmacology of social play. In: Olivier B, Mos J, Brain PF (eds) Ethopharmacology of agonistic behaviour in animals and humans. Martinus Nijhoff, Dodrecht, Holland
Pettibone DJ, Pfleuger AB, Totaro JA (1985) Comparison of the effects of recently developed α2-adrenergic antagonists with yohimbine and rauwolscine on monoamine synthesis in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1093–1097
Roberts DCS (1981) An evaluation of the role of noradrenaline in learning. In: Cooper SJ (ed) Theory in psychopharmacology, vol 1. Academic Press, London
Rossi III J, Zolovick AJ, Davies RF, Panksepp J (1982) The role of norepinephrine in feeding behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 6:195–204
Routledge C, Marsden CA (1987) Comparison of the effects of selected drugs on the release of hypothalamic adrenaline and noradrenaline measured in vivo. Brain Res 426:103–111
Siviy SM, Panksepp J (1987) Sensory modulation of juvenile play in rats. Dev Psychobiol 20:39–55
Stone EA (1983) Adaptation to stress and brain noradrenergic receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 7:503–509
Thor DH, Holloway WR (1983) Play-solicitation behavior in juvenile male and female rats. Anim Learn Behav 11:173–178
Thor DH, Holloway WR (1984) Social play in juvenile rats: a decade of methodological and experimental research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 8:455–464
Walter DS, Flockhart IR, Haynes MJ, Howlett DR, Lane AC, Burton R, Johnson J, Dettmar PW (1984) Effects of idazoxan on catecholamine systems in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 33:2553–2557
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siviy, S.M., Atrens, D.M. & Menendez, J.A. Idazoxan increases rough-and-tumble play, activity and exploration in juvenile rats. Psychopharmacology 100, 119–123 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245801
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245801