Abstract
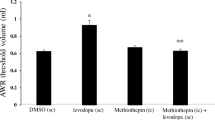
Doses ofd-amphetamine (3.2 mg/kg), fenfluramine (10 mg/kg) and quipazine (8 mg/kg) cause a significant reduction in food intake during a 30-min daily feeding session in food-deprived rats. Pirenperone and ritanserin, 5-HT2 receptor antagonists, significantly blocked the anorectic effect of quipazine, whiled-amphetamine and fenfluramine effects were not modified. Metergoline, a non-specific blocker of 5-HT receptors, significantly blocked the anorectic effects of fenfluramine and quipazine, but not thed-amphetamine effect. Pretreatment with alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists (prazosin, propranolol and pindolol), dopamine receptor antagonists (haloperidol and pimozide), the catecholamine synthesis inhibitor alphamethyl-para-tyrosine, and the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone failed to modify the anorectic effects of all three agents, with the exception that quipazine-induced anorexia was significantly reduced by pimozide. These results suggest that the quipazine anorexia is largely mediating through 5-HT2 receptors, although the effect of pimozide remains to be explained. Consistent with previous studies, the fenfluramine effect appears to be mediated through 5-HT1B receptors. Receptors involved in the anorectic effect of higher doses ofd-amphetamine are still unidentified by this analysis. Further investigation is required to define the mechanisms by which quipazine and larger doses ofd-amphetamine bring about a reduced appetite for food.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendotti C, Samanin R (1987) The role of putative 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors in the control of feeding in rats. Life Sci 41:635–642
Blundell JE, Latham CJ (1982) Behavioral pharmacology of feeding. In: Silverstone T (ed) Drugs and appetite. Academic Press, London, pp 41–80
Cunningham KA, Appel JB (1988) Hallucinogens and non-hallucinogenic 5-HT agonists: differences in subjective effects parallel differences in receptor dynamics. In: Rech RH, Gudelsky GA (eds) 5-HT agonists as psychoactive drugs. NPP Books, Ann Arbor, MI, pp 217–238
Diaz J, Huttenen MO (1972) Altered metabolism of serotonin in the brain of the rat after chronic ingestion ofd-amphetamine. Psychopharmacologia 23:365–372
Dourish CT, Clark ML, Fletcher A, Iversen SD (1989) Evidence that blockade of 5-HT1 receptors elicits feeding in satiated rats. Psychopharmacology 97:54–58
Fletcher PJ (1988) Increased food intake in satiated rats induced by the 5-HT antagonists methysergide, metergoline and ritanserin. Psychopharmacology 96:237–242
Friedman RL, Barrett RJ, Sanders-Bush E (1984) Discriminative stimulus properties of quipazine: mediation by serotonin2 binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 228:628–635
Garattini S, Samanin R (1976) Anorectic drugs and brain neurotransmitters. In: Silverstone T (ed) Appetite and food intake. Dahlem Konferenzen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 83–108
Garattini S, Borroni E, Mennini T, Samanin R (1978) Differences and similarities among anorectic agents. In: Garattini S, Samanin R (eds) Central mechanisms of anorectic drugs. Raven Press, New York, pp 127–143
Garattini S, Mennini T, Bendotti C, Invernizzi R, Samanin R (1986) Neurochemical mechanism of action of drugs which modify feeding via the serotonergic system. Appetite 7:15–38
Garattini S, Mennini T, Samanin R (1987) From fenfluramine racemate tod-fenfluramine: specificity and potency of the effects on the serotonergic system and food intake. Ann NY Acad Sci 499:156–166
Garattini S, Adalgisa B, Caccia S, Mennini T, Samanin R (1988) Progress in assessing the role of serotonin in the control of food intake. Clin Neuropharmacol [Suppl 1] 11:S8-S32
Gilbert DB, Cooper SJ (1985) Analysis of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor involvement ind- andl-amphetamine-induced anorexia in rats. Brain Res Bull 15:385–389
Glennon RA, Young R, Rosecrans JA (1983) Antagonism of the effects of the hallucinogen DOM and the purported 5-HT agonist quipazine by 5-HT2 antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 91:189–196
Henck JW, Rezabek DH, Rech RH (1985) Comparison of anorexia and motor disruption by cyclazocine and quipazine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:671–676
Hewson G, Leighton GE, Hill RG, Hughes J (1988) Ketanserin antagonises the anorectic effect of dl-fenfluramine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 145:227–230
van der Hoek GA, Cooper SJ, Jones BJ, Tyers MB (1989) Evidence that serotonin at 5-HT-3 receptors modulates amphetamine-induced reward. International Symposium on Serotonin: From Cell Biology to Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Florence, March 29–April 1 (Abstracts, p 55)
Jenck F, van Delft AML, Broekkamp CLE (1989) Serotonergic control of dorsal periaqueductal gray (PAG) induced aversion: a functional role for the brain 5HT1C receptors? International Symposium on Serotonin: From Cell Biology to Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Florence, March 29–April 1 (Abstracts, p 89)
Jones BJ, Costall B, Domeney AM, Kelly ME, Naylor RJ, Oakley NR, Tyers MB (1988) The potential anxiolytic activity of GR38032F, a 5-HT3-receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 93:985–993
Kennett GA, Curzon G (1988) Evidence that hypophagia induced by mCPP and TFMPP requires 5-HT1C and 5-HT1B receptors; hypophagia induced by RU 24969 only requires 5-HT1B receptors. Psychopharmacology 96:93–100
Kilpatrick GJ (1989) The central effects of antagonists of 5-HT3 receptors. International Symposium on Serotonin: From Cell Biology to Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Florence, March 29–April 1 (Abstracts, p 6)
Leibowitz SF, Shor-Posner G, Maaclow C, Grinker JA (1986) Amphetamine: effects on meal patterns and macronutrient selection. Brain Res Bull 17:681–689
Leibowitz SF, Weiss GF, Shor-Posner G (1988) Hypothalamic serotonin: pharmacological, biochemical and behavioral analyses of its feeding-suppressive action. Clin Neuropharmacol [Suppl 1] 11:S51-S71
Massi M, Marini S (1987) Effect of the 5-HT2 antagonist ritanserin on food intake and on 5-HT-induced anorexia in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:333–340
Mokler DJ, Stoudt KW, Rech RH (1985) The 5-HT2 antagonist pirenperone reverses disruption of FR-40 by hallucinogenic drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:677–682
Neill JC, Cooper SJ (1989) Evidence thatd-fenfluramine anorexia is mediated by 5-HT1 receptors. Psychopharmacology 97:213–218
Peroutka SJ (1988) 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Neurosci 11:45–60
Quattrone A, Bendotti C, Becchia M, Samanin R (1977) Various effects ofd-amphetamine in rats with selective lesions of brain noradrenaline-containing neurons or treated with penfluridol. Commun Psychopharmacol 1:525–531
Rech RH, Stolk JM (1970) Amphetamine - drug interactions that relate brain catecholamines to behavior. In: Costa E, Garattini S (eds) International symposium on amphetamines and related compounds. Raven Press, New York, pp 385–413
Rech RH, Tilson HA, Marquis WJ (1975) Adaptive changes in behavior after repeated administration of various psychoactive drugs. In: Mandell AJ (ed) Neurobehavioral mechanisms of adaptation and behavior. Raven Press, New York, pp 263–286
Rech RH, Borsini F, Samanin R (1984) Effects ofd-amphetamine andd-fenfluramine on performance of rats in a food maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:1–5
Rech RH, Commissaris RL, Mokler DJ (1988) Hallucinogenic 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists characterized by disruption of operant behavior. In: Rech RH, Gudelsky GA (eds) 5-HT agonists as psychoactive drugs. NPP Books, Ann Arbor, MI, pp 185–215
Samanin R, Garattini S (1982) Neuropharmacology of feeding. In: Silverstone T (ed) Drugs and appetite. Academic Press, London, pp 23–29
Samanin R, Bendotti C, Miranda F, Garattini S (1977) Decrease of food intake by quipazine in the rat: relation to serotoninergic receptor stimulation. J Pharm Pharmacol 29:53–54
Sanders-Bush E, Conn PJ (1988) Functional characterization of serotonin agonists based on effects on inositol lipid metabolism. In: Rech RH, Gudelsky GA (eds) 5-HT agonists as psychoactive drugs. NPP Books, Ann Arbor, MI, pp 61–71
Silverstone T, Fincham J, Wells B, Kyriakides M (1980) The effect of the dopamine receptor blocking drug pimozide on the stimulant and anorectic actions of dextroamphetamine in man. Neuropharmacology 19:1235–1237
Sugrue MF (1987) Neuropharmacology of drugs affecting food intake. Pharmacol Ther 32:145–182
Towell A, Muscat R, Willner P (1988) Behavioural microanalysis of the role of dopamine in amphetamine anorexia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:641–648
Weiner N (1972) Pharmacology of central nervous system stimulants. In: Zarafonetis CJD (ed) Drug abuse: proceedings of the international conference. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 243–251
Willner P, Towell A (1982) Microstructural analysis of the involvement of beta-receptors in amphetamine anorexia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:255–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, R., MacKenzie-Taylor, D. & Rech, R.H. Evidence for 5-HT2 receptor mediation in quipazine anorexia. Psychopharmacology 100, 115–118 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245800
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245800