Abstract
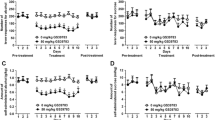
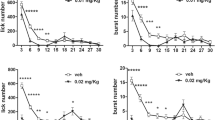
Two experiments examined the effect of the benzodiazepine receptor agonist, zolpidem, on palatable fluid intake in water-deprived rats. In the first experiment, pretreatment with 3.0 or 10.0 mg/kg zolpidem IP was found to increase consumption of a novel glucose drink (3% d-glucose and 0.1% sodium saccharine w/v in water). The increase in fluid consumption induced with zolpidem was comparable to the increases observed with diazepam and the benzodiazepine partial agonist, FG 8205. Experiment 2 demonstrated that this zolpidem-induced increase in drinking could be observed in both naive rats and in rats that had been habituated to the glucose drink and the testing environment: pretreatment with 3.0 mg/kg PO of zolpidem was found to increase fluid consumption in rats that had received either 0 or 8 days pre-exposure to the testing conditions. Contrary to earlier reports, these results support the conclusion that zolpidem, like other benzodiazepine agonists, can directly modulate ingestive behaviour.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbilla S, Depoortere H, George P, Langer SZ (1985) Pharmacological profile of the imidazopyridine zolpidem at benzodiazepine receptors and electrocorticogram in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 330:248–251
Cole SO (1983) Combined effects of chlordiazepoxide treatment and food deprivation on concurrent measures of feeding and activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:369–372
Cooper SJ (1985) Hyperphagic and anorectic effects of β-carbolines in a palatable food consumption test: comparisons with triazolam and quazepam. Eur J Pharmacol 120:257–265
Cooper SJ (1991) Benzodiazepines, appetite and stress. In: Soubrie P (ed) Anxiety, depression and mania. Animal models of psychiatric disorder, vol 3, Karger, Basel, Switzerland, pp 24–44
Cooper SJ, Desa A (1988) Pyrazoloquinolines and zolpidem: effect of hypertonic saline consumption in rehydrating rats. Drug Dev Res 14:161–168
Cooper SJ, Estall LB (1985) Behavioural pharmacology of food, water and salt intake in relation to drug actions at benzodiazepine receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 9:5–19
Cooper SJ, McClelland A (1980) Effects of chlordiazepoxide, food familiarization, and prior shock experience on food choice in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:23–28
Cooper SJ, Moores WR (1985) Benzodiazepine-induced hyperphagia in the nondeprived rat: comparisons with CL218,827, zopiclone, tracazolate and phenobarbital. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:169–172
Cooper SJ, Yerbury RE (1986) Benzodiazepine-induced hyperphagia: stereospecificity and antagonism by pyrazoloquinolines, CGS 9895 and CGS 9896. Psychopharmacology 89:462–466
Cooper SJ, Yerbury RE (1988) Clonazepam selectively increases saccharin ingestion in a two choice test. Brain Res 456:173–176
Cooper SJ, Barber DJ, Gilbert DB, Moores WR (1985) Benzodiazepine receptor ligands and the consumption of a highly palatable diet in non-deprived male rats. Psychopharmacology 86:348–355
Depoortere H, Zivkovic B, Lloyd KG, Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Langer SZ, Bartholini G (1986) Zolpidem, a novel nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic. I. Neuropharmacological and behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:649–658
Doble A, Martin IL (1992) Multiple benzodiazepine receptors: no reason for anxiety. TIPS 13:76–81
Sanger DJ, Zivkovic B (1988) Further behavioural evidence for the selective sedative action of zolpidem. Neuropharmacology 27:1125–1130
Taylor J K (1990) Statistical techniques of data analysis. Lewis, Chelsea, Michigan, USA
Tricklebank MD, Honoré T, Iversen SD, Kemp AR, Knight GR, Marshall GR, Rupniak NMJ, Singh L, Tye S, Watjen F, Wong EHF (1990) The pharmacological properties of the imidazobenzodiazepine FG 8205, a novel partial agonist at the benzodiazepine receptor. Br J Pharmacol 101:753–761
Yerbury RE, Cooper SJ (1989) Novel benzodiazepine receptor ligands: palatable food intake following zolpidem, CGS 17867A, or Ro23-0364, in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:303–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanhope, K.J., Roe, S., Dawson, G. et al. Effect of the benzodiazepine receptor agonist, zolpidem, on palatable fluid consumption in the rat. Psychopharmacology 111, 185–189 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245521
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245521