Abstract
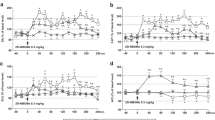
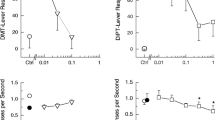
Like hallucinogenic 5-HT2 agonists, LSD (d-lysergic acid diethylamide) produces characteristic decreases in locomotor activity and investigatory behaviors of rats tested in a novel environment. Because LSD is an agonist at both 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors, however, the respective influences of these different receptors in the behavioral effects of LSD remain unclear. In particular, the paucity of selective 5-HT1A antagonists has made it difficult to assess the specific contribution of 5-HT1A receptors to the effects of LSD. An alternative approach to the delineation of receptor-specific effects is the use of cross-tolerance regimens. In the present studies, rats were pretreated with saline, 8-hydroxy-2(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) (0.5 mg/kg SC), 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) (1.0 mg/kg SC), or LSD (60 µg/kg SC), every 12 h for 5 or 8 days. Thirty-six hours later, rats were tested in a behavioral pattern monitor 10 min after injection of saline, 0.5 mg/kg 8-OH-DPAT, 1.0 mg/kg DOI, or 60 µg/kg LSD. As expected, tolerance to the decreases in locomotor activity produced by acute administrations of 8-OH-DPAT, DOI, or LSD occurred when rats were pretreated chronically with 8-OH-DPAT, DOI, or LSD, respectively. Furthermore, pretreatment with either 8-OH-DPAT or DOI produced cross-tolerance to LSD. These results support the hypothesis that the effects of LSD in this model reflect a combination of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 effects and support the view that there is an interaction between 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1982) LSD-induced alterations of locomotor patterns and exploration in rats. Psychopharmacology 77:179–185
Adams LM, Geyer MA (1985) A proposed animal model for hallucinogens based on LSD's effects on patterns of exploration in rats. Behav Neurosci 99:881–900
Appel JB, Freedman DX (1968) Tolerance and cross-tolerance among psychotomimetic drugs. Psychopharmacologia 13:267–274
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1989) Facilitation of 8-OH-DPAT-induced forepaw treading of rats by the 5-HT2 agonist DOI. Eur J Pharmacol 161:45–51
Backus LI, Sharp T, Grahame-Smith DG (1990) Behavioural evidence for functional interaction between central 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A receptors. Br J Pharmacol 166:793–799
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1990) Behavioural evidence for functional interactions between 5-HT-receptor subtypes in rats and mice. Br J Pharmacol 101:667–673
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1991) Attenuation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 but not 5-HT1C receptor mediated behaviour in rats following chronic treatment with 5-HT receptor agonists, antagonists or anti-depressants. Psychopharmacology 105:219–224
Bervoets K, Millan MJ, Colpaert FC (1990) Agonist action at 5-HT1C receptors facilitates 5-HT1A receptor-mediated spontaneous tail-flicks in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 191:185–195
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1980) Acute and chronic LSD effects on rat startle: data supporting an LSD-rat model of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 15:909–916
Bridger WH (1975) Good trip or bad trip: The roles of tolerance and stress in hallucinogenic drug action. In: Mandell AJ (ed) Advances in biochemical psychopharmacology, vol 13. Neurobiological mechanisms of adaptation and behavior. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–25
Buckholtz NS, Zhou D, Freedman DX (1988) Serotonin2 agonist administration down-regulates rat brain serotonin2 receptors. Life Sci 42:2439–2445
Carter RB, Appel JB (1978) LSD and 5-HTP: tolerance and cross-tolerance relationships. Eur J Pharmacol 50:145–148
Darmani NA, Martin BR, Glennon RA (1990a) Withdrawal from chronic treatment with (+)-DOI causes super-sensitivity to 5-HT2 receptor-induced head-twitch behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 186:115–118
Darmani NA, Martin BR, Pandey U, Glennon RA (1990b) Do functional relationships exist between 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:901–906
Eison AS, Wright RN (1992) 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors mediate discrete behaviors in the Mongolian gerbil. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:131–137
Geyer MA (1990) Approaches to the characterization of drug effects on locomotor activity in rodents. In: Adler MW and Cowan A (eds) Modern methods in pharmacology: testing and evaluation of drugs of abuse. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 81–99
Geyer MA, Krebs KM (1993) Serotonin receptor involvement in an animal model of the acute effects of hallucinogens. In: Lin G (ed) Hallucinogens: an update (NIDA research monograph series). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD (in press)
Geyer MA, Light RK (1979) LSD-induced alterations of investigatory responding in rats. Psychopharmacology 65:41–47
Geyer MA, Light RK, Rose GJ, Petersen LR, Horwitt DD, Adams LM, Hawkins RL (1979) A characteristic effect of hallucinogens on investigatory responding in rats. Psychopharmacology 65:35–40
Glennon RA, Titeler M, McKenney JD (1984) Evidence for 5-HT2 involvement in the mechanism of action of hallucinogenic agents. Life Sci 35:2505–2511
Hamon M, Lanfumey L, Mestikawy SE, Boni C, Miquel MC, Bolanos F, Schechter L, Gozlan H (1990) The main features of central 5-HT1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:349–360
Isbell H, Belleville RE, Fraser HF, Wikler A, Logan CR (1956) Studies on lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25). I. Effects in former morphine addicts and development of tolerance during chronic intoxication. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry 76:468–478
Johansson CE, Meyerson BJ, Hoglund AU (1990) The long-term effects of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propyl-amino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) on copulatory and exploratory behaviour in male rats. Eur J Pharmacol 178:1–9
Larsson LG, Renyi L, Ross SB, Svensson B, Angeby-Moller K (1990) Different effects on the responses of functional pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors by repeated treatment of rats with the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT. Neuropharmacology 29:85–91
McKenna DJ, Nazarali AJ, Himeno A, Saavedra JM (1989) Chronic treatment with (+)DOI, a psychotomimetic 5-HT2 agonist, downregulates 5-HT2 receptors in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:81–87
Mittman SM, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of 5HT-1A agonists on locomotor and investigatory behaviors in rats differ from those of hallucinogens. Psychopharmacology 98:321–329
Mittman SM, Geyer MA (1991) Dissociation of multiple effects of acute LSD on exploratory behavior in rats by ritanserin and propranolol. Psychopharmacology 105:69–76
Murray TF, Craigmill AL, Fischer GJ (1977) Pharmacological and behavioral components of tolerance to LSD and mescaline in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 7:239–244
Nash JF, Meltzer HY, Gudelsky GA (1989) Selective cross-tolerance to 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptor-mediated temperature and corticosterone responses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:781–785
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1979) Multiple serotonin receptors: differential binding of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine, [3H]lysergic acid diethylamide and [3H]spiroperidol. Mol Pharmacol 16:687–699
Pranzatelli MR (1990) Evidence for involvement of 5-HT2 and 5-HT1C receptors in the behavioral effects of the 5-HT agonist 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenylaminopropane)-2 (DOI). Neurosci Lett 115:74–80
Pranzatelli MR (1991) Regulation of 5-HT2 receptors in rat cortex: studies with a putative selective agonist and an antagonist. Biochem Pharmacol 42:1099–1105
Pranzatelli MR, Pluchino RS (1991) The relation of central 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors: Low dose agonist-induced selective tolerance in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:407–413
Rech RH, Tilson HA, Marquis WJ (1975) Adaptive changes in behavior after repeated administration of various psychoactive drugs. In: Mandell AJ (ed) Neurobiological mechanisms of adaptation and behavior. Raven Press, New York, pp 263–286
Sanders-Bush E, Breeding M (1988) Putative selective 5-HT-2 antagonists block serotonin 5-HT-1c receptors in the choroid plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:169–173
Sanders-Bush E, Burris KD, Knoth K (1988) Lysergic acid diethylamide and 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine are partial agonists at serotonin receptors linked to phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:924–928
Titeler M, Lyon RA, Glennon RA (1988) Radioligand binding evidence implicates the brain 5-HT2 receptor as a site of action for LSD and phenylisopropylamine hallucinogens. Psychopharmacology 94:213–216
Trulson ME (1985) Separation of tolerance to the behavioral effects of LSD from changes in serotonin receptor binding in cats. Eur J Pharmacol 111:385–388
Wing LL, Tapson GS, Geyer MA (1990) 5HT-2 mediation of acute behavioral effects of hallucinogens in rats. Psychopharmacology 100:417–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krebs, K.M., Geyer, M.A. Cross-tolerance studies of serotonin receptors involved in behavioral effects of LSD in rats. Psychopharmacology 113, 429–437 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245219
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245219