Abstract
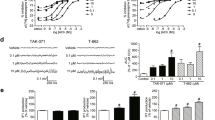
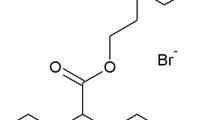
The cholinergic activities of SR 46559A, 3-[N-(2 diethyl-amino-2-methylpropyl)-6-phenyl-5-propyl] pyridazinamine sesquifumarate, have been investigated in vitro and in vivo, in rodents. Using rat brain cortical membranes, SR 46559A was a competitive ligand (Ki=112 nM) at muscarinic M1 receptors, its affinity for muscarinic M2 (cardiac) and M3 (glandular) receptors being 6–7 times lower. SR 46559A did not interact with brain nicotinic receptors and high affinity choline uptake sites nor did it inhibit brain acetylcholinesterase activity. In contrast to reference muscarinic agonists, SR 46559A (1 mM) did not inhibit the forskolin-induced activation of cAMP synthesis nor did it stimulate phosphoinositides breakdown in various brain preparations. However, this compound enhanced (+67% at 1 mM) diacylglycerol formation in rat striatal miniprisms, an effect fully reversed by atropine. As shown with reference agonists, SR 46559A inhibited (IC50=10 µM) the K+-evoked release of [3H]GABA from rat striatal slices and reduced at 0.5 and 1 µM, the population spike amplitude of the CA1 pyramidal cells induced by stimulation of the Schaffer's collateral commissural pathway in rat hippocampal slices. In mice, SR 46559A at a near lethal dose (200 mg/kg PO) did not induce the typical cholinergic syndrome nor did it modify at 30 mg/kg PO the oxotremorine-induced hypothermia. Like muscarinic agonists, SR 46559A (1 mg/kg PO) potentiated haloperidol-induced catalepsy in rats and inhibited (ED50=0.12 mg/kg PO) rotations induced in mice by intrastriatal injection of pirenzepine. SR 46559A prevented the scopolamine- or pirenzepine-induced deficit in passive avoidance learning, this compound being 3 times more potent on pirenzepine-induced amnesia. Moreover, using the social memory test, SR 46559A (0.1–3 mg/kg PO) enhanced short-term retention in adult rats and improved memory deficits observed in aged mice and in rats subjected to cerebral ischeamic insult. SR 46559A (1–3 mg/kg PO) also reversed the ischaemia-induced alterations of rats exploratory behaviour. Taken together, these results suggest that SR 46559A behaves as an atypical muscarinic compound which, at least in part, could stimulate muscarinic receptors coupled to phosphatidylcholine/phospholipases C or D signalling pathways. This drug has a marked ability to improve experimentally induced cognitive deficits in rodents without producing cholinergic symptomatology. Thus, SR 46559A could be a potential useful drug for the symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso R, Soubrié P (1991) Effects of serotonergic denervation on the density and plasticity of brain muscarinic receptors in the rat. Synapse 8:30–37
Araujo DM, Lapchak PA, Robitaille Y, Gauthier S, Quirion R (1988) Differential alteration of various cholinergic markers in cortical and subcortical regions of human brain in Alzeimer's disease. J Neurochem 50:1914–1923
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Flicker C (1987) Cholinergic psychopharmacology: an integration of human and animal research on memory. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology: the third generation of progress, Raven, New york, pp 219–232
Bidaut-Russell M, Devane WA, Howlett AC (1990) Cannabinoid receptors and modulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in the rat brain. J Neurochem 55:21–26
Chermat R, Simon P, Boissier JR (1976) Profils psychopharmacologiques de la pilocarpine, de l'oxotrémorine et de l'ésérine. J Pharmacol (Paris) 7:227–240
Diamant S, Atlas D (1989) Potentiation of [3H] inositol phosphate formation by receptor activation and membrane depolarization in brain cortical slices. Brain Res 503:55–61
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andress V, Featherstone M (1961) A new rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fisher A, Heldman E, Brandeis R, Karton I, Pittel Z, Dachir S, Levy A, Mizobe F (1987) (cis)-2-Methyl-spiro-(1,3-oxothiolane-5,3′)-quinuclidine (AF102B): a novel putative M1 agonist as a candidate drug for the treatment of senile dementia of Alzheimer's type. In; Cohen S, Sokolovsky M (eds) international symposium on muscarinic cholinergic mechanisms, Freund, London, pp 132–137
Fowler CJ, Court JA, Tiger G, Björklund PE, Candy JM (1987) Stimulation of inositol phospholipids breakdown in rat cortical and hippocampal miniprisms by noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and carbachol: some methodological aspects. Pharmacol Toxicol 60:274–279
Freedman SB, Harley EA, Iversen LL (1988) Relative affinities of drugs acting at cholinoceptors in displacing agonist and antagonist radioligands: the NMS/Oxo-M ratio as an index of efficacy at cortical muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 93:437–445
Freedman SB, Harley EA, Marwood RS, Patel S (1990a) In vivo characterisation of novel efficacious muscarinic receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 187:193–199
Freedman SB, Harley EA, Patel S, Newberry NR, Gilbert MJ, McKnight AT, Tang JK, Maguire JJ, Mundunkotuwa NT, Baker R, Street LJ, McLeod AM, Saunders J, Iversen LL (1990b) A novel series of non-quaternary oxadiazoles acting as full agonists at muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 101:575–580
Gil W, Wolfe BB (1985) Pirenzepine distinguishes between muscarinic receptors-mediated phosphoinositides breakdown and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:608–618
Hammer R, Giraldo E, Schiavi GB, Monferini E, Ladinsky H (1986) Binding profile of a novel cardioselective muscarinic receptor antagonist AFDX-116, to membranes of peripheral tissues and brain in the rat. Life Sci 38:1653–1662
Hargreaves RJ, McKnight AT, Scholey K, Newberry NR, Street LJ, Hutson PH, Semark JE, Harley EA, Patel S, Freedman SB (1992) L-689,660, a novel cholinomimetic with functional selectivity for M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol 107:494–501
Herman C, Stern RG, Losonzcy MF, Jaff S, Davidson M (1991) Diagnostic and Pharmacological approaches in Alzheimer's disease. Drugs Aging 1:144–162
Hulme EC, Birdsall NJM, Buckley NJ (1990) Muscarinic receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 30:633–673
Kan JP (1992) Current and future approaches to therapy of Alzheimer's diseases. Eur J Med Chem 27:565–570
Kesner RP, Crutcher KA, Omana H, (1990) Memory deficits following nucleus basalis magnocellularis lesions may be mediated through limbic, but not neocortical targets. Neuroscience 38:93–102
Klemm WR (1985) Evidence for a cholinergic role in haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Psychopharmacology 85:139–142
Komabayashi T, Yataka A, Isawa T, Fujinami H, Suda K (1992) Mechanism of carbachol-stimulated diacylglycerol formation in rat parotid acinar cell. Eur J Pharmacol 225:209–216
Majerus PW, Neufeld EJ, Wilson DB (1984) Production of phosphoinositide derived messengers. Cell 37:701–703
Marrion NV, Smart TG, Marsh SJ, Brown DA (1989) Muscarinic suppression of the M-current in the rat sympathetic ganglion is mediated by receptors of M1-subtype. Br J Pharmacol 98:557–573
Martinson EA, Goldstein D, Brown JH, (1989) Muscarinic receptor activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 264:14748–14754
Messer WS, Bohnett M, Stibbe J (1990) Evidence for a preferential involvement of M1 muscarinic receptors in representational memory. Neurosci Lett 116:184–189
Nakahara N, Fujise N, Kawanishi G, Mizobe F (1990) Central muscarinic activities of an M1-selective agonist: preferential effect on reversal of amnesia. Brain Res 507:172–175
Onodera H, Kogure K (1989) Mapping second messenger systems in the rat hippocampus after transient forebrain ischaemia: in vitro [3H] forskolin and [3H] inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate binding. Brain Res 487:343–349
Onodera H, Sato G, Kogure K (1987) Quantitative autoradiographic analysis of muscarinic cholinergic and adenosine A1 binding sites after transient forebrain ischaemia in the gerbil. Brain Res 415:309–322
Pério A, Terranova JP, Worms P, Bluthe RM, Dantzer R, Bizière K (1989) Specific modulation of social memory in rats by cholinomimeric and nootropic drugs, by benzodiazepine inverse agonists, but not by psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology 97:262–268
Potter LT, Ferrendelli CA (1989) Affinities of different cholinergic agonists for the high and low affinity states of hippocampal M1 muscarinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:974–978
Potter LT, Ferrendelli CA, Hanchett HE (1988) Two affinity states of muscarine receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 8:181–191
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1992) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischaemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Qian Z, Drewes LR (1990) A novel mechanism for acetylcholine to generate diacylglycerol in brain. J Biol Chem 265:3607–3610
Raiteri M, Marchi M, Paudice P, Pittaluga A (1990) Muscarinic receptors mediating inhibition ofγ-aminobutyric acid release in rat corpus striatum and their pharmacological characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:496–501
Sandmann J, Peralta EG, Wurtman RJ (1991) Coupling of transfected muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes to phospholipase D. J Biol Chem 266:6031–6034
Sheridan RD, Szabadi E, Bradshaw CM (1987) Inhibition by carbachol of the synaptically-evoked excitation of hippocampal CA1 neurones: mediation by M1 muscarinic receptors ? Br J Pharmacol 92:554P.
Tilson HA, McLamb RL, Shaw S, Rogerc BC, Pediabitakis P, Cook L (1988) Radial-arm maze deficits produced by colchicine administered into the area of the nucleus basalis are ameliorated by cholinergic agents Brain Res 438:83–94
Vickroy TW, Roeske WR, Yamamura HI (1984) Sodium-dependent high affinity binding of [3H] hemicholium -3 in the rat brain: a potentially selective marker for presynaptic cholinergic sites. Life Sci 35:2335–2343
Wanibuchi F, Konishi T, Harada M, Terai M, Hidaka K, Tamura T, Tsukamoto S, Usada S (1990) Pharmacological studies on novel muscarinic agonists, 1-oxa-8-azaspiro (4.5) decane derivatives, YM796 and YM954. Eur J pharmacol 187:479–486
Whitehouse PJ, Martino AM, Antuono PG, Lowenstein PR, Coyle JT, Price DJ, Kellar KJ (1986) Nicotinic acetylcholine binding sites in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 371:146–151
Worms P, Bizière K (1987) Antagonism by cholinomimetic drugs of the turning induced by intrastriatal pirenzepine in mice. Psychopharmacology 93:489–493
Worms P, Lloyd KG (1980) Biphasic effects of direct, but not indirect, GABA mimetics and antagonists on haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:179–184
Worms P, Gueudet C, Pério A, Soubrié P (1989a) Systemic injection of pirenzepine induces a deficit in passive avoidance learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 98:286–288
Worms P, Kan JP, Steinberg R, Terranova JP, Pério A, Bizière K (1989b) Cholinomimetic activities of minaprine. Naunyn-Schmiedberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:411–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kan, JP., Steinberg, R., Oury-Donat, F. et al. SR 46559A: a novel and potent muscarinic compound with no cholinergic syndrome. Psychopharmacology 112, 219–227 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244914
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244914