Abstract
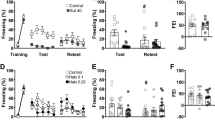
The development of classical conditioning of cocaine's locomotor effects can be dissociated from the development of sensitization to cocaine by co-administration of haloperidol, a dopamine D2-like receptor antagonist, and nimodipine, an L-type calcium channel antagonist. The effects of these agents on theexpression of conditioning and sensitization are described in the present report. Rats were given injections of vehicle or cocaine (10 mg/kg, IP) for 10 days before placement in a specific context in which locomotor activity was recorded. Neither haloperidol (0.05 mg/kg, IP) nor nimodipine (10 mg/kg, SC) influenced the expression of classical conditioning of cocaine's locomotor effects to the situational context on a subsequent cocaine-free test. Combined treatment of rats with both drugs did block classical conditioning with cocaine. Nimodipine, but not haloperidol, blocked the expression of behavioural sensitization to cocaine after a cocaine challenge. It is concluded that the expression of cocaine-induced classical conditioning can be pharmacologically dissociated from the expression of behavioural sensitization to cocaine. Furthermore, the effects of nimodipine and haloperidol on the expression of conditioning and sensitization are different from their effects on the development of these phenomena.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrist B (1983) Psychoses induced by central nervous system stimulants and related drugs. In: Creese I (ed) Stimulants: neurochemical, behavioral, and clinical perspectives, Raven, New York, pp 1–30
Baldo BA, Kelly AE (1991) Cross sensitization between cocaine and GBR 12909, a dopamine uptake inhibitor. Brain Res Bull 27:105–108
Barr GA, Sharpless NS, Cooper S, Schiff SR, Paredes W, Bridger WH (1983) Classical conditioning, decay and extinction of cocaine-induced hyperactivity and stereotypy. Life Sci 33:1341–1351
Bartko G, Horvath S, Zador G, Frecska E (1991) Effect of adjunctive verapamil administration in chronic schizophrenia patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:343–349
Beninger RJ, Hahn BL, (1983) Pimozide blocks establishment but not expression of amphetamine-produced environment-specific conditioning. Science 20:1304–1306
Beninger RJ, Herz RS (1986) Pimozide blocks establishment but not expression of cocaine-produced environment-specific conditioning. Life Sci 38:1425–1431
Carmen JS, Wyatt RJ (1979) Calcium: bivalent cation in the bivalent psychoses. Biol Psychiatry 14:295–336
Damianopoulos EN, Carey RJ (1992) Conditioning, habituation and behavioral reorganization factors in chronic cocaine effects. Behav Brain Res 49:149–157
DiLullo SL, Martin-Iverson MT (1991) Presynaptic dopaminergic neurotransmission mediates amphetamine-induced unconditioned but not amphetamine-conditioned locomotion and defecation in the rat. Brain Res 568:45–54
DiLullo SL, Martin-Iverson MT (1992a) Evidence for presynaptic dopamine mechanisms underlying amphetamine-conditioned locomotion. Brain Res 578:161–167
DiLullo SL, Martin-Iverson MT (1992b) Calcium channel blockade: a potential adjunctive treatment with neuroleptics for stimulant abuse and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 31:1143–1150
Gold LH, Swerdlow NR, Koob GF (1988) The role of mesolimbic dopamine in conditioned locomotion produced by amphetamine. Behav Neurosci 102:544–552
Kiess HO (1989) Statistical concepts for the behavioral sciences. Allyn and Bacon, Toronto.
Lapierre, YD (1978) A controlled study of penfluoridol in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 135:956–959
Martin-Iverson MT (1991) An animal model of stimulant psychoses. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Martin-Iverson MT (eds.) Neuromethods, vol 18: animal model in psychiatry 1. Humana, Clifton, N. J., pp 103–149
Martin-Iverson MT, Iversen, SD, Stahl SM (1988a) Long-term motor stimulant effects of (+)-4-propyl-9-hydroxynaphthoxazine (PHNO), a dopamine D-2 receptor agonist: interactions with a dopamine D-1 receptor antagonist and agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 149:25–31.
Martin-Iverson MT, Stahl SM, Iversen SD (1988b) Chronic administration of a selective dopamine D-2 agonist: factors determing behavioural tolerance and sensitization. Psychopharmacology 95:534–539
Martin-Iverson MT, McManus DJ (1990) Stimulant-conditioned locomotion is not affected by blockade of D1 and/or D2 dopamine receptors during conditioning. Brain Res 521:175–184
Mattingly BA, Gotsick JE (1989) Conditioning and experiential factors affecting the development of sensitization to apomorphine. Behav Neurosci 103:1311–1317
Muntaner C, Cascella NG, Kumor KM, Nagoshi C, Herning R, Jaffe J (1989) Placebo responses to cocaine administration in humans: effects of prior administrations and verbal instructions. Psychopharmacology 99:282–286
O'Brien CP, Ehrman R, Ternes J (1986) Classical conditioning in human opioid dependence. In: Goldberg SG, Stolerman IP (eds) Behavioral analysis of drug dependence. Academic Orlando, Fla. pp 329–356
O'Brien CP, Childress AR, Arndt IO, McLennan AT, Woody GE, Maany I (1988) Pharmacological and behavioral treatments of cocaine dependence: controlled studies. J Clin Psychiatry 49:17–22
Pani L, Kuzmin A, Martellotta MC, Gessa GL, Fratta W (1991) The calcium channel antagonist PN 200-110 inhibits the reinforcing properties of cocaine. Brain Res Bull 26:445–447
Post RM, Lockfeld A, Squillace KM, Contel NR (1981) Drug-environmental interaction: context dependency of cocaine- induced behavioral sensitization. Life Sci 28:755–760
Reimer AR, Martin-Iverson, MT (1993) Nimodipine and haloperidol attenuate behavioural sensitization to cocaine but only nimodipine blocks the establishment of conditioned locomotion induced by cocaine. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration. Brain Res Rev 11: 157–198
Schiff SR (1982) Conditioned dopaminergic activity. Biol Psychiatry 17:135–155
Silverstone PH, Grahame-Smith DG (1992) A review of the relationship between calcium channels and psychiatric disorders. J Psychopharmacol 6:462–482
Stewart J, Vezina P (1991) Extinction procedures abolish conditioned stimulus control but spare sensitized responding to amphetamine. Behav Pharmacol 2:65–71
Vitaliano PP (1982) Parametric statistical analysis of repeated measures experiments. Psychoneuroendocrinology 7:3–13
Weiss SR, Post RM, Pert A, Woodward R, Murman D (1989) Context-dependent cocaine sensitization: differential effect of haloperidol on development versus expression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:655–661
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin-Iverson, M.T., Reimer, A.R. Effects of nimodipine and/or haloperidol on the expression of conditioned locomotion and sensitization to cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 114, 315–320 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244854
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244854