Abstract
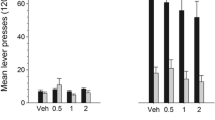
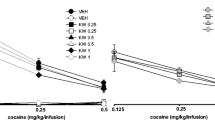
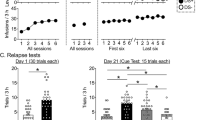
Dopamine (DA) D1 and D2 receptors are involved in mediating the behavioral effects of cocaine, including its discriminative stimulus properties. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the role of the nucleus accumbens and, in particular, accum bens DA D1 receptors in modulating the stimulus effects of cocaine. Thus, rats were trained to discriminate cocaine (10 mg/kg, IP) from saline using a two-lever, water-reinforced FR 20 drug discrimination task. In substitution tests, systemic (IP) administration of cocaine (0.625–20 mg/kg) produced a dose-related increase in cocaine-appropriate responding. Microinjections of cocaine (2.5–40 µg) into the nucleus accumbens also engendered dose-dependent and complete substitutions (> 80% drug-lever responding) for the systemic training dose of cocaine, whereas intra-accumbens artificial cerebrospinal fluid (1 µl/side) produced primarily saline-appropriate responding. In antagonism tests, pretreatment with the DA D1 antagonist SCH 23390 (3–12 µg/kg) completely antagonized (<20% drug-lever responding) a dose of cocaine (5 mg/kg) that produced greater than 90% cocaine-lever responding when given alone. Additionally, intra-accumbens injections of SCH 23390 (0.025–0.4 µg) prior to systemic cocaine (5 mg/kg) also significantly blocked the cocaine stimulus. The present results confirm the importance of the nucleus accumbens in mediating the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine and suggest a primary role of accumbens DA D1 receptors in modulating this behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allin R, Russel V, Lamm M, Taljaard J (1989) Regional distribution of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Brain Res 501:389–391
Bryan SK, Callahan PM, Cunningham KA (1993) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: effects of intra-amygdala microinjection of cocaine, dopamine and the D-1 antagonist SCH 23390. FASEB J Abstr 7: A856
Callahan PM, Cunningham KA (1993) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine in relation to dopamine D2 receptor function in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:585–592
Callahan PM, Appel JB, Cunningham KA (1991) Dopamine D-1 and D-2 mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties ofd-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology 103:50–55
Dworkin SI, Bimle C (1989) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens attenuate the discriminative stimulus effects ofd-amphetamine. Drug Dev Res 16:435–441
Dworkin SI, Smith JE (1988) Neurobehavioral pharmacology of cocaine. In: Clouet D, Ashgar K, Brown R (eds) Mechanisms of cocaine abuse and toxicity. Research Monograph88. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD, pp 185–197
Extance K, Goudie AJ (1981) Inter-animal olfactory cues in operant drug discrimination procedures in rats. Psychopharmacology 73:363–371
Kleven MS, Anthony EW, Woolverton WL (1990) Pharmacological characterization of the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:312–317
Maldonado R, Robledo P, Chover AJ, Caine SB, Koob GF (1993) D1 dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens modulate cocaine self-administration in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:239–242
Nielsen EB, Jepsen SA (1985) Antagonism of the amphetamine cue by both classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 111:167–176
Nielsen EB, Scheel-Kruger J (1986) Cueing effects of amphetamine and LSD: elicitation by direct microinjection of drugs into the nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 125:85–92
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Phillips AG, Broekkamp CL, Fibiger HC (1983) Strategies for studying the neurochemical substrates of drug reinforcement in rodents. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 7:585–590
Reith MEA, Meisler BE, Sershen H, Lajtha A (1986) Structural requirements for cocaine congeners to interact with dopamine and serotonin uptake sites in mouse brain and to induce stereotyped behavior. Biochem Pharmacol 35:1123–1129
Ritchie JM, Greene NM (1985) Local anesthetics. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Rall TW, Murad F (eds) Goodman and Gilman's The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. MacMillan, New York, pp 387–445
Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR, Kuhar MJ (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science 237:1219–1223
Robledo P, Maldonado-Lopez R, Koob GF (1992) Role of dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens in the rewarding properties of cocaine. In: Kalivas PW, Samson HH (eds) The neurobiology of drug and alcohol addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 654:509–512
Ross SB, Renyi AL (1967) Inhibition of the uptake of tritiated catecholamines by antidepressant and related agents. Eur J Pharmacol 2:181–186
Spealman RD, Bergman J, Madras BK, Melia KF (1991) Discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in squirrel monkeys: involvement of dopamine receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:945–953
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1987) Manual of pharmacological calculations with computer programs. Springer, New York.Berlin Heidelberg
Witkin JM, Nichols DE, Terry P, Katz JL (1991) Behavioral effects of selective dopaminergic compounds in rats discriminating cocaine injections. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:706–713
Wood DM, Emmett-Oglesby MW (1989) Mediation in the nucleus accumbens of the discriminative stimulus produced by cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:453–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Callahan, P.M., De La Garza, R. & Cunningham, K.A. Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: modulation by dopamine D1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 115, 110–114 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244759
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244759