Abstract
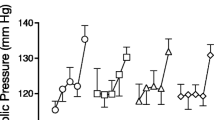
A double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study was conducted to determine the effects of carbamazepine on the acute physiological and subjective responses to a single dose of smoked cocaine-base. Male cocaine users (N=6) were given 400 mg carbamazepine or placebo, each for a period of 5 days. At the end of the 5-day period, a 40 mg dose of smoked cocaine was administered. The results showed a significantly higher heart rate, diastolic blood pressure elevation, and blood pressure-heart rate product under the carbamazepine compared to the placebo condition. There were no effects of carbamazepine on the subjective responses from cocaine. The increase in cardiovascular functions indicates a need to be cautious in the use of carbamazepine in the treatment of cocaine abusers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazett HC (1920) An analysis of the time relations of electrocardiograms. Heart 7:353–370
Beerman B, Edhag O (1978) Depressive effects of carbamazepine on idioventricular rhythm in man. Br Med J 2:171–172
Beerman B, Edhag O, Vallin H (1975) Advanced heart block aggravated by carbamazepine. Br Heart J 37:668–671
Benassi E, Bo GP, Cocito L, Maffini M, Leob C (1987) Carbamazepine and cardiac conduction disturbances. Ann Neurol 22:280–281
Browne KF, Zipes DP, Heger JJ, Prystowsky EN (1982) Influence of the autonomic nervous system on the Q-T interval in man. Am J Cardiol 50:1099–1103
Durelli L, Mutani R, Sechi GP, Monaco F, Glorioso N, Gusmaroli G (1985) Cardiac side effects of phenytoin and carbamazepine. A dose-related phenomenon? Arch Neurol 42:1067–1068
Fischman MW, Schuster CR, Hatano Y (1983) A comparison of the subjective and cardiovascular effects of cocaine and lidocaine in humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:123–127
Halikas J, Kemp K, Kuhn K, Carlson G, Crea F (1989) Carbamazepine for cocaine addiction? Lancet 1:623–624
Hatsukami D, Keenan R, Carroll M, Colon E, Gieske D, Wilson B, Huber M (1990) A method for delivery of precise doses of smoked cocaine-base to humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:1–7
Herzberg L (1978) Carbamazepine and bradycardia. Lancet 1:1097–1098
Jaffe JH, Cascella NG, Kumor KM, Sherer MA (1989) Cocaine-induced cocaine craving. Psychopharmacology 97:59–64
Lecocg B, Jaillon P (1989) Physiologic relation between cardiac cycle and QT duration in healthy volunteers. Am J Cardiol 63:481–486
Leslie PJ, Heyworth R, Prescott LF (1983) Cardiac complications of carbamazepine intoxication: treatment by hemoperfusion. Br Med J 286:1018
Levy RH, Pitlick WH, Troupin AS, Green JR, Neal JM (1975) Pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in normal man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17:657–688
Post RM, Weiss SR (1988) Psychomotor stimulant vs. local anesthetic effects of cocaine: roles of behavioral sensitization and kindling. In: Clouet D, Asghar K, Brown R (eds) Mechanisms of cocaine abuse and toxicity. National Institute on Drug Abuse Monograph #88, US Govt. Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 217–238
Post RM, Weiss SR, Pert A, Uhde TW (1987) Chronic cocaine administration: sensitization and kindling effects. In: Fisher R, Raskin A, Uhlenhuth EH (eds) Cocaine: clinical and biobehavioral aspects. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 109–173
Rall TW, Schleifer LS (1985) Drugs effective in the therapy of the epilepsies. In: Goodman LS, Gilman A, Raul TW, Murad F (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, seventh edition. Macmillan, New York, pp 446–472
Steiner C, Wit AL, Weiss MB, Damato AN (1970) The antiarrhythmic actions of carbamazepine (Tegretol). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 173:323–335
Sullivan JB, Rumack BH, Peterson RG (1981) Acute carbamazepine toxicity resulting from overdose. Neurology 31:621–624
Thompson LK, Yousefnejad D, Kumor K, Shever M, Cone EJ (1987) Confirmation of cocaine in human saliva after intravenous use. J Anal Toxicol 11:36–38
Waldmeier PC, Baumann B, Fehr P, Delteredt P, Maitre L (1984) Carbamazepine decreases catecholamine turnover in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231:166–172
Weaver DF, Camfield P, Fraser A (1988) Massive carbamazepine overdose: clinical and pharmacologic observations in five episodes. Neurology 38:755–759
Wilkerson RD (1988) Cardiovascular effects of cocaine in conscious dogs: importance of fully functional autonomic and central nervous systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:466–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Grant No. DA05844
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatsukami, D., Keenan, R., Halikas, J. et al. Effects of carbamazepine on acute responses to smoked cocaine-base in human cocaine users. Psychopharmacology 104, 120–124 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244565
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244565