Abstract
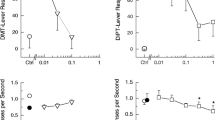
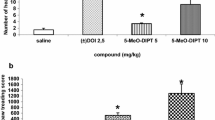
The effects of chronic (10 days) treatment with serotonin (5-HT) receptor agonists on 5-HT1A receptor mediated lower lip retraction (LLR), 5-HT1C receptor mediated penile erections (PE) or 5-HT2 receptor mediated head shakes (HS) were studied in rats. It was found that the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptor mediated behaviour could be attenuated after chronic treatment, whereas 5-HT1C receptor mediated behaviour remained unchanged. The ED50 for the 5-HT1A receptor mediated, 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT)-induced LLR showed an increase from 0.07 mg/kg in placebo pretreated rats to 0.13 in 8-OH-DPAT (1mg/kg/day) pretreated rats. The number of 5-HT2 receptor mediated (±)-1-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) (0.46 and 1 mg/kg)-induced HS was significantly reduced (67% and 50%, respectively) after 10 days' pretreatment with DOI (1 mg/kg/day). In the same animals the number of 5-HT1C receptor mediated PE was increased. Ten days' pretreatment with MK 212 (0.46 mg/kg/day) failed to affect MK 212 (0.22 and 0.46 mg/kg)-induced PE. In addition, the effects of chronic treatment with some antidepressants were studied. The monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor tranylcypromine (4 mg/kg/day) given for 10 days caused an increase in the ED50 for 8-OH-DPAT induced LLR (ED50 values were 0.06 and 0.14 mg/kg, respectively, in placebo — and tranylcypromine — pretreated rats) and attenuated MK 212 (0.22 and 0.46 mg/kg)-induced PE. Chronic treatment with mianserin (10 mg/kg/day), a tetracyclic antidepressant with 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 receptor antagonistic properties, did not change PE induced by MK 212, but caused an increase of PE induced by DOI and a decrease of DOI-induced HS. Ten days' pretreatment with the 5-HT re-uptake inhibitor Org 6997 (5 mg/kg/day) had no effect on MK 212-induced PE. The results demonstrate that 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 but not 5-HT1C receptor mediated behaviour can be attenuated by chronic treatment with agonists for these receptors. The 5-HT1C receptor mediated behaviour remains unchanged in response to chronic agonist treatment. Chronic treatment with antidepressants have differential effect on these behaviours. The possible implication for the mechanism of action of antidepressants is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asberg M, Thoren P, Träskman LH (1976) “Serotonin depression” — a biochemical subgroup within the affective disorders? Science 191:478–480
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1987) Drug-induced penile erections in rats: indications of serotonin-1B receptor mediation. Eur J Pharmacol 135:279–287
Berendsen HHG, Broekkamp CLE (1990) Behavioural evidence for functional interactions between 5-HT-receptor subtypes in rats and mice. Br J Pharmacol 101:667–673
Berendsen HHG, Jenck F, Broekkamp CLE (1989) Selective activation of 5-HT1A-receptors induces lower lip retraction in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:821–827
Berendsen HHG, Jenck F, Broekkamp CLE (1990) Involvement of 5-HT1C-receptors in drug-induced penile erections in rats. Psychopharmacology 101:57–61
Biegon A, Weizman A, Karp L, Ram A, Tiano S, Wolff M (1987) Serotonin 5-HT2-receptor binding on blood platelets — a peripheral marker for depression? Life Sci 41:2485–2492
Biegon A, Essar N, Israeli M, Elizur A, Bruch S, Bar-Nathan AA (1990a) Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor binding on blood platelets as a state dependent marker in major affective disorder. Psychopharmacology 102:73–75
Biegon A, Grinspoon A, Blumenfeld B, Bleich A, Apter A, Mester R (1990b) Increased serotonin 5-HT2-receptor binding on blood platelets of suicidal men. Psychopharmacology 100:165–167
Blackshear A, Sanders-Bush (1982) Serotonin receptor sensitivity after acute and chronic treatment with mianserin. Pharmacol Exp Ther 221:303–308
Blackshear MA, Martin LL, Sanders-Bush E (1986) Adaptive changes in the 5-HT2-binding site after chronic administration of agonists and antagonists. Neuropharacology 25:1267–1271
Buckholtz NS, Freedman DX, Middaugh LD (1985) Daily LSD administration selectively decreases serotonin2 receptor binding in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 109:421–425
Buckholtz NS, Zhou D, Freedman DX (1988) Serotonin2 agonist administration down-regulates rat brain serotonin2 receptors. Life Sci 42:2439–2445
Darmani NA, Martin BR, Glennon RA (1990) Withdrawal from chronic treatment with (±)-DOI causes super-sensitivity to 5-HT2 receptor-induced head-twitch behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 186:115–118
Dijcks FA, Ruigt GSF, De Graaf JS (1991) Antidepressants affect the amine modulation of neurotransmission in the rat hippocampal slice II: acute effects. Neuropharmacology (in press)
Dourish CJ, Hutson PH, Curzon G (1985a) Low doses of the putative serotonin agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) elicit feeding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 86:197–204
Dourish CJ, Hutson PH, Curzon G (1985b) Characteristics of feeding induced by the serotonin agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT). Brain Res Bull 15:377–384
Glassman AH, Kantor SJ, Shostak M (1975) Depression, delusions and drug response. Am J Psychiatry 132:716–719
Goodwin GM, Green AR (1985) A behavioural and biochemical study in mice and rats of putative agonists and antagonists for 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 84:743–753
Goodwin GM, Green AR, Johnson P (1984) 5-HT2 receptor characteristics in frontal cortex and 5-HT2 receptor mediated head-twitch behaviour following antidepressant treatment to mice. Br J Pharmacol 83:235–242
Goodwin GM, De Souza RJ, Green AR (1985) The pharmacology of the hypothermic response in mice to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT). Neuropharmacology 24:1187–1194
Green AR, Johnson P, Nimgaonkar VL (1983) Increased 5-HT2 receptor number in brain as a probable explanation for the enhanced 5-hydroxytryptamine-mediated behaviour following repeated electroconvulsive shock administration to rats. Br J Pharmacol 80:173–177
Gudelski GA, Koenig JI, Meltzer HY (1986) Thermoregulatory responses to serotonin (5-HT) receptor stimulation in the rat: evidence for opposing roles of 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology 25:1307–1313
Hoyer D (1988a) Molecular pharmacology and biology of 5-HT1C receptors. TIPS 9:89–93
Hoyer D (1988b) Functional correlates of serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites. J Recept Res 8:59–81
Kellar KJ, Cascio CS, Butler JA, Kurtzke RN (1981) Differential effects of electroconvulsive shock and antidepressant drugs on serotonin-2 receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 69:515–518
Liebowitz MR, Quitking FM, Stewart JW, Grath PJ, Harrison WM, Markowitz JS, Rabkin JG, Tricamo E, Goetz DM, Klein DF (1988) Antidepressant specificity in atypical depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:129–137
Lucki I, Frazer A (1982) Prevention of the serotonin syndrome in rats by repeated administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors but not tricyclic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology 77:205–211
Mann JJ, Arango V, Marzuk PM, Theccanat S, Reis DJ (1989). Evidence for the 5-HT hypothesis of suicide: a review of postmortem studies. Br J Psychiatry 155 [suppl 8]:7–14
May PC, Morgan DG, Finch CE (1986) Regional serotonin receptor studies: chronic methysergide treatment induces a selective and dose-dependent decrease in serotonin-2 receptors in mouse cerebral cortex. Life Sci 38:1741–1747
McKenna DJ, Nazarati AJ, Himeno A, Saavedra JH (1989) Chronic treatment with (±) DOI, a psychotomimetic 5-HT2 agonist, downregulates 5-HT2 receptors in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:81–87
Meltzer HY (1990) Role of serotonin in depression. In: Whitaker — Azmitia PM, Peroutka SJ (eds) Neuropharmacology of serotonin. Ann NY Acad Sci 600:486–500
Pericic D, Manev H (1988) Behavioural evidence for simultaneous dual changes of 5-HT-receptor subtypes: mode of antidepressant action? Life Sci 42:2593–2601
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1980) Long-term antidepressant treatment decreases spiroperidol-labeled serotonin receptor binding. Science 210:88–90
Peroutka SJ, Lebovitz RM, Snyder SH (1981) Two distinct central serotonin receptors with different physiological functions. Science 212:827–829
Quitkin F, Rifkin A, Klein DF (1976) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors. A review of antidepressant effectiveness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 36:749–760
Scott JA, Crews FT (1986) Down-regulation of serotonin2, but not of Beta-adrenergic receptors during chronic treatment with amitriptyline is independent of stimulation of serotonin2 and beta-adrenergic receptors. Neuropharmacology 25:1301–1306
Siever LJ, Murphy DL, Slater S, De la Vega E, Lipper S (1984) Plasma prolactin changes following fenfluramine in depressed patients compared to controls: an evaluation of central serotonergic responsivity in depression. Life Sci 34:1092–1039
Spiker DG, Weiss JC, Dealy RS, Griffin SJ, Hanin I, Neil JF, Perel JM, Rossi AJ, Soloff PH (1985) The pharmacological treatment of delusional depression. Am J Psychiatry 142:430–436
Stanley MM, Mann JJ (1983) Increased serotonin-2 binding sites in frontal cortex of suicide victims. Lancet i:214–216
Tricklebank MD, Forler C, Fozard JR (1984) The involvement of subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor and of catecholamine systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 106:271–282
Van Praag HM (1982a) Neurotransmitters and CNS disease. Depression. Lancet IV:1259–1264
Van Praag HM (1982b) Depression, suicide and the metabolism of serotonin in the brain. J Affect Dis 4:275–290
Wozniak KM, Aulakh CS, Hill JL, Murphy DL (1988) The effect of 8-OH-DPAT on temperature in the rat and its modification by chronic antidepressant treatments. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:451–456
Yap CY, Taylor DA (1983) Involvement of 5-HT2 receptors in the wet dog shake behaviour induced by 5-hydroxy-tryptophan in the rat. Neuropharmacology 22:801–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berendsen, H.H.G., Broekkamp, C.L.E. Attenuation of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 but not 5-HT1C receptor mediated behaviour in rats following chronic treatment with 5-HT receptor agonists, antagonists or antidepressants. Psychopharmacology 105, 219–224 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244313
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244313