Summary
For a study of the effect of motility on the propulsion and absorption of the luminal contents in a 25-cm. segment of human jejunum, a method was devised that allowed simultaneous recording of intraluminal pressure changes, determination of transit time by indicator-dilution technics, and assessment of the absorption of glucose and xylose under basal conditions.
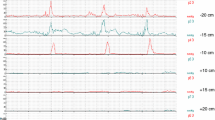
The motility of the segment of jejunum under study influenced the speed of propulsion of the intraluminal contents. The motility and the transit time were not influenced by the presence of a constant infusion of an isotonic solution at 37° C and a rate of 10 ml./min. Increased motility per minute resulted in shorter transit times.
More physiologically significant than the quantitative values were the patterns of motility. The caudad propagation of waves and the extent of the propagation—regardless of wave type—produced shortening of the transit time. The shortest transit times were obtained in experiments during which caudad propagation of motility involved the entire segment under study. Glucose was almost completely absorbed by the time it reached the sampling point. A significant correlation was observed between the values of xylose absorption and transit time, suggesting that longer exposure to the intestinal mucosa increases xylose absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pfungen, V. Versuche über die Bewengungen des Antrum pylorikum beim Menschem.Centralbl Physiol 1:220, 1887.
Pfungen, V., andUllman, L. Ueber die Bewegungen des Antrum pylori beim Menschem.Centralbl Physiol 1:275, 1887.
Posey, L. E., Jr., Dearing, W. H., Saver, W. G., Bargen, A. J., andCode, C. F. The recording of intestinal motility.Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin 23:297, 1948.
Code, C. F., Hightower, N. C., Jr., andMorlock, C. G. Motility of the alimentary canal in man. Review of Recent Studies.Amer J Med 13:328, 1952.
Fink, S. The intraluminal pressures in the intact human intestine.Gastroenterology 36:661, 1959.
Connell, A. M. The motility of the small intestine.Postgrad Med 37:703, 1961.
Edwards, D. A. W. Techniques and interpretations of measurement of gastrointestinal pressures.Ann Roy Coll Surg 37:275, 1965.
Templeton, R. D., andLawson, H. Studies in the motor activity of the large intestine. I. Normal motility in the dog, recorded by the tandem balloon method.Amer J Physiol 96:667, 1931.
Posey, L. E., Jr., andBargen, J. A. Observations of normal and abnormal human intestinal motor function.Amer J Med Sci 10:221, 1951.
Adler, H. F., Atkinson, A. J., andIvy, A. C. A study of the motility of the human colon: An explanation of dysynergia of the colon, or of the “unstable colon.”Amer J Dig Dis 8:197, 1941.
Atkinson, A. J., Adler, H. F., andIvy, A. C. Motility of the human colon. The normal pattern, dyskinesia and the effect of drugs.JAMA 121:646, 1943.
Friedman, G., Wayne, J. D., Weingarten, L. A., andJanowitz, H. D. The patterns of simultaneous intraluminal pressure changes in the human proximal small intestine.Gastroenterology 47:258, 1964.
Beck, I. T., McKenna, R. D., Peterfy, G., Siderov, J., andStrawczynski, H. Pressure studies in the normal human jejunum.Amer J Dig Dis 10:436, 1965.
Barreiro, M. A., McKenna, R. D., andBeck, I. T. A simple device for timed sampling in physiological studies of human small bowelin vivo.Gastroint Endosc 13:28, 1967.
Barreiro, M. A., McKenna, R. D., andBeck, I. T. Determination of transit time in the human jejunum by the single-injection indicator-dilution technique.Amer J Dig Dis 13:222, 1968.
Hydén, S. A turbidimetric method for the determination of higher polyethylene glycols in biological materials.Ann Agric Coll (Sweden)22:139, 1955.
Roe, J. H., andRice, E. W. Photometric method for determination of free pentoses in animal tissues.J Biol Chem 173:507, 1948.
Wood, E. H., andSwan, H. J. C. Definition of terms and symbols for the description of circulatory indicator-dilution curves.J Appl Physiol 6:797, 1954.
Jacobson, E. D., Bondy, D. C., Broitman, S. A., andFordtran, J. S. Validity of polyethylene glycol in estimating intestinal water volume.Gastroenterology 44:761, 1963.
Cantor, M. O. Intestinal Intubation. Thomas, Springfield, Ill., 1949, p. 116.
Hirsch, J., Ahrens, E. H., Jr., andBlakehorn, D. H. Measurement of the human intestinal lengthin vivo and some causes of variation.Gastroenterology 31:274, 1956.
Fordtran, J. S. Marker perfusion techniques for measuring intestinal absorption in man.Gastroenterology 51:1089, 1966.
Borgstrom, B., Dahlqvist, A., Lundh, G., andSjovall, J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human.J Clin Invest 36:1521, 1957.
Fordtran, J. S., Soergel, K. H., andIngelfinger, F. J. Intestinal absorption of D-xylose in man.New Engl J Med 267:274, 1962.
Barreiro, M. A. McGill University thesis, 1966, p. 116 (a).
Higgins, J. A., Code, C. F., andOruis, A. L. The influence of motility on the rate of absorption of sodium and water from the small intestine of healthy persons.Gastroenterology 31:708, 1956.
Cummins, A. J., andAlmy, T. P. Studies on the relationship betwen motility and absorption in the human small intestine.Gastroenterology 23:179, 1953.
Ingelfinger, F. J., Moss, R. E., andHeim, J. D., Jr. The effect of atropine upon the absorption of Vitamin A.J Clin Invest 22:699, 1943.
Alvarez, W. C., andFreedlander. B. L. The rate of progress of food residues through the bowel.JAMA 83:576, 1924.
Mulinos, M. G. The value of selective drugs in the treatment of constipation.Rev Gastroenterol 2:292, 1935.
Hansky, J., andConnell, A. M. Measurement of gastrointestinal transit using radioactive chromium.Gut 3:187, 1962.
Farrar, J. T., andBernstein, J. S. Recording of intraluminal gastrointestinal pressures by a radiotelemetering capsule.Gastroenterology 35:603, 1958.
Dillard, R. L., Eastman, H., andFordtran, J. S. Volume-flow relationship during the transport of fluid through the human small intestine.Gastroenterology 49:58, 1965.
Chapman, W. P., andPelazzo, W. L. Multiple balloon kymograph recording of intestinal motility in man with observations on the correlation of the tracing patterns with barium movements.J Clin Invest 28:1517, 1949.
Ramorino, M. L., andColagrande, C. Intestinal motility. Preliminary studies with telemetering capsules and synchronized fluorocinematography.Amer J Dig Dis 9:64, 1964.
Abbott, W. O., andPendergrass, E. P. Intubation studies of the human small intestine. V. The motor effects of single clinical doses of morphine sulphate in normal subjects.Amer J Roentgen Rad Ther 35:289, 1936.
Connell, A. M., McCall, J., Misiewicz, J. J., andRowlands, E. N. Observations on the clinical use of radio pills.Brit Med J 2:771, 1963.
Deller, D. J., andWangel, A. G. Intestinal motility in man. I. A study combining the use of intraluminal pressure recording and cineradiography.Gastroenterology 48:45, 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Grant MA-1890 from the Medical Research Council of Canada, and by the Donner Canadian Foundation.
The authors thank Dr. M. Stephens, Department of Mathematics, McGill University, for his contribution in the development of the methods, and Miss D. Dannacker for her technical assistance.
The work reported here formed part of the M.Sc. thesis of M. A. Barreiro (McGill University, 1966).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barreiro, M.A., McKenna, R.D. & Beck, I.T. The physiologic significance of intraluminal pressure changes in relation to propulsion and absorption in the human jejunum. Digest Dis Sci 13, 234–251 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02236598
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02236598