Abstract
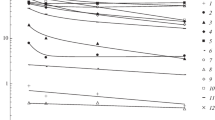
The contents of oxyanionic elements (V, Se and Mo) and cationic transition metals (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) in sediments from near-shore to deep-sea environments were measured to clarify factors regulating the distribution of these elements in marine sediments. For cationic transition metals of which contents increase from near-shore to deep-sea environments, the chemical composition of pelagic clays is modeled by a mixture of aluminosilicates having the chemical composition of average shale and Fe−Mn oxides having the chemical composition of associated manganese nodules. The content of V is fairly constant in sediments from near-shore to deep-sea areas. The mixture model of average shale and manganese nodules holds also for V, although most of the V is located in the aluminosilicate lattices. The content of Se in the near-shore sediments is higher and that in the deep-sea sediments is lower than that in average shale. The high content in the near-shore sediments is interpreted as the addition of biogenic materials to aluminosilicates with average shale composition and the low content in deep-sea sediments is explained by oxidative release of Se from aluminosilicates. The content of Mo in sediments increases from near-shore to deep-sea environments. The general distribution of Mo in marine sediments is expressed by the mixture model. An anomalously high content of Mo in a near-shore sediment is attributed to adsorption of molybdate on manganese oxides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addy, S. K. (1979): Rare earth element patterns in manganese nodules and micronodules from northwest Atlantic.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,43, 1105–1115.
Aplin, A. C. and D. S. Cronan (1985): Ferromanganese oxide deposits from the Central Pacific Ocean, II. Nodules and associated sediments.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,49, 437–451.
Balistrieri, L. S. and T. T. Chao (1987): Selenium adsorption by goethite.Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 1145–1151.
Bar-Yosef, B. and D. Meek (1987): Selenium sorption by kaolinite and montmorillonite.Soil. Sci. 144, 11–19.
Baturin, G. N. (1988):The Geochemistry of Manganese and Manganese Nodules in the Ocean. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, Boston, Lancaster and Tokyo, 342 pp.
Baturin, G. N., T. F. Boyko, I. V. Kislova and I. I. Nazarenko (1986): Selenium in oceanic phosphates.Oceanology,26, 577–580.
Belzile, N. and J. Lebel (1988): Selenium profiles in the sediments of the Laurentian Trough (northwest North Atlantic).Chem. Geol.,68, 99–103.
Berrag, P. G. and E. V. Grill (1974): The effect of manganese oxide scavenging on molybdenum in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia.Mar. Chem.,2, 125–148.
Bertine, K. K. and K. K. Turekian (1973): Molybdenum in marine deposits.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,37, 1415–1434.
Brewer, P. G., Y. Nozaki, D. W. Spencer and A. P. Fleer (1980): Sediment trap experiments in the deep North Atlantic: isotopic and elemental fluxes.J. Mar. Res.,38, 703–728.
Brongersma-Sanders, M., K. M. Stephan, T. G. Kwee and M. De Bruin (1980): Distribution of minor elements in cores from the Southwest Africa shelf with notes on plankton and fish mortality.Mar. Geol.,37, 91–132.
Calvert, S. E. and N. B. Price (1977): Geochemical variation in ferromanganese nodules and associated sediments from the Pacific Ocean.Mar. Chem.,5, 43–74.
Calvert, S. E. and N. B. Price (1983): Geochemistry of Namibian shelf sediments. p. 337–376. InCoastal Upwelling ed. by E. Suess and J. Thiede, Plenum Press, New York and London.
Calvert, S. E., N. B. Price, G. R. Heath and T. C. Moore, Jr. (1978): Relationship between ferromanganese nodule compositions and seidmentation in a small survey area of the equatorial Pacific.J. Mar. Res. 36, 161–183.
Chau, Y. K. and J. P. Riley (1965): The determination of selenium in sea water, silicates and marine organisms.Anal. Chem. Acta,33, 36–49.
Chester, R. and M. J. Hughes (1969): The trace element geochemistry of a North Pacific pelagic clay core.Deep-Sea Res.,16, 639–654.
Chester, R. and R. G. Messiha-Hanna (1970): Trace element partition patterns in North Atlantic deep-sea sediments.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,34, 1121–1128.
Corliss, J. B., M. Lyle, J. Dymond and K. Crane (1978): The chemistry of hydrothermal mounds near the Galapagos Rift.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,40, 12–24.
Cowen, J. P. and K. W. Bruland (1985): Metal deposits associated with bacteria: implications for Fe and Mn marine biogeochemistry.Deep-Sea Res.,32, 253–272.
Cowen, J. P. and Y. H. Li (1991): The influence of a changing bacterial community on trace metal scavenging in a deep-sea particle plume.J. Mar. Res.,49, 517–542.
Cowen, J.P. and M. W. Silver (1984): The association of iron and manganese with bacteria on marine macroparticulate material.Science,224, 1340–1342.
Cronan, D. S. (1980):Underwater Minerals. Academic Press, London, 362 pp.
Cutter, G. A. (1985): Determination of selenium speciation in biogenic particles and sediments.Anal. Chem.,57, 2951–2955.
Cutter, G. A. and K. W. Bruland (1984): The marine biogeochemistry of selenium: A re-evaluation.Limnol. Oceanogr.,29, 1179–1192.
Delany, A. C., Audrey Claire Delany, D. W. Parkin, J. J. Griffin, E. D. Goldberg and B. E. F. Reimann (1967): Airborne dust collected at Barbados.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,31, 885–909.
Edmond, J. M., C. Measures, B. Mangum, B. Grant, F. R. Sclater, R. Collier, A. Hudson, L. I. Gordon and J. B. Corliss (1979): On the formation of metal-rich deposits at ridge crests.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,46, 19–30.
Elderfield, H. (1972): Compositional variations of the manganese oxide component of marine sediments.Nature,237, 110–112.
Emerson, S., S. Kalhorn, L. Jacobs, B. M. Tebo, K. H. Nealson and R. A. Rosson (1982): Environmental oxidation rate of manganese (II): bacterial catalysis.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 46, 1073–1079.
Fowler, S. W. and G. A. Knauer (1986): Role of large particles in the transport of elements and organic components through the oceanic water column.Prog. Oceanogr.,16, 147–194.
Froerich, P. N., G. P. Klinkhammer, M. L. Bender, N. A. Luedtke, G. R. Heath, D. Cullen, P. Dauphin, D. Hammond, B. Hartman and V. Maynard (1979): Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,43, 1075–1090.
Glasby, G. P., R. Gwozdz, H. Kunzendorf, G. Friedrich and T. Thijssen (1987): The distribution of rare earth and minor elements in manganese nodules and sediments from the equatorial and S. W. Pacific.Lithos,20, 97–113.
Govindaraju, K. (1989): 1989 compilation of working values and sample description for 272 geostandards.Geostandards Newsl.,13, Special Issue, 1–113.
Graybeal, A. L. and G. R. Heath (1984): Remobilization of transition metals in surficial pelagic sediments from the eastern Pacific.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,48, 965–975.
Grill, E. V., R. L. Chase, R. D. Macdonald and J. W. Murray (1981): A hydrothermal deposit from Explorer Ridge in the northeast Pacific Ocean.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,52, 142–150.
Heggie, D., G. Klinkhammer and D. Cullen (1987): Manganese and copper fluxes from continental margin sediments.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,51, 1059–1070.
Jacobs, L., E. Emerson and S. S. Huested (1987): Trace metal geochemistry in the Cariaco Trench.Deep-Sea Res.,34, 965–981.
Jones, C. J. and J. W. Murray (1985): The geochemistry of manganese in the northeast Pacific Ocean off Washington.Limnol. Oceanogr.,30, 81–92.
Kato, Y. (1988): Early diagenesis of continental slope sediments. p. 165–179. InOcean Science for the Subtropical Region of the Western North Pacific: Proc. The 10th Seminar on Science and Technology Dec. 6–10, 1988, Interchange Association Japan.
Klinkhammer, G., D. T. Heggie and D. W. Graham (1982): Metal diagenesis in oxic marine sediments.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,61, 211–219.
Kunzendorf, H., R. Gwozdz, G. P. Glasby, P. Stoffers and R. M. Renner (1989): The distribution of rare earth elements in manganese micronodules and sediments from the equatorial and southwest Pacific.Appl. Geochem.,4, 183–193.
Kuroda, P. K. and E. B. Sandell (1954): Geochemistry of molybdenum.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,6, 35–63.
Li, Y.-H. (1981): Geochemical cycles of elements and human perturbation.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,45, 2073–2084.
Martin, J. H. and G. A. Knauer (1973): The elemental composition of plankton.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,37, 1639–1653.
Martin, J. H. and G. A. Knauer (1984): VERTEX: manganese transport through oxygen minima.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,67, 35–47.
Martin, J. H., G. A. Knauer and W. W. Broenkow (1985): VERTEX: the lateral transport of manganese in the northeast Pacific.Deep-Sea Res.,32, 1405–1427.
Martin, J.-M. and M. Whitfield (1983): The significance of the river input of chemical elements to the ocean. p. 265–296. InTrace Metals in Sea Water, ed. by C. S. Wong, E. Boyle, K. W. Bruland, J. D. Burton and E. D. Goldberg, Plenum Press, New York and London.
Mason, B. and C. B. Moore (1982):Principles of Geochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 344 pp.
Masuzawa, T., S. Noriki, T. Kurosaki, S. Tsunogai and M. Koyama (1989): Compositional change of settling particles with water depth in the Japan Sea.Mar. Chem.,27, 61–78.
Matsumoto, E. and Y. Kinoshita (1977): Sedimentation of polluted bottom sediments, 2. The bottom sediments in Suruga Bay. p. 35–76. InEnvironmental Research in Japan, Vol. II, Environment Agency, Japan (in Japanese with English abstract).
Minai, Y., R. Matsumoto and T. Tominaga (1985): Geochemistry of deep sea sediments from the Nankai Trough, the Japan Sea Trench, and adjacent regions.Int. Repts. DSDP,87, 643–657.
Mita, N. and S. Nakao (1984): Minor chemical composition of deep-sea sediments from the GH80-5 area in the Central Pacific Basin. p. 215–226. InMarine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules in the Northern Vicinity of the Magellan Trough August-October 1980 (GH80-5 Cruise). Cruise Report No. 20, ed. by S. Nakao and T. Moritani, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Mita, N. and S. Nakao (1986): Minor chemical composition of deep-sea sediments from the GH81-4 area in the Central Pacific Basin. p. 209–218. InMarine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules around Deep-Sea Hills in the Central Pacific Basin August–October 1981 (GH81-4 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 21 ed. by S. Nakao, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Mita, N., S. Nakao and K. Kato (1982): Minor chemical composition of bottom sediments from the Central Pacific Wake-Tahiti Transect. p. 313–337. InRegional Data of Marine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules: the Wake-Tahiti Transect in the Central Pacific January–March 1980 (GH80-1 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 18, ed. by A. Mizuno and S. Nakao, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Mizuno, A., S. Nakao, M. Joshima, O. Matsubayashi, Y. Okuda, K. Onodera, T. Saito, K. Tsurusaki and A. Usui (1982): The GH80-1 cruise: general remarks. p. 1–35. InRegional Data of Marine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules: the Wake-Tahiti Transect in the Central Pacific January–March 1980 (GH80-1 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 18 ed. by A. Mizuno and S. Nakao, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Moorby, S. A., D. S. Cronan and G. P. Glasby (1984): Geochemistry of hydrothermal Mn-oxide deposits from the S.W. Pacific island arc.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,48, 433–441.
Noriki, S. and S. Tsunogai (1986): Particulate fluxes and major components of settling particles from sediment trap experiments in the Pacific Ocean.Deep-Sea Res.,33, 903–912.
Piper, D. Z. (1988): The metal oxide fraction of pelagic sediment in the equatorial North Pacific Ocean: A source of metals in ferromanganese nodules.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,52, 2127–2145.
Piper, D. Z., K. Leong and W. F. Cannon (1979): Manganese nodule and surface sediment compositions: DOMES Sites A, B, and C. p. 437–473. InMarine Geology and Oceanography of the Pacific Manganese Nodule Province, ed. by J. L. Bischoff and D. Z. Piper, Plenum Press, New York and London.
Priyadarshini, U. and S. G. Tandon (1961): Spectrophotometric determination of vanadium (V) with N-Benzoyl-N-phenylhydroxylamine.Anal. Chem.,33, 435–438.
Quinby-Hunt, M. S. and K. K. Turekian (1983): Distribution of elements in seawater.EOS, Trans. Am. Geophys. Union,64, 130–131.
Sato, Y. (1989): The rate of oxidation of ferrous iron in seawater and the partition of elements between iron oxides and seawater.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,45, 270–278.
Sato, Y. (1990): Studies on the behavior of elements accompanied with the formation of manganese and iron oxides. Doctor Thesis, Tokai University, 162 pp. (in Japanese).
Sawlan, J. J. and J. W. Murray (1983): Trace metal remobilization in the interstitial waters of red clay and hemipelagic marine sediments.Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.,64, 213–230.
Shaw, T. J., J. M. Gieskes and R. A. Jahnke (1990): Early diagenesis in differing depositional environments: The response of transition metals in pore water.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,54, 1233–1246.
Stoffers, P., G. P. Glasby, T. Thijssen, P. C. Shrivastava and M. Melguen (1981): The geochemistry of coexisting manganese nodules, micronodules, sediments and pore waters from five areas in the equatorial and S.W. Pacific.Chem. Erde,40, 273–297.
Stoffers, P., G. P. Glasby and G. Frenzel (1984): Comparison of the characteristics of manganese micronodules from the equatorial and south-west Pacific.TMPM Tschermaks Min. Petr. Mitt.,33, 1–23.
Sugawara, K., M. Tanaka and S. Okabe (1959): Separation and determination of microgram quantities of molybdenum in natural waters.Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan,32, 221–222.
Sugawara, K., S. Okabe and M. Tanaka (1961): Geochemistry of molybdenum in natural waters (II).J. Earth Sci. Nagoya Univ.,9, 114–128.
Sugisaki, R., M. Ohashi, K. Sugitani and K. Suzuki (1987): Compositional variations in manganese micronodules: A possible indicator of sedimentary environmentsJ. Geol.,95, 433–454.
Takematsu, N. (1978): The chemical forms of transition elements in marine sediments.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,34, 242–249.
Takematsu, N. (1979): Sorption of transition metals on manganese and iron oxides, and silicate minerals.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,35, 36–45.
Takematsu, N. (1981): Enrichment of transition metals in deep-sea sediments relative to near-shore sediments.La mer,19, 125–131.
Takematsu, N. (1987): Ultimate removal of trace elements from seawater and adsorption.J. Earth Sci. Nagoya Univ.,35, 227–248.
Takematsu, N., Y. Sato, S. Okabe and E. Nakayama (1985): The partition of vanadium and molybdenum between manganese oxides and sea water.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta,49, 2395–2399.
Takematsu, N., Y. Sato and S. Okabe (1989): Factors controlling the chemical composition of marine manganese nodules and crusts: a review and synthesis,26, 41–56.
Takematsu, N., Y. Sato, S. Okabe and A. Usui (1990): Uptake of selenium and other oxyanionic elements in marine ferromanganese concretions of different origins.Mar. Chem.,31, 271–283.
Tamari, Y. (1978): Studies on the state analysis of selenium in sediments. Doctor Thesis, Kinki University, 51 pp.
Tamari, Y. (1984): Fluorimetric determination of nano gram amounts of selenium in rocks.Bunseki Kagaku,33, E115-E122.
Tamari, Y., K. Hiraki and Y. Nishikawa (1979): Fluorimetric determination of selenium in sediments with 2,3-diaminonaphthalene.Bunseki Kagaku,28, 164–169 (in Japanese with English summary).
Tsunogai, S. (1987): “Train-passengers model” as an oceanic removal mechanism of chemical elements in seawater.Chikyu Kagaku (Geochemistry),21, 75–82 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Tsunogai, S., T. Suzuki, T. Kurata and M. Uematsu (1985): Seasonal and areal variation of continental aerosol in the surface air over the western North Pacific region.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,41, 427–434.
Turekian, K. K. (1967): Estimates of the average Pacific deep-sea clay accumulation rate from material balance calculations. p. 227–244. InProgress in Oceanography, Vol. 4, ed. by M. Sears, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Turekian, K. K. and K. H. Wedepohl (1961): Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth' crust.Geol. Soc. Am. Bull.,72, 175–192.
Uchio, T. (1979): Studies of deep-sea manganese nodules (Part 3): Quantitative distributions of manganese micronodules and metal contents of the pelagic sediments in the north eastern tropical Pacific south of the Hawaian Islands.J. Fac. Eng., Univ. Tokyo (B),35, 71–108.
Uematsu, M. (1987): Study of continental material transported through the atmosphere to the ocean—Lecture by the member awarded the Okada Prize for 1987.J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,43, 395–401 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Usui, A. (1983): Regional variation of manganese nodule facies on the Wake-Tahiti Transect: morphological, chemical and mineralogical study.Mar. Geol.,54, 27–51.
Usui, A. and T. Mochizuki (1984) Local variability of manganese nodule chemistry and its relationship to mineralogy in the GH80-5 area. p. 242–262. InMarine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules in the Northern Vicinity of the Magellan Trough August–October 1980 (GH80-5 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 20, ed. by S. Nakao and T. Moritani, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Usui, A. and S. Terashima (1986): Local variability of manganese nodule chemistry around the small abyssal hills in the GH81-4 area. p. 231–249. InMarine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules around Deep-Sea Hills in the Central Pacific Basin August–October 1981 (GH81-4 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 21 ed. by S. Nakao, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Wedepohl, K. H. (1960): Spurenanalytische Untersuchungen an Tiefseetonen aus dem Atlantik. Ein Beitrag zur Deutung der geochemischen Sonderstellung von pelagischen Tonen.Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 18, 200–231.
Wedepohl, K. H. (1969): Die Zusammensetzung der Erdkruste.Fortschr. Miner.,46, 145–174.
Yamamoto, K. and R. Sugisaki (1986): Geochemical characteristics of deep-sea sediments around 3°N, 169°W, the Pacific Ocean: samples for GH81-4 cruise, Geological Survey of Japan. p. 195–208. InMarine Geology, Geophysics, and Manganese Nodules around Deep-Sea Hills in the Central Pacific Basin August–October 1981 (GH81-4 Cruise), Cruise Report No. 21 ed. by S. Nakao, Geological Survey of Japan, Tsukuba-shi.
Yamamoto, T. (1983):Distribution of Trace Element in Marine Algae. Kyoto University of Education, Kyoto, 499 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takematsu, N., Sato, Y., Kato, Y. et al. Factors regulating the distribution of elements in marine sediments predicted by a simulation model. J Oceanogr 49, 425–441 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02234958
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02234958