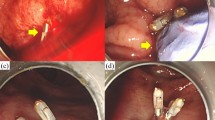
Abstract
Dieulafoy's lesion is an uncommon cause of gastrointestinal bleeding that occurs after rupture of an exposed submucosal artery. The vast majority of lesions are found in the stomach, but cases have been described in the esophagus, small intestine, colon, and rectum. We describe an elderly patient who presented with severe lower gastrointestinal bleeding caused by a rectal Dieulafoy's lesion. This is the first report of a rectal Dieulafoy's lesion treated successfully with endoscopic epinephrine injection followed by thermocoagulation. We review the physiopathology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallard T. Aneurysmes miliaires de l'estomac, donnant lieu à des hématémèses mortelles. Bull Soc Med Hop Paris 1884;1:84–91.
Dieulafoy G. Exulceratio simplex. L'intervention chirurgicale dans les hématémèses foudroyantes consecutives a l'exulceration simple de l'estomac. Bull Acad Natl Med 1898;39:49–84.
Fockens P, Tytgat GN. Dieulafoy's disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1996;6:739–52.
Donaldson GA, Hamlin E. Massive hematemesis resulting from rupture of a gastric artery aneurysm. N Engl J Med 1950;243:369–73.
Juler GL, Labitzke HG, Lamb R, Allen R. The pathogenesis of Dieulafoy's gastric erosion. Am J Gastroenterol 1984;79:195–200.
Goldman RL. Submucosal arterial malformation (“aneurysm”) of the stomach with fatal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology 1964;46:589–94.
Barbier P, Luder P, Triller J, Ruchti C, Hassler H, Stafford A. Colonic hemorrhage from a solitary minute ulcer. Report of three cases. Gastroenterology 1985;88:1065–8.
Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Bartelsman JF, Schipper ME, Tytgat GN, Recurrent massive hematemesis from Dieulafoy vascular malformations—a review of 101 cases. Gut 1986;27:213–22.
Reilly HF, Al-Kawas FH. Dieulafoy's lesion: diagnosis and management. Dig Dis Sci 1991;36:1702–7.
Richards WO, Grove-Mahoney D, Williams LF. Hemorrhage from a Dieulafoy type ulcer of the colon: a new cause of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Am Surg 1998;54:121–4.
Baettig B, Haecki W, Lammer F, Jost R. Dieulafoy's disease: endoscopic treatment and follow up. Gut 1993;34:1418–21.
Pointner R, Schwab G, Königsrainer A, Dietze O. Endoscopic treatment of Dieulafoy's disease. Gastroenterology 1988;94:563–6.
Franko E, Chardavoyne R, Wise L. Massive rectal bleeding from a Dieulafoy's type ulcer of the rectum: a review of this unusual disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1991;86:1545–7.
Abdulian JD, Santoro MJ, Chen YK, Collen MJ. Dieulafoy's-like lesion of the rectum presenting with exsanguinating hemorrhage: successful endoscopic sclerotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol 1993;88:1939–41.
Tooson JD, Marsano LS, Gates LK. Pediatric rectal Dieulafoy's lesion. Am J Gastroenterol 1995;90:2232–3.
Yeoh KG, Kang JY. Dieulafoy's lesion in the rectum. Gastrointest Endosc 1996;43:614–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Amaro, R., Petruff, C.A. & Rogers, A.I. Rectal Dieulafoy's lesion. Dis Colon Rectum 42, 1339–1341 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02234226
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02234226