Abstract
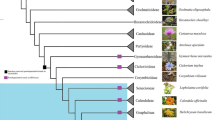
The deletion of an approximately 700-bp intron in the chloroplast-encoded generpoC1 was shown in 21 representative species of the subfamily Cactoideae of the angiosperm family Cactaceae. Members of the subfamilies Pereskioideae and Opuntioideae were found to possess the intron, as did members of the related families Aizoaceae, Basellaceae, Didiereaceae, Phytolaccaceae, and Portulacaceae. These results support a monophyletic origin for the most-speciose subfamily of the cactus family, and represent a first report of the loss of this intron in dicots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthlott W, Hunt DR (1993) Cactaceae. In: Kubitski K (ed) The families and genera of vascular plants vol. II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 161–197
Bruneau A, Doyle JJ, Palmer JD (1990) A chloroplast DNA inversion as a subtribal character in the Phaseoleae (Legunimosae). Systematic Bot 15:378–386
Buxbaum F (1958) The phylogenetic division of the subfamily Cereoideae, Cactaceae. Madroño 14:177–216
Cronquist, A (1981) An integrated system of classification of flowering plants. Columbia, New York
Cummings MP, King LM, Kellogg EA (1994) Slipped-strand mispairing in a plastid gene:rpoC2 in grasses (Poaceae). Mol Biol Evol 11:1–8
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh tissue. Phytochem Bull 19: 11–15
Doyle JJ, Davis JI, Soreng RJ, Garvin D, Anderson MJ (1992) Chloroplast DNA inversions and the origin of the grass family (Poaceae). Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 89: 7722–7726
Downie SR, Palmer JD (1992) Use of chloroplast DNA rearrangements in reconstructing plant phylogeny. In: Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Doyle JJ (eds) Molecular systematics of plants. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 14–35
Downie SR, Olmstead RG, Zurawski G, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Watson JC, Palmer JD (1991) Six independent losses of the chloroplast DNArpl2 intron in dicotyledons:molecular and phylogenetic implications. Evolution 45: 1245–1259
Gibson AC, Nobel PS (1986) The Cactus Primer. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Gyllensten U (1989) Direct sequencing of in vitro amplified DNA. In: Erlich HA (ed) PCR technology. Stockton Press, New York, pp 45–60
Igloi, GL, Meinke A, Döry I, Kössel H (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the maize chloroplastrpoB/C1/C2 operon: comparison between the derived protein primary structures from various organisms with respect to functional domains. Mol Gen Genet 221:379–394
Jansen RK, Palmer JD (1987) A chloroplast DNA inversion from lettuce andBarnadesia (Asteraceae): structure, gene localization, and characterization of a large inversion. Curr Genet 11:553–564
Katayama H, Ogihara Y (1993) Structural alterations of the chloroplast genome found in grasses are not common in monocots. Curr Genet 23:160–165
Liston A (1992) Variation in the chloroplast genesrpoC1 andrpoC2 of the genusAstragalus (Fabaceae): evidence from restriction-site mapping of a PCR-amplified fragment. Am J Bot 79:953–961
Olmstead RG, Palmer JD (1994) Chloroplast DNA systematics: a review of methods and data analysis. Am J Bot 81: 1205–1224
Palmer JD (1987) Chloroplast DNA evolution and biosystematic uses of chloroplast DNA variation. Am Nat 130 (Supplement): S6-S29
Palmer JD, Jansen RK, Michaels HJ, Chase MW, Manhart JR (1988) Chloroplast DNA variation and plant phylogeny. Ann Mo Bot Gard 75:1180–1206
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shimada H, Fukuta M, Ishikawa M, Sugiura M (1990) Rice chloroplast RNA polymerase genes: the absence of an intron inrpoC1 and the presence of an extra sequence inrpoC2. Mol Gen Genet 221:395–402
Shinozaki K, Ohme M, Tanaka M, Wakasugi T, Hayashida N, Matsubayashi T, Zaita N, Chunwongse J, Obokata J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ohto C, Torazawa K, Meng B-Y, Sugita M, Deno H, Kamagoshira T, Yamada K, Kusuda J, Takaiwa F, Kato A, Tohdoh N, Suguira M (1986) The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J 5:2043–2049
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Zurawski G, Bottomley W, Whitfield PR (1984) Junctions of the large single-copy region of the inverted repeats inSpinacia oleracea andNicotiana debneyi chloroplast DNA: sequence of the genes for tRNAHIS and the ribosomal proteins S19 and L2. Nucleic Acids Res 12:6547–6558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by B.B. Sears
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallace, R.S., Cota, J.H. An intron loss in the chloroplast generpoC1 supports a monophyletic origin for the subfamily Cactoideae of the Cactaceae. Curr Genet 29, 275–281 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221558
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02221558