Abstract
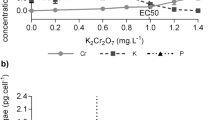
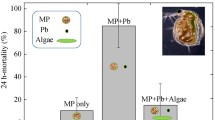
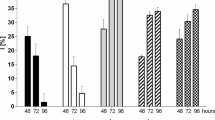
The toxicity of tetramethyl lead (Me4Pb) towards freshwater algae was studied by bubbling biologically generated Me4Pb from one flask containing 5 mg of Pb l−1 as Me3PbOAc into the culture medium in another flask where a test algaScenedesmus quadricauda was grown. As Me4Pb is not soluble in water and is volatile, the exposure of an alga to this lead compound was only momentary. It was estimated that less than 0.5 mg of Pb (Me4Pb) had passed through the culture medium. The primary productivity and cell growth (determined by dry weight), however, decreased by 85% and 32% respectively, as compared with the controls without exposure to Me4Pb. Furthermore, cells exposed to Me4Pb tended to clump together and striking alterations in cell fine-structure were observed. An electron microscopic analysis by an energy dispersive spectrometer revealed that Pb ions had penetrated the cell and were deposited within concretion bodies. Similar results were obtained with the green algaeAnkistrodesmus falcatus andChlorella pyrenoidosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T.F.: Techniques for the preservation of three-dimensional structure in preparing specimens for the electron microscope. Trans. N.Y. Acad. Sci. Ser. 11,13, 13 (1951).
Arntzen, C.J., R.A. Dilley, G.A. Peters, and E.R. Shaw: Photochemical activity and structural studies of photosystems derived from chloroplast grana and stroma lamellae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta256, 85 (1972).
Cairns, J., G.R. Lanza, and B.C. Parker: Pollution related structural and functional changes in aquatic communities with emphasis on freshwater algae and protozoa. Proceed. Acad. Nat. Sci. (Philadel.)124, 79 (1972).
Chau, Y.K., P.T.S. Wong, and H. Saitoh.: Determination or tetramethyl lead compounds in the atmosphere. J. Chromatogr. Sci. In press (1975).
Chu, S.P.: The influence of the mineral composition of the medium on the growth of planktonic algae. I. Methods and culture media. J. Ecol.30, 284 (1942).
Goyer, R.A., and R. Krall: Ultrastructural transformation in mitochondria isolated from kidneys of normal and lead intoxicated rats. J. Cell. Biol.41, 393 (1969).
Lind, O.T., and R.S. Campbell: Comments on the use of liquid scintillation for routine determination of14C activity in production studies. Limnol. Oceanogr.14, 787 (1969).
Malanchuk, J.L., and G.K. Gruendling: Toxicity of lead nitrate to algae. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution2, 181 (1973).
Miller, M.M., and P.S. Nobel: Light-induced changes in the ultrastructure of pea chloroplastsin vivo. Relationship to development and photosynthesis. Pl. Physiol.49, 535 (1972).
Spurr, A.R.: A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31 (1969).
Whitton, B.A.: Toxicity of heavy metals to freshwater algae: a review. Phykos9, 116 (1970).
Wong, P.T.S., Y.K. Chau, and P.L. Luxon: Methylation of lead in the environment. Nature253, 263 (1975).
Wood, J.M.: Biological cycles for toxic elements in the environment. Science183, 1049 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silverberg, B.A., Wong, P.T.S. & Chau, Y.K. Effect of tetramethyl lead on freshwater green algae. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 5, 305–313 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220912
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220912