Abstract
In human medicine it has been shown that the bromocresol green (BCG) dye-binding method for the determination of serum albumin is not entirely specific, the dye reacting also with certain human serum globulins. This causes over-estimation of albumin when reaction times are prolonged beyond 30 seconds.
In the present study, serum albumin values obtained from three animal species by the “immediate”, i.e. less than 30 seconds, BCG reaction were compared with those by the 10-minute BCG reaction. Albumin-depleted sera were prepared using an affinity chromatography technique and their reactions and those of purified gamma globulin preparations with the dye were studied.
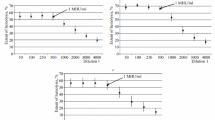
In cattle, sheep and horses, serum albumin values obtained by the 10-minute reaction were higher than those obtained by the “immediate” BCG reaction, the differences being statistically significant. Purified gamma globulin did not react with the BCG dye after 10 minutes, but other globulins did. There were differences between the species in the magnitude of the reaction of their globulins with BCG dye.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doumas, B. T., Watson, W. A. and Biggs, H. G., 1971. Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clinica Chimica Acta, 31: 87–96.
Ek, N., 1977. Identification of the Pr albumins in horse serum. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 78: 458–470.
Ferreria, P. and Price, C. P., 1974. A comparison of bromocresol green and immunoprecipitin methods for the determination of serum albumin. Clinica Chimica Acta, 55: 259–262.
Gentry, P. A. and Lumsden, J. H., 1978. Determination of serum albumin in domestic animals using the immediate BCG reaction. Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 7: 12–15.
Green, S. A., Jenkins, S. J. and Clark, P. A., 1982. A comparison of chemical and electrophoretic methods of serum protein determination in clinically normal animals of various ages. Cornell Veterinarian, 72: 416–426.
Gustafsson, J. E. C., 1976. Improved specificity of serum albumin determination and estimation of “acute phase reactants” by use of the BCG reaction. Clinical Chemistry, 22: 616–622.
Gustafsson, J. E. C., 1978. Automated serum albumin determination by use of the immediate reaction with BCG reagent. Clinical Chemistry, 24: 369–373.
Keay, G., 1981. Serum albumin measurement in some species of domestic animals: a dye-binding and electrophoretic technique compared. Fellowship Thesis, Institute of Science Technology.
Keay, G. and Doxey, D. L., 1983. Serum albumin values from healthy cattle, sheep and horses determined by the immediate bromocresol green (BCG) reaction and by agarose gel electrophoresis. Research in Veterinary Science, in press.
Kristensen, F. and Firth, E. C., 1977. Analysis of serum proteins and CSF in clinically normal horses, using agarose gel electrophoresis. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 38 (7): 1089–1092.
Matthews, A. G., 1979. Identification and characterisation of the major antiproteases in equine serum and an investigation of their role in the onset of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh.
Matthews, A. G., 1982. Serum protein electrophoresis in horses and ponies. Equine Veterinary Journal, 14: 322–324.
Osbaldiston, G. W., 1972. Serum protein fractions in domestic animals. British Veterinary Journal, 128: 386–392.
Pemberton, J. R. and De Jong, J., 1971. Relative dye-binding capacity of albumin from several species with HABA, Bromocresol Green and Spectru AB-2. Analytical Biochemistry, 43: 575–581.
Rodkey, F. L., 1965. Direct spectrophotometric determination of albumin in human serum. Clinical Chemistry, 11: 478–487.
Travis, J. and Pannell, R., 1973. Selective removal of albumin from plasma by affinity chromatography. Clinica Chimica Acta, 49: 49–52.
Travis, J. and Pannell, R., 1974. A method for preparing albumin-free plasma. Behring Institute Mitteilungen, 54: 30–32.
Travis, J., Bowen, J., Tewksbury, D. J. and Pannell, R., 1976. Isolation of albumin from whole human plasma and fractionation of albumin-depleted plasma. Biochemical Journal, 157: 301–306.
Webster, D., 1974. A study of the interaction of BCG with isolated globulin fractions. Clinica Chimica Acta, 53: 109–115.
Webster, D., 1977. The immediate reaction between BCG and serum as a measure of albumin content. Clinical Chemistry, 23: 663–665.
Wille, L. E., 1976. A simple and rapid method for isolation of serum lipoproteins and other serum protein constituents. Clinica Chimica Acta, 71: 355–357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keay, G., Doxey, D.L. A study of the interaction between bromocresol green dye and bovine, ovine and equine serum globulins. Vet Res Commun 8, 25–32 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02214691
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02214691