Abstract
Objective
Our purpose was to determine whether urinary estrone conjugates (E1C) as measured by enzyme immunoassay correlate with serum estradiol (E2) in women undergoing controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with human menopausal gonadotropins.
Design
This was a prospective, clinical study.
Setting
The study took place in an outpatient, university-affiliated in vitro fertilization (IVF) unit.
Interventions
First morning urine samples were analyzed for E1C using a competitive solid-phase microtiter enzyme immunoassay and the value was corrected for urinary creatinine (E1C/Cr). The value was compared to morning serum E2 as determined by radioimmunoassay.
Results
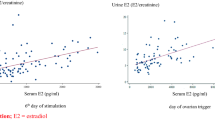
Mean E2 and E1C/Cr levels demonstrated a similar pattern on the days before hCG administration. The correlation between E1C and E2 was 0.85 (P<0.0001). Furthermore, the correlation between the number of follicles greater than 12 mm was as high for E1C/Cr (ρ =0.71, P<0.001) as it was for E2 (ρ = 0.74, P<0.0001).
Conclusions
Urinary E1C/Cr levels in women receiving hMG correlate with serum E2. Further studies are necessary to determine whether E1C is clinically useful to predict ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gelety TJ, Kerin JF, Surrey ES: Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: Diagnosis and treatment. Infertil Reprod Med 1992;3:795–809
Lasley BL, Stabenfeldt GH, Overstreet JW, Hansen FW, Czekala N, Munro CJ: Urinary hormone levels at the time of vulation and implantation. Fertil Steril 1985;43:861–867
Czekala NM, Overstreet JW, Hanson FW, Stabenfeldt GH, Lasley BL: Assessment of follicular function in women by measurement of urinary estrone conjugates. Fertil Steril 1986;46:604–609
Munro CJ, Stabenfeldt GH, Cragun JR, Addiego LA, Overstreet JW, Lasley BL: Relationship of serum estradiol and progesterone concentrations to the excretion profiles of their major urinary metabolites as measured by enzyme immunoassay and radioimmunoassay. Clin Chem 1991;37:838–844
Taussky HH: A microcolorimetric determination of creatinine in urine by the Jaffe reaction. J Biochem 1954;208:853–861
Ishikawa M, Hoshiai H, Tozawa H, Fukaya T, Yajima A: Monitoring follicular maturation through measurement of urinary estrogen excretion by latex agglutination inhibition reaction. Fertil Steril 1987;48:688–690
Lessing JB, Peyser MR, Gilad S, Amit A, Kogosowski A, Yovel I, Barak Y, David MP: Estrone-3-glucuronide chemiluminescence immunoassay: An alternative method for monitoring induction of ovulation with human menopausal gonadotropin in an in vitro fertilization program. Fertil Steril 1987;48:450–453
Baker TS, Jennison KM, Kellie AE: The direct radioimmunoassay of glucuronides in human female urine. Biochem J 1979;177:729–738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alper, M.M., Halvorson, L., Lasley, B. et al. Relationship between urinary estrone conjugates as measured by enzyme immunoassay and serum estradiol in women receiving gonadotropins for in vitro fertilization. J Assist Reprod Genet 11, 405–408 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02211727
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02211727