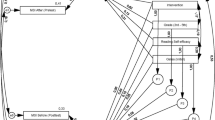
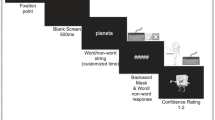
Abstract
This article explores the interplay between low-level reading subcomponents, metacognitive aspects of reading, and how this relation changes developmentally. First, theories relevant to the question of how subcomponent efficiencies, available resources, and metacognitive aspects of reading interrelate are reviewed. Second, research documenting increases in a reader's subcomponent efficiencies is briefly surveyed. Next, research revealing the child's developing metacognitive competencies is explored. To conclude, compensatory-encoding theory (Walczyk, 1993) is used to propose a model of the development of the interplay between resources, subcomponent efficiencies, and metacognitive aspects of reading. Diagnotic and intervention implications are considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ander, M. E., and Anderson, T. H. (1978–1979). The development and evaluation of self-questioning study techniques.Reading Res. Quart. 14: 605–623.
Anderson, J. R. (1983).The Architecture of Cognition, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Baker, L. (1979). Comprehension Monitoring: Identifying and Coping with Text Confusion. Technical Report No. 145, Center for the Study of Reading, Urbana, Illinois.
Baker, L., and Brown, A. L. (1984). Metacognitive skills and reading. In Pearson, D. P., Barr, R., and Mosenthal, P. (eds.),Handbook of Reading Research, Longman New York.
Bransford, J. D., Stein, b. S., Vye, N. J., Franks, J. J., Auble, P. M., Mezynski, K. J., and Perfetto, G. A. (1982). Differences in approaches to learning: An overview.J. Exp. Psychol.: General 111: 390–398.
Case, R. (1985).Intellectual Development: A Systematic Reinterpretation, Academic Press, New York.
Chabot, R. J., Petros, R. V., and McCord, G. (1983). Developmental and reading ability differences in accessing information from semantic memory.J. Exp. Child Psychol. 35: 128–142.
Frederiksen, J. R., and Warrne, B. M. (1987). A cognitive framework for developing expertise in reading. In Glaser, R. (ed.),Advances in Instructional Psychology (Vol. 3), Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ.
Just, M. A., Carpenter, P. A., and Wholley, J. D. (1982). Paradigms and processes in reading comprehension.J. Exp. Psychol.: General 111: 228–238.
Laberge, D., and Samuels, S. J. (1974). Toward a theory of automatic information processing in reading.Cognit. Psychol. 6: 293–323.
Markman, E. M. (1979). Reading that you don't understand: Elementary school children's awarencess of inconsistencies.Child Dev. 50: 643–655.
McKeachie, W. J., Pintrich, P. R., Lin, Yi-Guang, Smith, D. A., and Sharma, R. (1990).Teaching and Learning in the College Classroom: A Review of the Research Literature (2nd Ed.), National Center for Research in Postsecondary Teaching and Learning, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan.
McKoon, G., and Ratcliff, R. (1980). The comprehension processes and memory structures involved in anaphorical reference.J. Verbal Learning Verbal Behav. 19: 668–682.
Paris, S. G., Cross, D., and Lipson, M. Y. (1986). Informed strategies for learning: A program to improve children's reading awareness and comprehension.J. Educ. Psychol. 78.
Perfetti, C. A. (1985).Reading Ability, Oxford University Press, New York.
Perfetti, C. A. (1988). Verbal efficiency in reading ability. In Daneman, M., MacKinnon, G. E., and Waller, T. G. (eds.),Reading Research: Theory and Practice, Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Perfetti, C. A., and Goldman, S. R. (1976). Discourse memory and reading comprehension skill.J. Verbal Learning Verbal Behav. 14: 33–42.
Rayner, K., and Pollatsek (1989).The Psychology of Reading, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Roth, S. F., and Beck, I. L. (1987). Theoretical and instructional implications of assessment of two microcomputer sword recognition programs.Reading Res. Quart. 22: 197–218.
Schneider, W., Dumais, S., and Shiffrin, R. M. (1984). Automatic and control processing and attention. In Parasuraman, R., Davies, D. R. (eds.),Varieties of Attention, Academic Press, San Diego.
Stanovich, K. E. (1980). Toward an interactive-compensatory model of individual differences in the development of reading fluency.Reading Res. Quart. 16: 32–71.
Stanovich, K. E. (1990). Concepts in developmental theories of reading skill: Cognitive resources, automaticity, and modulatory.Dev. Rev. 10: 72–100.
Walczyk, J. J. (1990). Relation among error detection, sentence verification, and low-level reading skills in fourth graders.J. Educ. Psychol. 82: 491–497.
Walczyk, J. J. (1993). Are general resource notions still viable in reading research?J. Educ. Psychol. 85.
Walczyk, J. J., and Raska, L. J. (1992). the relation between low- and high-level reading skills in children.Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 17: 38–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walczyk, J.J. The development of verbal efficiency, metacognitive strategies, and their interplay. Educ Psychol Rev 6, 173–189 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02208972