Summary
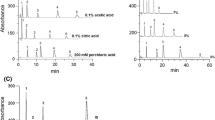
A massfragmentographic method for determination of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) is described. Deuterium labelled DOPAC was used as internal standard. Derivatives suitable for GC-MS were prepared by reacting standard solutions and rat brain extracts with pentafluoropropanol and pentafluoropropionic anhydride. Fragments set into focus were m/e 592/597 (M+) and m/e 415/420 (M+ −177). The sensitivity was in the pmole range with high specificity as tested by multiple ion analysis. The DOPAC level in rat striatum was 6.0 ± 1.1 nmoles/g with an experimental error below 8.5%. The recovery of 575 pmoles DOPAC added to brain extracts was 91 %. Treatment of rats with pargyline (150 mg/kg i.p.) reduced the DOPAC level by about 95% whereas a slight elevation was obtained after administration of chlorpromazine (10 mg/kg i.p.). DOPAC and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid (HVA) could be determined concomitantly in the same sample, by using the described technique for derivative preparation and an AVA allowing simultaneous recording of 4 mass numbers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., B.-E. Roos, andB. Werdinius: Effects of chlorpromazine, haloperidol and reserpine on the levels of phenolic acids in rabbit corpus striatum. Life Sci.3, 149–158 (1964).
Bunney, B. S., J. R. Walters, R. H. Roth, andG. K. Aghajaman: Dopaminergic neurons: Effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.185, 560–571 (1973).
Carlsson, A., andM. Lindqvist: Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. et Toxicol.20, 140–144 (1963).
Costa, E., A. R. Green, S. H. Koslow, H. F. Lefevre, A. V. Revuelta, andC. Wang: Dopamine and Norepinephrine in Noradrenergic Axons: A study in vivo of their precursor-product relationship by mass fragmentography. Pharmacol. Rev.24, 167–190 (1972).
von Euler, H. S.: Distribution and metabolism of catechol hormones in tissues and axones. Rec. Progr. Hormone Res.14, 483–512 (1958).
Fri, C.-G., F.-A. Wiesel, andG. Sedvall: Mass fragmentometric analysis of homovanillic acid and its homoiso analogue in cerebrospinal fluid using theα-dideutero acid as internal standard. Psychopharmacologia35, 294–304 (1974 a).
Fri, C.-G., F.-A. Wiesel, andG. Sedvall: Simultaneous quantification of homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid by mass fragmentography. Life Sci. (1974 b, in press).
Holmstedt, B., andL. Palmér: Mass Fragmentography: Principles, Advantages and Future Possibilities. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol.7, 1–14 (1973).
Kägi, J., M. Burger, andK. Giger: Modifikation zur Fluorescenzmethode von Well-Malherbe und Bone zur Bestimmung von Adrenalin and Noradrenalin im menschlichen Blutplasma. Arch. exper. Path. u. Pharmakol.230, 470–478 (1957).
Murphy, G. F., D. Robinson, andD. F. Sharman: The effect of tropolone on the formation of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid in the brain of the mouse. Brit. J. Pharmacol.36, 107–115 (1969).
Nybäck, H., andG. Sedvall: Effect of chlorpromazine on accumulation and disappearance of catecholamines formed from tyrosine-14C in brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.162, 294–301 (1968).
Rosengren, E.: On the role of monoamine oxidase for the inactivation of dopamine in brain. Acta physiol. scand.49, 370–375 (1960).
Ryhage, R.: (1974) to be published.
Walters, J. R., andR. H. Roth: Effect of gammahydroxybutyrate on dopamine and dopamine metabolites in the rat striatum. Biochem. Pharmacol.24, 2111–2121 (1972).
Wilk, S., andM. Orlowski: The occurrence of free L-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in body fluids and tissues. FEBS Letters33, 157–160 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 4 Figures
Part of the study was presented as a preliminary report at the 2nd International Symposium on Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry, Milan, Italy, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiesel, F.A., Fri, C.G. & Sedvall, G. Simultaneous mass fragmentographic determination of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid in brain tissue. J. Neural Transmission 35, 319–326 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02205228
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02205228