Abstract
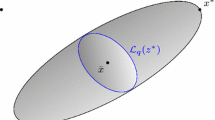
Ellipsoids that contain all optimal dual slack solutions and those that contain all optimal primal solutions and that are independent of the algorithm used are derived. Based upon these ellipsoids, two criteria each for detecting optimal basic and nonbasic variables prior to optimality in interior-point methods are obtained. Using these results, we then derive a sufficient condition for a linear program to be feasible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima, M.,Determining Basic Variables of Optimal Solutions in Karmarkar's New LP Algorithm, Algorithmica, Vol. 1, pp. 499–515, 1986.
Todd, M. J.,Improved Bounds and Containing Ellipsoids in Karmarkar's Linear Programming Algorithm, Mathematics of Operations Research, Vol. 13, pp. 650–659, 1988.
Ye, Y. Recovering the Optimal Basis in Karmarkar's Polynomial Algorithm for Linear Programming Mathematics of Operations Research, Vol. 15, pp. 564–572, 1990.
Ye, Y.,The Build-Down Scheme for Path-Following Algorithms, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 46, pp. 61–72, 1990.
Ye, Y., andTodd, M. J.,Containing and Shrinking Ellipsoids in the Path-Following Algorithm, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 47, pp. 1–9, 1990.
Dikin, I. I.,Iterative Solution of Problems of Linear and Quadratic Programming, Soviet Mathematics Doklady, Vol. 8, pp. 674–675, 1967.
Barnes, E. R.,A Variation on Karmarkar's Algorithms for Linear Programming, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 36, pp. 174–182, 1986.
Karmarkar, N. K.,A New Polynomial-Time Algorithm for Linear Programming, Combinatorica, Vol. 4, pp. 373–395, 1984.
Renegar, J.,A Polynomial-Time Algorithm, Based on Newton's Method, for Linear Programming, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 40, pp. 59–93, 1988.
Kojima, M., Mizuno, S., andYoshise, A. A Polynomial-Time Algorithm for a Class of Linear Complementarity Problems, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 44, pp. 1–26, 1989.
Monteiro, R. C., andAdler, I.,Interior Path Following Primal-Dual Algorithms, Part 1: Linear Programming, mathematical Programming, Vol. 44, pp. 27–41, 1989.
Freund, R. M.,Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Linear Programming Based on Primal Scaling and Projected Gradients of a Potential Function, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 51, pp. 203–222, 1991.
Ye, Y., An O(n3L) Potential Reduction Algorithm for Linear Programming, Mathematical Programming, Vol. 50, pp. 239–258, 1991.
Burrell, B. P., andTodd, M. J.,The Ellipsoid Method Generates Dual Variables, Mathematics of Operations Research, Vol. 10, pp. 668–700, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. A. Tapia
This research was supported in part by NSF Grant DMS-85-12277, DMS-91-06195, CDR-84-21402 and ONR Contract N00014-87-K-0214.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, I.C., Goldfarb, D. On solution-containing ellipsoids in linear programming. J Optim Theory Appl 80, 161–173 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02196599
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02196599